Art and Culture
Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi participates in Veer Baal Diwas programme in New Delhi - PIB
The Prime Minister recently participated in Veer Baal Diwas. Addressing the gathering on the occasion of the 3rd Veer Baal Diwas, he said their Government had started the Veer Baal diwas in memory of the unparalleled bravery and sacrifice of the Sahibzades.
Veer Baal Diwas
- Date: Observed annually on December 26 since 2022.
- Purpose: To honour the martyrdom of Baba Fateh Singh and Zorawar Singh, sons of Guru Gobind Singh Ji.
- Historical Context:
- Guru Gobind Singh and his family fled the Mughal Army encircling Anandpur fort.
- Zorawar Singh and Fateh Singh were captured during the escape.

- Martyrdom: Refused to abandon their faith and were bricked alive on December 26, 1705, by Wazir Khan.
- Declaration: Declared by the Government of India in 2022 to annually commemorate their sacrifice.
Guru Gobind Singh
- About: 10th Sikh Guru, succeeding his father, Guru Tegh Bahadur.
- Khalsa: Established the principles of Khalsa, symbolized by the Five K’s:
- Kesh (uncut hair), Kangha (wooden comb), Kara (iron/steel bracelet), Kirpan (dagger), and Kachera (short breeches).
- Battle of Muktsar: Fought against the Mughals in 1705.
- Guru Granth Sahib: Declared it as Sikhism's holy scripture in 1708, before his death.
Society
PM to distribute over 50 lakh property cards to property owners under SVAMITVA Scheme - PIB
Prime Minister will distribute over 50 lakh property cards under SVAMITVA Scheme to property owners in over 46,000 villages in 200 districts across 10 States and 2 Union territories soon.
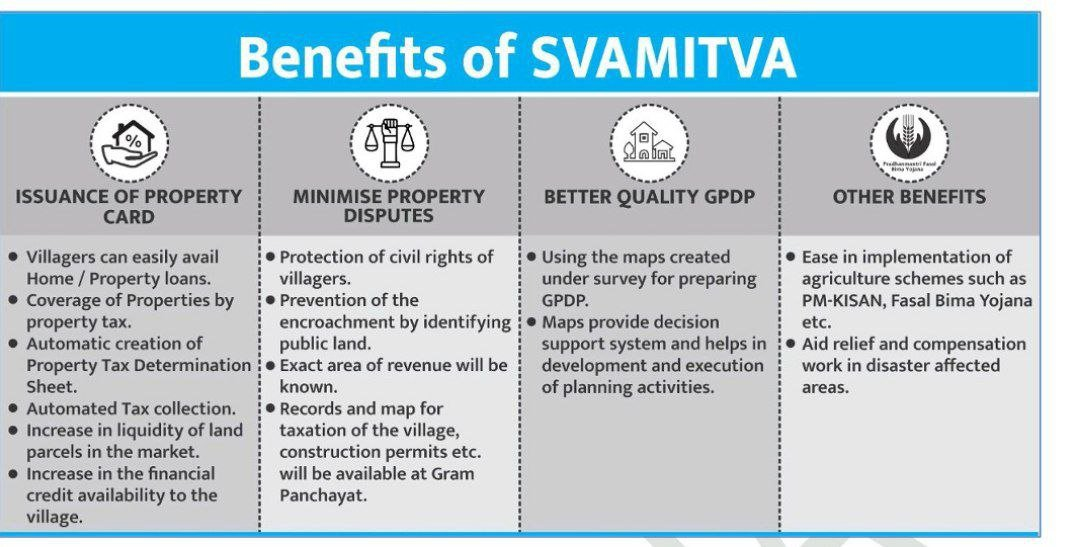
SVAMITVA Scheme

- About: A central sector scheme launched in 2020.
- Objective: Provide Record of Rights to rural households using drone-based survey technology.
- Objectives:
- Enable rural citizens to use property as financial assets for loans.
- Facilitate rural planning and property tax determination.
- Create GIS maps for departmental use.
- Dispute Reduction: Minimize property-related disputes and legal cases.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Panchayati Raj (MoPR).
Polity
Uncertainty looms over Delhi Assembly special session to table CAG reports - The Hindu
Uncertainty looms over the tabling of the 14 Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) reports related to several policy initiatives of the Delhi government ahead of the Assembly poll due in February next year.
Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG)
About: Established under Article 148 to oversee financial administration.
Functions:
- Acts as the guardian of the public purse.
- Ensures accountability and transparency in managing public funds.
- Promotes financial discipline and democratic checks and balances.
Article 148:
- Appointment: By the President under hand and seal.
- Tenure: Set by Parliament; cannot hold further office.
- Salary and allowances: Charged on Consolidated Fund of India.
- Article 149: Powers and functions prescribed by Parliament.
- Article 150: Prescribes accounting formats for Union and States on Presidential advice.
- Article 151: Submits audit reports to Parliament (Union) and State Legislatures (State).
- Article 279: Certifies net proceeds of taxes and duties, which are binding.
CAG’s (Duties, Powers, and Conditions of Service) Act, 1971:
- Tenure: Six years or up to 65 years of age, whichever is earlier.
- Removal: Same procedure as for a Supreme Court judge.
- Resignation: Addressed to the President.
- Service conditions: Cannot be altered to CAG's disadvantage.
World Affairs
UN Secretary General pays tribute to Brigadier Amitabh Jha who led UN peacekeeping force - Indian Express
UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has paid tributes to Brigadier General Amitabh Jha of India, who was serving with the UNDOF at Golan Heights, and said he will be remembered for his “leadership and unwavering commitment to United Nations peacekeeping.”
United Nations Disengagement Observer Force (UNDOF)
- Establishment: Created by UNSC Resolution 350 (1974) on 31 May 1974 after the Israel-Syria disengagement agreement.
- Mandate:
- Maintain the ceasefire.
- Supervise the demilitarized buffer zone and areas restricting Israeli and Syrian troops and equipment in the Golan.
- Renewal: Extended every six months; current mandate valid till June 2025.
- Financing: Annually through a separate account approved by UNGA.
- India’s Role: Third-largest contributor of troops and police to the mission.
- Headquarters: Camp Faouar, Syria.

China approves world’s largest, $137-billion dam on the Brahmaputra close to the Indian border - The Hindu
China has approved the construction of the world's largest dam, stated to be the planet's biggest infra project costing $137 billion, on the Brahmaputra River in Tibet close to the Indian border, raising concerns in riparian states — India and Bangladesh.
China’s Brahmaputra Dam Project
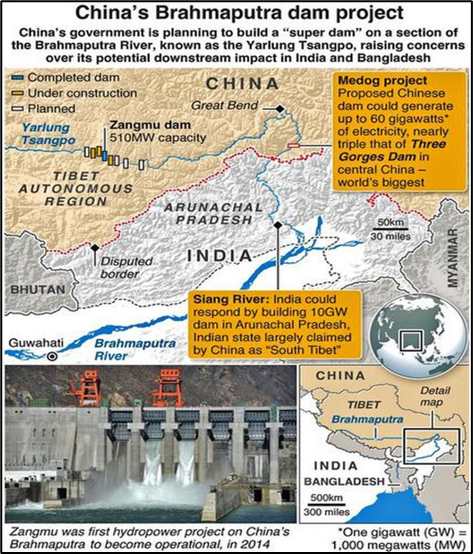
- Location: Medog County, Tibet Autonomous Region, on Yarlung Tsangpo.
- Purpose: To achieve carbon neutrality by 2060 and promote regional development in Tibet.
- Cost: $137 billion under China’s 14th Five-Year Plan (2021–2025).
- Capacity: 60 GW, three times that of the Three Gorges Dam.
- Annual Output: 300 billion kWh of clean energy.
- Revenue: 20 billion yuan ($3 billion) annually for Tibet.
- Contribution: Supports China’s clean energy and water security goals.
Concerns
- Agriculture: Retention of silt may affect soil fertility in India.
- Hydropower Claims: China asserts it is a run-of-the-river project.
- Risks: May reduce water flow in dry seasons and increase flood risks during monsoons.
- Geopolitical Leverage: China’s control over Brahmaputra’s flow raises concerns, as seen during 2017 Doklam standoff when hydrological data was withheld.
- Earthquake Risk: Himalayas’ seismic vulnerability poses risks to downstream populations.
- Environment: Threatens & affects critically endangered species.
Economy
Average household spending rose 3.5% through Aug. 2023-July 2024, shows government survey - The Hindu
India’s average household consumption spends on a per capita basis rose about 3.5% in real terms through August 2023 to July 2024 from a year ago, as per the Household Consumption Expenditure Survey.
Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) 2023-24
- Food Expenditure: Increased share due to higher food prices:
- Rural: 47.04% (2023-24) vs. 46.38% (2022-23).
- Urban: 39.68% (2023-24) vs. 39.17% (2022-23).
- Non-Food Expenditure: Declined slightly:
- Rural: 52.96% (2023-24) vs. 53.62% (2022-23).
- Urban: 60.32% (2023-24) vs. 60.83% (2022-23).
- Urban-Rural Consumption Gap: Narrowed further to 69.7% (2023-24) from 71.2% (2022-23).
- Monthly Per Capita Expenditure (MPCE):
- Rural: ₹4,122 (9.3% increase from 2022-23).
- Urban: ₹6,996 (8.3% increase from 2022-23).
- Spending Trends by Population Segment
- Bottom 5%: Significant increase in spending.
- Top 5%: Decline in spending—Rural: ₹10,137 (2023-24) vs. ₹10,501 (2022-23); Urban: ₹20,310 vs. ₹20,824.
- Gini Coefficient: Declined, indicating reduced consumption inequality:
- Rural: 0.237 (2023-24) vs. 0.266 (2022-23).
- Urban: 0.284 (2023-24) vs. 0.314 (2022-23).
- Food:
- Higher spending on cereals, eggs, fish, meat, and beverages.
- Non-Food:
- Rural: Conveyance, medical expenses, clothing, and footwear.
- Urban: Conveyance, rent, durable goods, and entertainment.
- State-Wise Spending Trends:
- Below National Average: West Bengal, Bihar, Assam, Odisha, UP, MP, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh.
- Above National Average: Maharashtra, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Kerala, Karnataka, Haryana, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh.
- Rajasthan: Higher-than-average rural spending but lower-than-average urban spending.
Should wealth tax be brought back to address inequality in India? - The Hindu
At a recent panel discussion in New Delhi, French economist Thomas Piketty suggested that a wealth and inheritance tax be imposed on the super-rich in India, which, in turn, could fund health and education. India’s Chief Economic Advisor, Anantha Nageswaran, opposed the idea, arguing that higher taxes could encourage fund outflows.
Wealth Tax
- Definition: Tax on the net market value of assets like cash, bank deposits, shares, real property, etc.
- Global imposition: France, Portugal, and Spain.
- Objective: Targets unproductive and non-essential assets.
- Wealth Tax in India: Introduced in 1957 based on Kaldor Committee recommendations (1955).
- Discontinuation: In 2015 & replaced by an increased surcharge on super-rich.
- Provision: Imposed 1% tax on earnings exceeding ₹30 lakh for individuals, HUFs, and companies.
Related Economic Concepts
- Tobin Tax: Tax on financial transactions, especially currency exchanges.
- Pigovian Tax: Imposed to correct negative externalities (e.g., pollution tax).
- Laffer Curve: Shows the relationship between tax rates and revenue.
- Tax-GDP Ratio: Measures tax revenue as a percentage of GDP, essential for fiscal analysis.
Environment
MP to translocate 15 tigers to Chhattisgarh, Rajasthan and Odisha - Indian Express
Chief Minister Mohan Yadav has directed for the translocation of 15 tigers from Madhya Pradesh to Rajasthan, Chhattisgarh and Odisha. The tigers will be relocated from the Bandhavgarh, Pench, and Kanha Tiger Reserves.
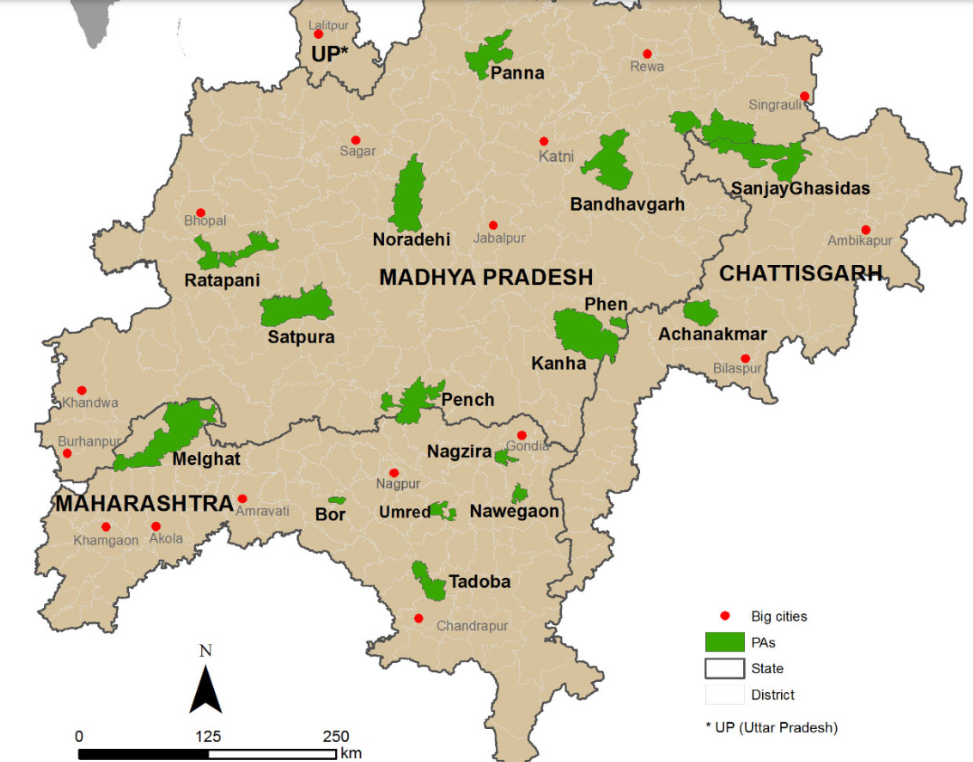
Kanha Tiger Reserve (KTR)
- About: Largest national park in Madhya Pradesh in the Maikal range of Satpuras.
- Designation: Established as a national park on June 1, 1955, and declared a Tiger Reserve in 1973.
- Mascot: First in India to introduce an official mascot, Bhoorsingh the Barasingha.
- Lowland Forests: Dominated by sal (Shorea robusta) and mixed trees with meadows.
- Highland Forests: Tropical moist deciduous trees with bamboo on slopes.
- Fauna: Royal Bengal Tigers, leopards, sloth bears, and Indian wild dogs.
Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve
- Location: Umaria district, Madhya Pradesh, between the Vindhyan and Satpura ranges.
- History: Declared a national park in 1968 and a Tiger Reserve in 1993.
- Significance: Features Bandhavgarh Fort.
- Vegetation: Tropical moist deciduous forests with sal, grasslands, and bamboo.
- Flora: Saj, Dhaora, Tendu, Arjun, Amla, and Palas.
- Fauna: Highest density of Royal Bengal Tigers globally; leopards, wild dogs, wolves, and jackals, Chital, sambar, barking deer, nilgai, and chowsingha.
Pench Tiger Reserve
- Location: Madhya Pradesh, extending into Nagpur district, Maharashtra.
- Components: Indira Priyadarshini Pench National Park, Pench Mowgli Sanctuary, and a buffer zone.
- Terrain: Undulating landscape with small hills and steep slopes.
- Vegetation: Ranges from moist valleys to dry deciduous forests.
- Flora : Teak, saag, mahua, grasses, and shrubs.
- Fauna: Chital, sambar, nilgai, gaur (Indian bison), and wild boar; tigers, leopards, wild dogs, and wolves.
Defence
China launches amphibious warship to boost naval power - The Hindu
China launched a new amphibious assault ship recently, capable of launching fighter jets and designed to strengthen the navy’s combat ability in distant seas.
Sichuan
- About: The first Type 076 ship.
- Specifications:
- Displaces 40,000 tons.
- Has electromagnetic catapult and arrestor technology for fighter jet operations.
- Capable of launching ground troops and providing air support.
- Development:
- Builds on Type 075 amphibious assault ships launched in 2019.
- Electromagnetic technology previously tested on the Fujian aircraft carrier.
- Strategic Importance
- Part of China’s effort to transition its Navy into a global force.
- Described as a “light aircraft carrier” by experts.
- Navy Size: China has the world’s largest navy and continues upgrading its fleet for distant sea operations.