Society
Should assisted dying be legalised? - The Hindu
Britain’s House of Commons recently voted by a majority to legalise assisted dying — a less controversial synonym for assisted suicide in England and Wales. The step signals a seismic social shift on an emotive issue. Advocates regard the new Bill as a humane and compassionate intervention that should — for those who want to exercise the option — bring closure to a painful, debilitating and degrading dependence on the immediate family.
Current Law on Assisted Dying
- Legal Status of Suicide: Suicide and attempted suicide are not criminal offences in England and Wales.
- Criminal Offence: Assisting or encouraging suicide is a criminal offence under the 1961 Assisted Suicide Act, punishable by up to 14 years in prison.
Proposed Law on Assisted Dying
- Eligibility: Applies to terminally ill, mentally competent adults with less than six months to live.
- Approval Process: Requires authorization from two doctors and a High Court judge.
Position in India on Assisted Dying
- Right to Die with Dignity: Affirmed by SC in Common Cause vs. Union of India (2018) under Article 21.
- Legalization of Passive Euthanasia: Permits withdrawal of life support for terminally ill patients or those in a permanent vegetative state.
- Guidelines for Passive Euthanasia: Living will must be executed with two witnesses and attested by a Judicial Magistrate.
Polity
Dr. Jitendra Singh Launches ‘Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi’ Initiative to Empower Grassroots Governance - PIB
In a significant step towards strengthening grassroots governance, Union Minister Dr. Jitendra Singh launched the ‘Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi’ initiative on Good Governance Day, celebrated to mark the Good governance day.
Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi Initiative
- Campaign: Part of the Prashasan Gaon Ki Aur campaign.
- Objective: Strengthen Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) by enhancing the capacity of representatives and officials.
- Pilot States: Odisha, Assam, Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Technology: Utilizes e-learning platforms, AI-powered chatbots, and mobile apps to improve knowledge and service delivery.
- Goal: Promote decentralized governance and participatory decision-making at the grassroots level.
- Outcome: Develop scalable, citizen-centric governance models for equitable and sustainable rural development.
Other Initiatives launched
- New Dashboard on iGOT Karmayogi Platform: Empowers ministries, departments, and state administrators with tools to monitor user registrations, course completions, and capacity-building progress.
- CPGRAMS Annual Report 2024: Highlights achievements such as resolving over 25 lakh grievances annually and implementing the Grievance Redressal Assessment and Index (GRAI).
Economy
Why is strengthening fisheries extension services crucial? - The Hindu
India possesses diverse fisheries resources that provide livelihood opportunities to approximately three crore fishers and fish farmers. The country has witnessed an 83% increase in the national fish production since 2013-14, that stands at a record 175 lakh tons in 2022-23. With 75% of this coming from inland fisheries, India is the second-largest fish and aquaculture producer globally.
Matsya Seva Kendras (MSKs)
- Objective: One-stop centers for aquaculture services under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Samapada Yojana (PMMSY).
- Government Assistance:
- 60% support for women and weaker sections to establish MSKs.
- Funding for 102 Kendras across States and Union Territories.
- Examples:
- Thrissur, Kerala: Lab for water, soil, and microbial analysis, including disease tests.
- Nasik and Sangli, Maharashtra: Capacity building for fishers on seed/feed inputs and technology.
- Collaborative Approach:
- Engage start-ups, cooperatives, fish farmers’ producer organisations, and SHGs.
- Promote best practices in fisheries management.
Role of Sagar Mitras in Supporting Fishers
- Sagar Mitra: Serve as intermediaries between govt and sea-borne fishers in coastal States and Union Territories.
- Key Functions:
- Collect data on marine catch, price fluctuations, and marketing needs at landing centers/harbors.
- Provide fishers with information on:
- Local regulations and weather forecasts.
- Natural calamities and hygienic fish handling.
- Potential fishing zones.
Improving Extension Services in Fisheries and Aquaculture
- Institutional Convergence: Integrate initiatives with Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs) and State/UT extension services.
- Digital Outreach: Utilize the AquaBazaar platform by the National Fisheries Development Board for virtual learning, demonstrations, etc.
- World Bank-Assisted Project: Formalize fisheries sector by creating digital work-based identities for fishers.

What is the Ken-Betwa River Linking Project? Why is it controversial? - Indian Express
Prime Minister recently laid the foundation stone of the Ken- Betwa River Linking National Projecton the 100th birth anniversary of former Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee. The move was criticised on the basis that this project poses a threat to the Panna Tiger Reserve.
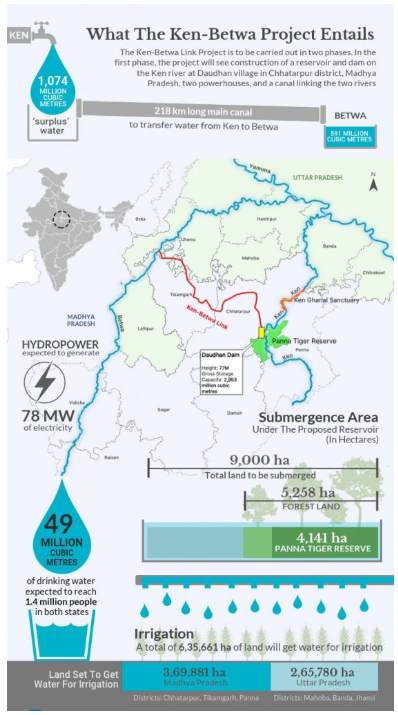
Ken-Betwa Link Project (KBLP)
- Objective: Transfer water from the Ken River to the Betwa River.
- Canal: 221 km long (including a 2-km tunnel).
- Submergence Area: Covers parts of UP (Jhansi, Banda, Lalitpur, Mahoba) and MP (Tikamgarh, Panna, Chhatarpur).
- Significance: First Interlinking Project under the National Perspective Plan (1980).
- Completion Target: Within 8 years (Ministry of Jal Shakti).
- Key Components:
- Irrigation: 10.62 lakh ha (8.11 lakh ha in MP; 2.51 lakh ha in UP).
- Drinking Water: Benefits ~62 lakh people.
- Energy Generation: 103 MW hydropower + 27 MW solar power.
- Phases:
- Phase-I: Includes Daudhan Dam, tunnels, canal, and powerhouses.
- Phase-II: Includes Lower Orr Dam, Bina Complex Project, and Kotha Barrage.
- Rivers:
- Ken River: Origin- Ahirgawan (MP), flows through Bundelkhand, and joins the Yamuna near Chilla village (UP).
- Betwa River: Origin- Vindhya Range (near Hoshangabad, MP), flows through Bundelkhand, and meets the Yamuna at Hamirpur (UP).
Criticism
- Deforestation: Submergence of ~98 sq km of the park and felling of 2-3 million trees.
- Wildlife: Threat to tiger reintroduction efforts and gharial population in Ken Gharial Sanctuary.
- Hydrological Concerns: A potential 12% rainfall deficit in September due to land-atmosphere feedback.
- Economic Viability: Supreme Court's Central Empowered Committee (CEC) questioned economic feasibility.
- Displacement and Protests: Displacement of 5,228 families in Chhatarpur and 1,400 in Panna districts.
Environment
African wild cat (Felis lybica) - The Hindu
The South Bengal Frontier of the Border Security Force (BSF) rescued an African wild cat (Leptailurus serval) from an alleged wildlife smuggling attempt along the India-Bangladesh border of Nadia district of West Bengal recently.
African wild cat
- Size: Head-body length 45-80 cm; tail length 24.1-36.8 cm; weight 3-8 kg.
- Appearance: Resembles a large housecat with longer legs.
- Notable features: reddish-brown ear backs, black-banded legs, tapering tail with black rings.

- Range: Africa, southwest and central Asia, India, China, and Mongolia.
- Habitat: Deserts, savannahs, grasslands, forests, and rocky terrains.
- Social Structure: Solitary but forms temporary groups of females and offspring.
- Activity: Mainly nocturnal but active in mornings and afternoons.
- Diet: Rodents, hares, birds, insects, reptiles, and scavenges occasionally.
- Lifespan: Up to 16 years.
- Threats: Hybridization with domestic cats; competition and disease from feral cats, habitat encroachment, vehicle collisions, and predator control measures.
- CITES: Appendix II
- IUCN status: Least Concern
Science and Technology
A global polio resurgence and the need to reevaluate the basics - The Hindu
The World Health Organization (WHO) has reported that poliovirus had been detected through routine surveillance of wastewater systems in five countries in the WHO European Region (Finland, Germany, Poland, Spain, and the United Kingdom) since September this year.

Rwanda declares end of Marburg outbreak - The Hindu
Rwanda has successfully managed its first-ever Marburg Virus Disease (MVD) outbreak officially declared over after a 42-day countdown, with no new cases since the last patient tested negative twice for the virus.
Marburg Virus Disease (MVD)
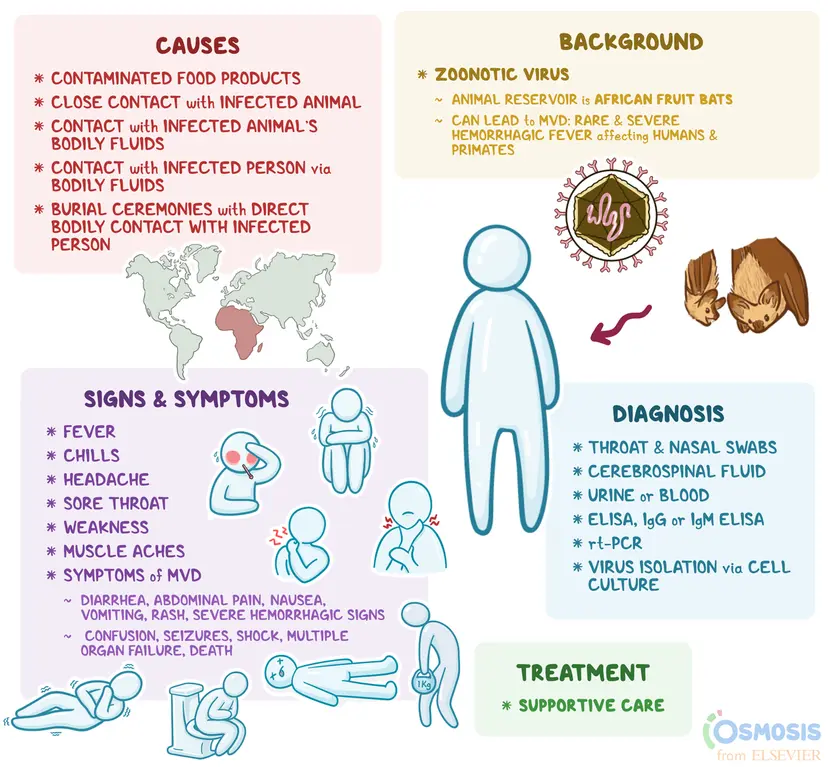
- Nature: Severe and often fatal hemorrhagic fever.
- Origin: 1967 in Marburg, Germany, linked to green monkeys from Uganda.
- Geographical Spread: Sub-Saharan Africa (e.g., Tanzania, Uganda, Angola, Ghana, Kenya, Zimbabwe).
- Primary Source of transmission: Fruit bats (Rousettus aegyptiacus).
- Human Spread: Direct contact with bodily fluids or contaminated surfaces.
- Symptoms:
- Early Stage: High fever, severe headache, malaise.
- Advanced Stage: Severe bleeding, liver failure, multi-organ dysfunction, shock, and death (within 8-9 days).
- Case Fatality: ~50%, ranging from 24% to 88% based on strain and care quality.
- Diagnosis: RT-PCR tests and virus isolation in biohazard facilities.
- Treatment: No specific cure; supportive care - rehydration and symptom management.
Why imaging of underwater hot spring active with microbial life is significant for India’s Deep Ocean Mission - Indian Express
In a first, Indian oceanographers have captured the image of an active hydrothermal vent located 4,500 metres below the surface of the Indian Ocean. This site holds potential for mineral exploration as part of the Rs 4,000-crore Deep Ocean Mission under the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
Significance of the Discovery for India
- Mineral Exploration: Boosts India's ability to explore and utilize deep-sea hydrothermal sulfide fields for mineral resources.
- Samudrayaan Mission: Supports India's deep-sea mineral extraction initiatives.
- Microbial Research: Advances understanding of chemosynthetic organisms with potential biotechnological applications.
Hydrothermal Vents
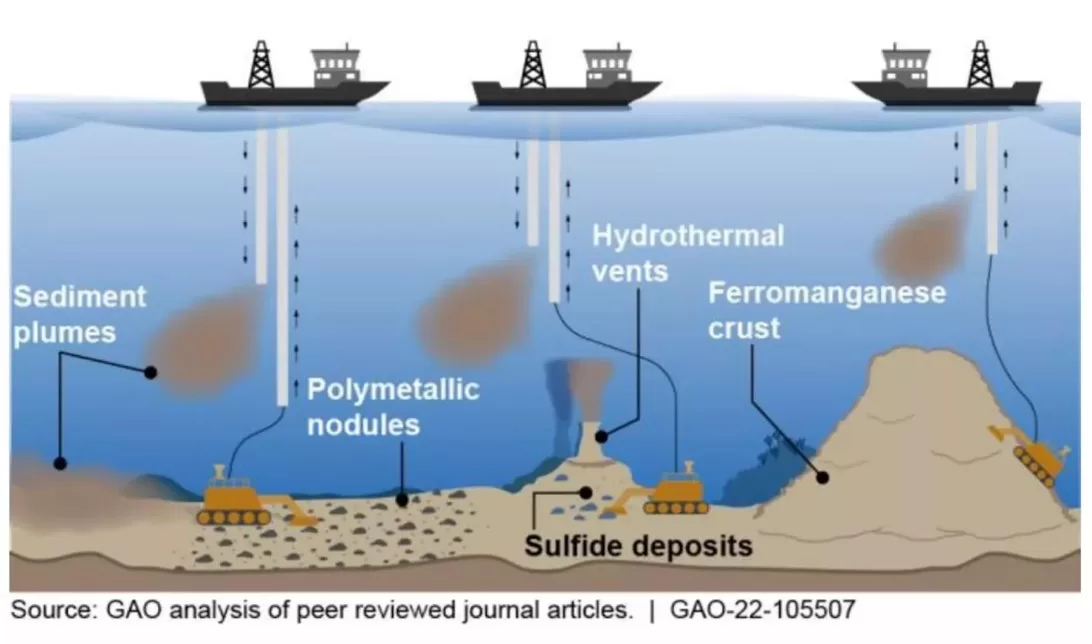
- Definition: Underwater hot springs near tectonic plate boundaries expelling hot, mineral-rich water.
- Discovery: 1977 near the Galapagos Islands, Ecuador.
- Formation Process:
- Cold seawater (~2°C) seeps into oceanic crust near tectonic activity.
- Water heats upon contact with magma (up to 370°C or higher).
- Superheated, mineral-rich fluids resurface, creating vents and plumes.
- Types:
- Black Smokers: Emit iron sulfides, forming black chimney structures.
- White Smokers: Emit barium, calcium, and silicon, forming white chimneys.
