World Affairs
Why has Trump called the Panama Treaty ‘foolish’? The Hindu
Recently, Donald Trump threatened to take back the Panama Canal, calling the transfer treaty "foolish." Panama’s President José Raúl Mulino rejected Trump’s threat.
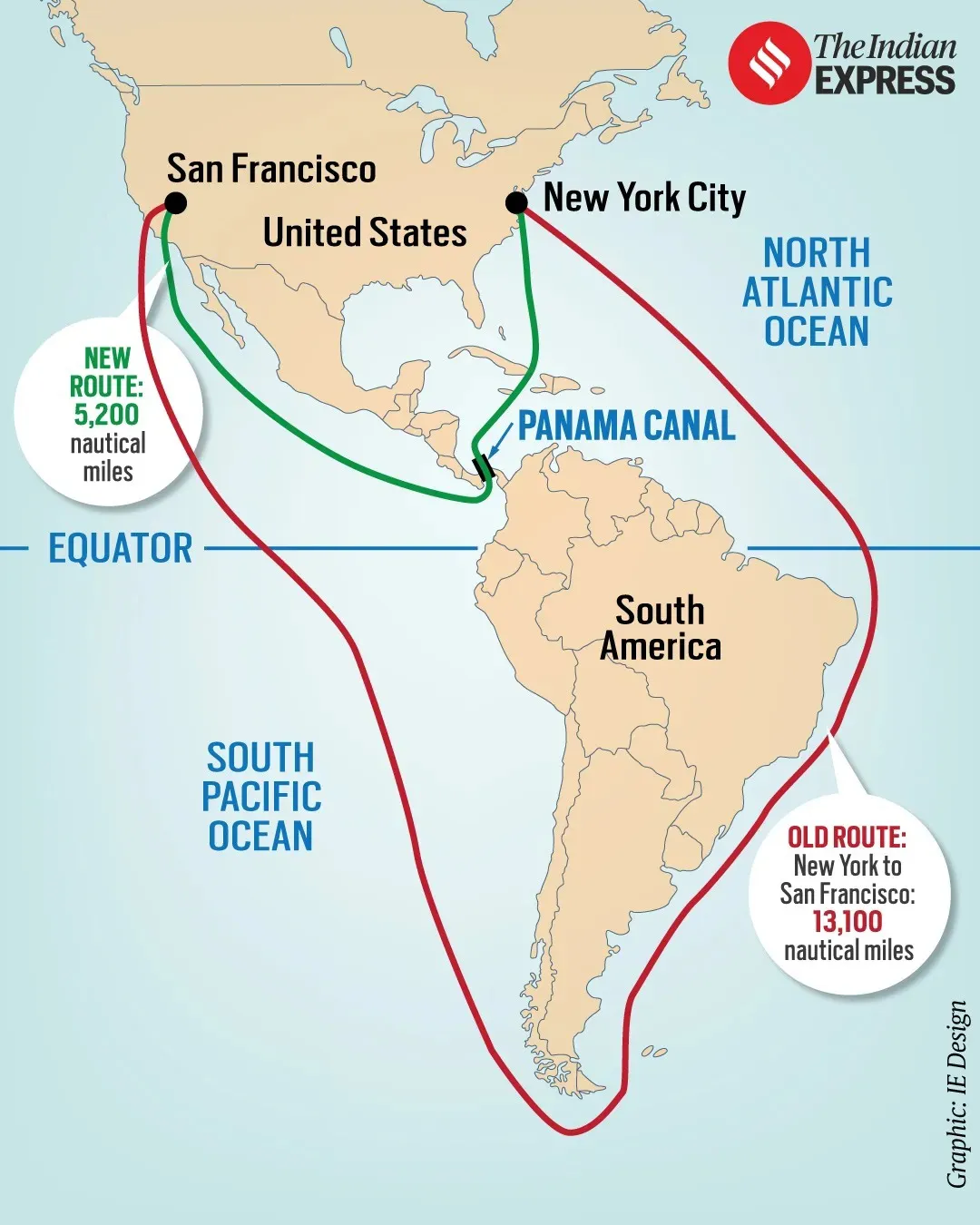
U.S.-Panama Treaty
- About: Connects Atlantic & Pacific Oceans, reducing cost, time, & distance for global shipping.
- Significance: Handles 6% of maritime world trade.
- History: Built by the U.S. and opened in 1914; controlled by the U.S. until 1999.
- Major treaties
- Panama Canal Treaty: Ended U.S. control over the canal zone. & transferred control to Panama on December 31, 1999.
- Permanent Neutrality Treaty: Declared the canal neutral and open to all nations' vessels. U.S. retains the right to defend canal neutrality.
Economy
Experts on GM crop panels to declare conflict of interest - The Hindu
The Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has amended the rules governing the selection of experts to the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC), the apex technical body regulating genetically modified (GM) seeds in India.
Amendment to GEAC Rules
- Conflict of Interest Disclosure: Expert members must disclose any conflict of interest & take steps to ensure conflicts do not influence GEAC decisions.
- Recusal Protocol: Members associated with matters under discussion must disclose this prior to meetings. Unless requested otherwise, they are expected to recuse themselves.
- Professional Affiliations: Selected members must submit details of their affiliations over the past decade.
Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC)
- Establishment: Under the “Rules for the Manufacture, Use/Import/Export and Storage of Hazardous Microorganisms/Genetically Engineered Organisms or Cells (Rules, 1989)”.
- Functions:
- Approves activities involving large-scale use of hazardous microorganisms and recombinants in research and industry.
- Appraises proposals for releasing genetically engineered (GE) organisms and products into the environment.
- Clearance is mandatory for the environmental release of GM crops.
- Authorized to take punitive action under the Environment Protection Act.
- Composition:
- Chairman: Special Secretary/Additional Secretary of MoEF&CC
- Co-chairman: A representative from DBT.
- Members: 24 experts from ministries and institutions like ICAR, ICMR, etc.
- Meetings: Conducted monthly to review applications.
Environment
Pallas’s cat - The Hindu
- Other names: Manul, Steppe Cat, or Rock Wildcat.
- About: A small-sized cat with stocky build and thick, soft fur.
- Distribution: Central Asia (from Caspian Sea to Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, northern India, central China, Mongolia, and southern Russia).
- Habitat: Steppe grasslands and cold, arid regions up to 4,800 m altitude.
- Threats:
- Habitat Loss
- Prey Depletion due to poisoning of rodents etc.
- Predation and Exploitation for fur, demand as exotic pets, etc.
- Conservation Efforts:
- Pallas’s Cat Working Group (PCWG)- 2012.
- Pallas’s Cat International Conservation Alliance (PICA) - 2016
Researchers identify another species of the genus Stellaria in West Bengal—the Hindu
After a plant species of the genus Stellaria (family Caryophyllaceae) was reported from Kerala earlier this year, researchers have identified another member of the same genus at Kalimpong district in West Bengal.
S. bengalensis
- About: Annual herb of genus Stellaria (family Caryophyllaceae).
- Location: Found in Sangser forest, Kalimpong, at 2,245-2,450 meters.
- Characteristics:
- Grows to 8-10.5 cm, with white flowers and sharp, pointed seeds.
- Petals are shorter, included within sepals, and lack bracts.
- Flowering/Fruiting: May to September.
- Distribution: India has 22 Stellaria species, mostly in the Himalayan region.
- Conservation status: ‘Data deficient’ under IUCN criteria.
Science and Technology
Indian researchers develop injectable hydrogel for targeted cancer treatment—The Hindu
Researchers from the Indian Institute of Technology-Guwahati (IIT-G) and the Bose Institute, Kolkata, have developed an advanced injectable hydrogel for localised cancer treatment.This hydrogel serves as a stable reservoir for anti-cancer drugs, releasing it in a controlled manner while sparing healthy cells from harm.
About the advanced injectable hydrogel
- Purpose: Targets drug delivery to tumour sites for localized action.
- Composition: Ultra-short peptides, insoluble in biological fluids.
- Advantages:
- Biomedical Suitability: Mimics living tissues, enhancing compatibility.
- Precision: Ensures effective treatment by harmonizing with the biological environment.
Hydrogels
- About: 3-dimensional networks made of hydrophobic polymers formed by crosslinking water-soluble polymers.
- Water Retention: Can absorb and retain large quantities of water without altering their structure.
- Properties: Exhibit flexibility and swelling due to their unique network design.
How in-flight Internet works—Indian Express
Air India rang in the new year by announcing the rollout of Wi-Fi Internet connectivity services on board domestic and international flights serviced by select aircraft in its fleet. This makes the airline the first in India to offer Internet connectivity on domestic flights.
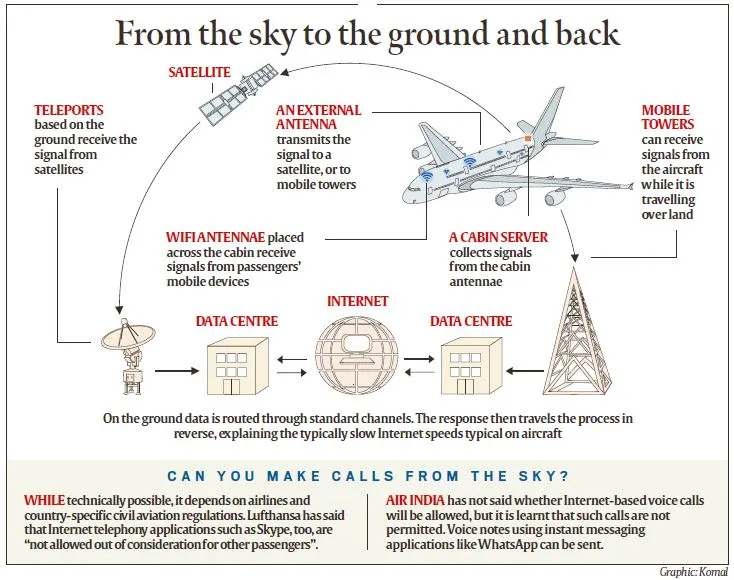
Technologies for In-Flight Internet Connectivity
|
Ground-Based Cellular Towers (ATG Technology)
|
Satellite-Based Connectivity
|
- Uses an antenna on the aircraft's belly to connect to ground-based towers.
- Provides stable connectivity unless flying over areas without towers (e.g., large water bodies or remote regions).
- Limited by the availability of cellular towers.
|
- The Internet is transmitted from ground stations to aircraft via satellites.
- Antennae mounted on top of the aircraft receive signals.
- Offers wider coverage, suitable for regions without ground towers.
|
Working of In-Flight Wi-Fi
- Inside the Aircraft:
- Wi-Fi antennae in the cabin receive signals from passengers' devices.
- Signals are routed to an on-board server.
- Satellite-Based Connectivity: Signals are transmitted via an antenna on an aircraft's top to a satellite, which relays them to a ground station & back.
- ATG Technology: Signals from the on-board server are sent directly to ground-based cellular towers using an antenna on the aircraft's belly.