Art & Culture
A colossal Buddha head, a giant palm unearthed amid ASI excavation in Ratnagiri - Indian Express
In December, when Archaeological Survey of India’s superintending archaeologist D B Garnayak and his team took up excavations at the 5th-13th Century Buddhist complex in Ratnagiri, in Odisha’s Jajpur district, after a gap of 60 years, their aim was two-fold – to uncover more of the complex and to find material evidence of the state’s link to the larger Southeast Asian culture.
Buddhism in Odisha
- History: Ashoka embraced Buddhism after the Kalinga War (261 BC).
- Expansion in Odisha: Under the Bhaumakara dynasty (8th–10th centuries).
- Trade Links with Southeast Asia: Pepper, cinnamon, cardamom, silk, camphor, gold, and jewellery
.
- Baliyatra Festival: Annual 7 -day event commemorating 2,000-year-old maritime links with Bali, Java, Sumatra, Borneo, Myanmar, and Sri Lanka.
Ratnagiri
- Location: 100 km northeast of Bhubaneswar, Odisha situated on a hill between Birupa and Brahmani rivers.
- Significance: Most famous and extensively excavated Buddhist site in Odisha.
- Period: Dated to the 5th–13th centuries, with peak construction between the 7th–10th centuries.
Importance:
- Center for Mahayana and Tantrayana (Vajrayana) Buddhism.
- Possibly visited by Chinese monk Hiuen Tsang in 638–639 AD.
- Discoveries by ASI: Colossal Buddha head, massive palm, ancient wall, and inscribed relics from the 8th–9th centuries.
World Affairs
What is U.S.’s new rule for exporting AI chips? - The Hindu
With an objective to advance increased control over circulation of Artificial Intelligence (AI) chips and technology, the U.S. Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) introduced a tiered framework for licensing and exports. It held the regulations were in tandem with “national security and foreign policy interests”. Further, it would help “cultivate a secure and trusted technology ecosystem for the responsible use and diffusion of AI”.
Country Tiers
- Tier 1: No restrictions for 18 U.S. allies (e.g., Australia, Canada, U.K., Japan).
- Tier 2:
- Caps on volume; exemptions based on specifications.
- Requires Validated End User (VEU) authorisation for transactions aiding advanced AI development.
- Chips with combined power of ~1,700 GPUs exempted.
- Includes China and India.
- Tier 3:
- Arms-embargoed countries (e.g., North Korea, Iran, Russia).
- No access to advanced technology.
Reasons for Curtailing Access
- Objectives:
- Prevent advanced technology from reaching U.S. adversaries or countries of concern.
- Ensure model weights are stored securely and advanced IC clusters are built in low-risk destinations.
- Concerns Raised by BIS: Adversaries could leverage AI systems for:
- Enhanced military decision-making and logistics.
- Development of weapons of mass destruction.
- Cyber-offensive operations.
- Human rights violations (e.g., mass surveillance).
- Chinese companies use foreign subsidiaries in uncontrolled destinations to procure ICs.
- Risk to U.S. innovation leadership globally: Rules control globally available technology (e.g., gaming PCs) without enhancing security.
Impact on India
- Indian data centres deploying advanced AI chips may require VEU authorisation for faster access.
- VEU allows use for civilian and military purposes except nuclear-related applications.
- India’s exclusion from the trusted allies category likely due to concerns about chip leakages to Russia.
Environment
5.2K birds of 117 species in Uttarakhand’s Asan wetland - Indian Express
In a significant citizen science effort, a bird counting campaign at the Asan Wetland in Dehradun district of Uttarakhand has yielded impressive results, with volunteers identifying 5,225 birds across 117 different species.
Asan Conservation Reserve (ACR)
- About: A 444-hectare stretch of the Asan River in Dehradun district, Uttarakhand.
- Designation: Declared a Conservation Reserve in 2005 under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Significance: First Ramsar site in Uttarakhand; Important Bird Area (BNHS & BirdLife International).
- Location: Located on the Central Asian Flyways (CAF).
- Fauna:
- Critically Endangered: White-rumped vulture, Baer's pochard.
- Endangered: Egyptian vulture, steppe eagle, black-bellied tern.
- Vulnerable: Marbled teal, common pochard, Indian spotted eagle.
- Fish: 49 fish species, including the endangered Putitor mahseer.
India's NMDC to extract diamonds worth $3.4 mln from mine near tiger reserve - The Hindu
India's state-run miner NMDC is expected to extract 6,500 carats of diamonds, worth $3.4 million, this fiscal year from ores in a mine near a tiger reserve, after receiving mining clearances last year, two sources said.
National Mineral Development Corporation (NMDC)
- About: Established in 1958 as a fully owned Government of India enterprise.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Steel and holds "Navratna" status since 2008.
- Operations:
- Exploration of minerals.
- Largest iron ore producer in India.
- Producing >45 million tonnes annually from Bailadila (Chhattisgarh) and Donimalai (Karnataka).
- Operates India’s only mechanized diamond mine in Panna, MP.
- Significance:
- One of the world's low-cost producers of iron ore.
- Supplies high-grade iron ore to Indian steelmakers.
- All mining complexes rated 5-star by the Indian Bureau of Mines.
- Headquarters: Hyderabad, Telangana.
Defence
Pralay missile - The Hindu
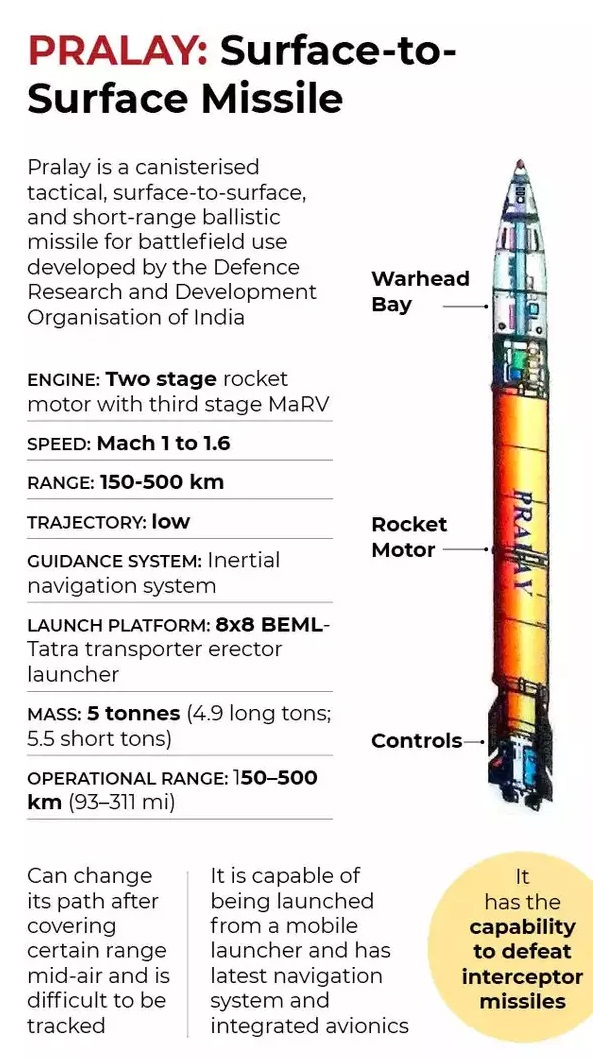
Indigenously developed Pralay missile will be showcased during the Republic Day Parade for the first time.
Pralay Missile
- About: Indigenously developed short-range, quasi-ballistic surface-to- surface missile by DRDO.
- Basis: Prithvi Defence Vehicle from the Indian Ballistic Missile Programme.
- Deployment: Along the LAC and LoC.
- Propulsion: Solid-propellant rocket motor.
- Range: 150-500 km; launched from a mobile launcher.
- Payload: 500-1,000 kg; capable of carrying conventional warheads.
- Accuracy: A Circular Error Probable (CEP) of less than 10 meters.
- Targeting: Engages radar installations, command centers, and airstrips.
- Maneuverability: Can alter its path mid-air.