Art and Culture
Tamil Nadu CM Stalin offers $1-millon prize for decoding Indus Valley script
Tamil Nadu Chief Minister M.K. Stalin announced on Sunday a $1-million prize for experts or organisations that succeeded in deciphering the scripts of the Indus Valley Civilisation for everyone to understand.
Indus Valley Civilization/ Indus-Sarasvati Civilization
- Origin: Emerged in the Indus River basin.
- Location: Sites also found along the Ghaggar-Hakra river bed.
- Discovery: Announced in 1924 by John Marshall.
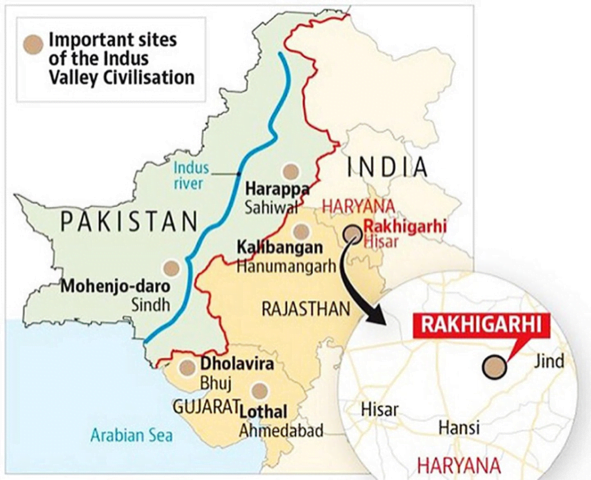
- Harappa: First identified by Charles Masson as the ancient city of Sangala.
- Key excavations: Harappa by Daya Ram Sahni (1920) and Mohenjo-daro by Rakhaldas Banerjee (1921).
- Geographical Factors: Fertile plains and annual floods deposited rich alluvial soil, supporting agriculture.
- Chronology: 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE (Radiocarbon dating).
- Phases: Early Harappan, Mature Harappan, and Late Harappan.
Polity
Why 1978 'anti-conversion' law in Arunachal could now be enforced - Indian Express
The Arunachal Pradesh government is working to bring a 1978 Act against “forceful” conversion out of cold storage by framing rules for its implementation, 46 years after it was enacted.
Arunachal Pradesh Anti-Conversion Act, 1978
- Purpose: Prohibits religious conversion through force, inducement, or fraudulent means.
- Punishment:
- Imprisonment up to 2 years and a fine of up to ₹10,000.
- Failure to report conversions to the Deputy Commissioner also attracts penalties.
- Definition of Religious Faiths: Includes "indigenous" faiths such as:
- Buddhism (as practiced by Monpas, Membas, Sherdukpens, Khambas, Khamptis, and Singphos).
- Nature worship (e.g., Donyi-Polo).
- Vaishnavism (among Noctes and Akas).
- Implementation Status: Enacted in 1978 but dormant for nearly five decades due to lack of implementation rules.
Reason for Introduction of the Act
- Diverse Religious Practices:
- Mahayana Buddhism: Practiced by Monpas and Sherdukpens in West Arunachal.
- Theravada Buddhism: Practiced by Khamptis and Singphos in East Arunachal.
- Nature Worship: Polytheistic practices, including institutionalized Donyi-Polo worship by Tani tribes.
- Late Spread of Christianity: Christianity became prevalent only post-1950s due to difficult terrain and colonial restrictions on missionary activity under the Inner Line system.
- Growth in Christianity: Rise from 0.79% (1971) to 4.32% (1981), especially among communities like Padam, Adi, Nocte, and Nyishi.
- Concerns: Missionary activity raised debates on proselytization, socio-cultural changes, and threats to indigenous faiths.
World Affairs
Defence deals in last leg ahead of PM’s Paris visit - The Hindu
Two large defence deals in the pipeline between India and France are being finalised, amid expectations that Prime Minister Narendra Modi will visit Paris in February for the Artificial Intelligence Action Summit to be hosted by French President Emmanuel Macron.
India-France Defence Deals

- Two deals worth over $10 billion for:
- 26 Rafale-M fighter jets for Indian Navy.
- Three additional Scorpene-class submarines.
- Rafale-M Deal: 22 single-seater Rafale-M jets and 4 twin-seater trainers.
- Scorpene Submarine Deal: Builds on a prior contract of six submarines, with five already inducted and the sixth, Vagsheer, to be commissioned in January 2024.
- Naval Significance: Rafale-M to operate from aircraft carriers INS Vikramaditya and INS Vikrant.
Economy
Congress urges PM to set up panel to review Great Nicobar Project—The Hindu
The Congress recently said the Prime Minister should set up an independent panel to review the Great Nicobar Island project.
Great Nicobar Island Project
- About: Launched in 2021, located at the southern end of Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Components: Trans-shipment port, international airport, township development, and 450 MVA gas and solar-based power plant.
- Implementation: ANIIDCO.
- Infrastructure: International Container Transshipment Terminal (ICTT) and greenfield airport.
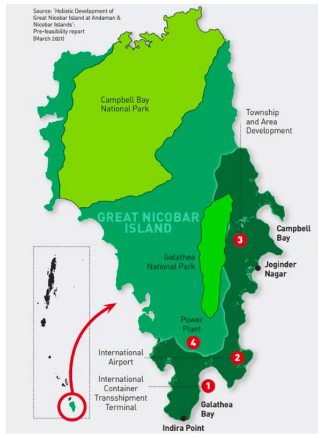
- Site: Galathea Bay, uninhabited southeastern corner of Great Nicobar Island.
Strategic Importance:
- Facilitates deployment of military assets .
- Enhances surveillance and strengthens military deterrence in the region.
- Critical for India’s maritime security.
- Addresses concerns over China’s military facility on Coco Islands.
Personal data protection rules: The center promises adequate time for compliance—The Hindu
The Government of India recently released the draft Digital Personal Data Protection Rules, 2025, under the Digital Data Protection Act, 2023, outlining provisions for data privacy, compliance, and processing mechanisms.
Major Provisions of the Draft Rules
- Parental Consent for Children's Data: Platforms must obtain verifiable parental consent before children create accounts.
- Exemptions: Health, education, mental health, and daycare institutions.
- Data fiduciaries: Entities collecting and processing personal data.
- Data Retention: Retain data only during the consent period; must delete afterward.
- Security: Ensure encryption, access control, and monitoring against unauthorized access.
- Consent Managers: Entities managing consent must follow robust verification protocols.
- Grievance Redressal: Fiduciaries must establish mechanisms for grievance handling.
- Data Localisation:
- Restrictions: Certain personal and traffic data transfers outside India may be restricted.
- Oversight: A government committee will define data categories for localisation.
- Data Breach Reporting: Fiduciaries must promptly inform affected users and the Data Protection Board of breaches.
- Uniform Treatment: All breaches, minor or major, must be reported.
- Government Data Processing Safeguards: Processing must comply with lawful provisions, addressing concerns over exemptions for national security and public order.
Implications of China’s mega-dam project: The Hindu
The ambitious plan to build a mega-hydropower dam across the Brahmaputra at the Great Bend region of the Medog county in the Tibetan Autonomous Region (TAR) in China, has been in the drawing boards of Chinese hydrocracy for decades.
China’s mega-dam project
- Location: Transboundary Himalayan river basin across four riparian countries: China, India, Bhutan, and Bangladesh.
- Origin: Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR) as Yarlung Zangbo.
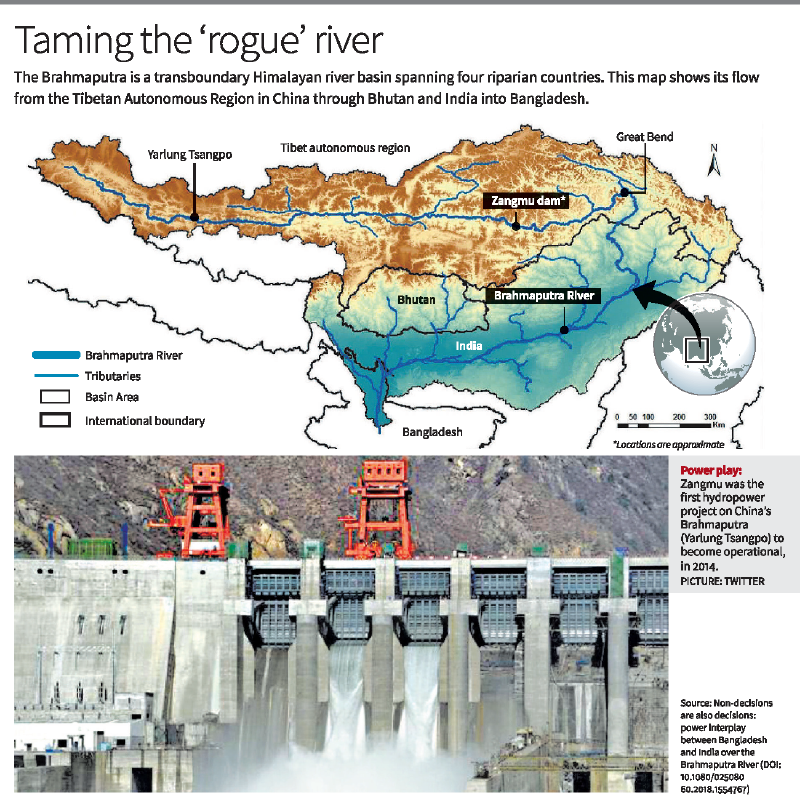
- Course: Flows through India and Bhutan before entering Bangladesh and draining into the Bay of Bengal.
Riparian Relations:
- China: Uppermost riparian nation.
- India and Bhutan: Lower riparian to China, middle riparian to Bangladesh.
- Bangladesh: Lowermost riparian nation.
Infrastructure Projects: Hydropower dams, irrigation dams, embankments for river control, and barrages planned by all riparian nations.
Risks for Communities in the Brahmaputra River Basin
- Impact of Mega-Hydropower Dams: Adverse effects on lands and livelihoods of upstream and downstream communities.
- Perennial Flow Disruption: Blocking the flow for mega-dams may reduce surface water levels, alter monsoon patterns, and impact groundwater systems.
- Agrarian and Ecological Consequences: Severe effects on agrarian communities downstream.
- Ecological Consequences: Threats to the sensitive Himalayan bioregion and its ecology.
Science and Technology
Quarantine animals with symptoms of avian flu, the Center tells States after deaths of tiger and leopard—The Hindu
With Maharashtra reporting India’s first case of avian influenza among animals, the Union Animal Husbandry Ministry sent a circular to all states on Sunday, urging them to quarantine infected or symptomatic tigers and other feline species to prevent transmission to humans and other animals.
