Geography
150 years of IMD: What the weather agency has planned for the future - Indian Express
The India Meteorological Department (IMD) celebrated its 150th anniversary recently.
Improvements in Weather Forecasting by IMD
- Forecast Accuracy: Improved by 40% over the last decade.
- Doppler weather radars: Increased from 15 (2014) to 39 (2024).
- Automatic weather stations: Increased from 675 to 1,208.
- High wind speed recorders: Increased from 19 to 37.
- Rainfall monitoring stations: Increased from 3,995 to 6,095.
- New systems: 7 automated & heliport weather observing systems.
- Satellite Monitoring: INSAT 3DR and 3DS monitor weather continuously, replacing INSAT 3D (2014).
- Improved Weather Model Resolution: Resolution enhanced from 25 km to 12 km for medium-range forecasts (up to 10 days).
- Specific Forecast Improvements:
- Heatwaves: Predictable with 95% accuracy (up from 50% in 2014).
- Thunderstorms: Hourly detection accuracy increased to 86% (from 50% in 2017).
- Heavy rainfall: Predictable up to three days with 78% accuracy (from 50% a decade ago).
- Cyclone prediction: Improved by 35-40%.
IMD Vision Document 2047
- Aim: Making India climate-smart and weather-ready by 2047.
- Targets for Forecast Accuracy:
- Block-level severe weather forecasts (up to 3 days)
- 5-day advance forecasts: 90% accuracy.
- Week-long forecasts: 80% accuracy.
- 10-day advance forecasts: 70% accuracy.
Forecasting to Weather Management: IMD Initiatives
- Mission Mausam: Roadmap for weather modification and management.
- Establishment of a cloud chamber at IITM, Pune: To study cloud physics and develop cloud seeding techniques.
- Technological Advancements: Use of unmanned aerial vehicles, IoT-based sensors, and automated weather stations for remote observations.
- Enhanced Observation: Round-the-clock upper atmosphere monitoring at 100 km x 100 km grid using satellites, aircraft profilers, radars, and wind profilers.
- Improved Forecasting Accuracy: Goal of 100% detection for all weather phenomena.
Society
Does ‘blood money’ have a legal standing? - The Hindu
The death sentence awarded by a Yemen court to nurse Nimisha Priya from Kerala for murdering her business partner, and the subsequent debates and efforts surrounding her acquittal and repatriation, which involves monetary compensation paid to the victim’s family, have brought the focus back on ‘blood money’ and its implications.
Blood Money (Diya)
- Concept: Based on Islamic Sharia law.
- Meaning: Compensation paid by the perpetrator to the victim or their family for unintentional murder/ culpable homicide/ retribution (‘qisas’).
- Aim: Alleviate suffering and financial loss of the victim’s family.
- Legal Provisions: ‘Blood money’ does not prevent the state or community from imposing additional penalties.
- Factors influencing compensation: Gender, religion, and nationality.
- Contemporary Applications:
- Saudi Arabia: Mandatory in road accidents and workplace incidents.
- Iran: Compensation for women is half of men’s.
- Pakistan: Incorporated into law through Criminal Laws (Amendment) Ordinance, 1991.
- Yemen: Compensation decided through mutual agreement.
India’s Stand on ‘Diya’ (Blood Money)
- Legal Provisions: No provisions for ‘blood money’.
- Plea Bargaining: Allows the accused to plead guilty in exchange for concessions on charges or sentences.
- Introduction: Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 2005.
- Key Features of Plea Bargaining:
- Applicable only for offences with imprisonment of < 7 years.
- Excludes crimes against women, children below 14, heinous crimes (e.g., murder, rape), and socio-economic offences.
- Requires voluntary admission of guilt without coercion.
- Compensation to Victims: Section 265E resembles compensatory aspect of ‘blood money’.
- Limitations: Minimal use in India due to judicial delays and prolonged trials.
Historical Practices Similar to 'Blood Money'
- Irish Brehon Law (7th Century AD):
- Éraic (Body Price): Compensation based on offence severity.
- Log nEnech (Honour Price): Amount varied with victim's social status.
Welsh Galanas:
- Compensation linked to the victim’s status.
- Mandatory in murder cases unless justified or excused by circumstances.
- German Wergeld:
- Formalised in early medieval Germany.
- Closely resembles the concept of 'blood money'.
- Medieval States: Prescribed payments to victims' kin for homicide or severe crimes, as noted by Roscoe Pound in The Ideal Element in Law.
Instances of Indians Pardoned with ‘Blood Money’
- Arjunan Athimuthu (2019, Kuwait): Death sentence commuted to life imprisonment after ₹30 lakh was paid.
- Abdul Rahim (2006, Saudi Arabia): Pardoned after ₹34 crore was paid; remains in prison.
- Ten Indians (2017, UAE): Pardoned for murder after 200,000 dirhams was paid.
- Seventeen Indians (2009, UAE): Pardoned for the murder of a Pakistani national after ₹4 crore (in dirhams) was paid.
- Nimisha Priya’s Case: Pending decision; Iran has assured to take up the case.
World Affairs
Unpacking Israel-Hamas deal - Indian Express
Mediators in Doha, Qatar, have agreed on a phased ceasefire deal in Gaza on the some terms.
Ceasefire Deal
- First Phase:
- Hamas to release 33 hostages. Israel to release 900-1,650 Palestinian detainees.
- IDF to withdraw from central Gaza, Netzarim Corridor, and eventually the Philadelphi Corridor.
- Expected full Israeli withdrawal from Gaza and release of remaining hostages by Hamas in exchange for Palestinian detainees.
- Third Phase:
- Full reopening of border crossings.
- Reconstruction of Gaza to begin.
Impact of the Ceasefire Agreement for Israel and Hamas
|
For Hamas
|
For Israel
|
- Allows Hamas to recover from the extensive damage caused by Israeli military actions.
- Poses a threat with guerrilla attacks.
- Local command structures remain intact in Beit Hanoun.
- Aims to maintain a role in Gaza's future government, similar to Hezbollah's post-Civil War role in Lebanon.
|
- Its goal of removing Hamas from Gaza remains unmet.
- Domestically, it may fuel protests from families of those still in Gaza.
|
How US curbs on Russia shadow fleet may impact India oil imports - Indian Express
The outgoing administration in the United States announced sweeping new curbs on Russia’s oil trade last week, imposing sanctions on 183 tankers, the bulk of the so-called “shadow fleet” that has kept Russian oil flowing to consumers such as India and China.
Impact on India
- Import: Russia is India’s largest crude oil supplier, so sanctions may have significant effects.
- Impact of US Sanctions on Indian Oil Trade:
- Wind-Down Period: Indian refiners will accept cargoes on sanctioned vessels booked until Jan. 10, with deliveries until March 12.
- India's Position: India is not part of sanctions against Russia but avoids violating them to prevent secondary US sanctions.
- Impact on Oil Imports: India’s oil trade with Russia may be impacted beyond March 12, but overall imports may not be disrupted.
Economy
HOW FTI-TTP WILL ENSURE FASTER, SMOOTHER IMMIGRATION CLEARANCE - Indian Express
Union Home Minister Amit Shah will inaugurate the Fast Track Immigration – Trusted Traveller Programme (FTI-TTP) at Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Cochin and Ahmedabad airports recently from Ahmedabad.
FTI-TTP
- About: Part of the Centre's ‘Viksit Bharat @2047’ initiative, aiming for India to become a developed nation by 2047.
- Launch: First deployed in June 2024 at Terminal 3, IGI Airport.
- Purpose: Facilitate faster, smoother, and more secure immigration clearance for Indian Nationals and OCI passengers.
- Implementation: By Bureau of Immigration under Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Phases:
- Phase 1: Indian citizens and OCI cardholders.
- Phase 2: Foreign travellers.
How FTI-TTP Works
- Registration: On the online portal (https://ftittp.mha.gov.in) with personal details and required documents.
- Verification: Post verification, a whitelist of ‘Trusted Travellers’ is created for e-gate implementation.
- Biometric Capture: Biometrics are captured either at the FRRO or during airport passage.
- Validity: Until passport expiry or 5 years, whichever is earlier, and can be renewed.
- e-Gate Process: Passengers scan boarding passes and passports at e-gates. Upon successful verification, e-gate opens for clearance.
Documents Required for FTI-TTP
- Passport-Size Photograph:
- Must meet Indian passport standards.
- Face (including ears) should occupy 3/4 of the image.
- Photograph should be < 6 months with a plain white background.
- Passport Copy:
- At least six months of validity.
- Scanned copy of front page and final page.
- OCI Cardholders:
- Scanned copy of first page (biographic details) and last page (family and address details).
Environment
28 spotted deer dot every sq. km of Nagarahole Tiger Reserve in Karnataka - The Hindu
Wildlife spotting at any reserve is a matter of time, luck, and patience. But those visiting the Nagarahole Tiger Reserve in Karnataka will most likely catch a glimpse of the spotted deer. Officials of the reserve say their population has seen a steady increase in recent years. At present, there are 28 spotted deer for every sq. km of the reserve.
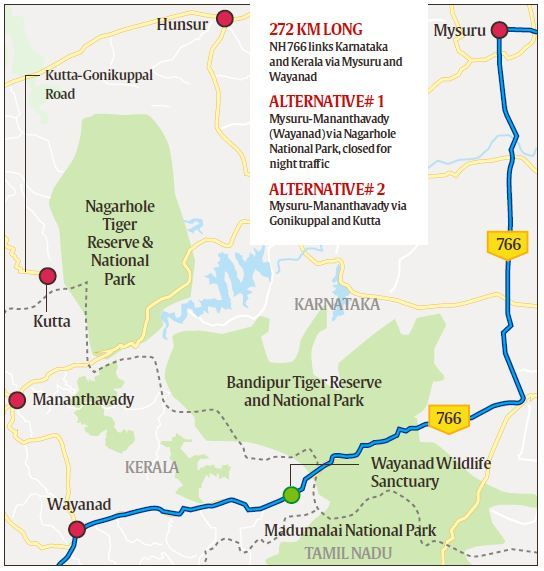
Bandipur Tiger Reserve (BTR)
- Location: At the tri-junction of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Kerala.
- Significance: Confluence of Western and Eastern Ghats & part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve (UNESCO World Heritage Site).
- History: Established in 1931 as Venugopala Wildlife Park.
- Renaming: Expanded as Bandipur Tiger Reserve under Project Tiger in 1973.
- Surroundings:
- Nagarahole Tiger Reserve (North-West, separated by Kabini Reservoir).
- Mudumalai Tiger Reserve (South).
- Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary (South-West).
- Rivers: River Kabini (North) & River Moyar (South).
- Climate: Tropical with distinct wet and dry seasons.
- Vegetation: Dry deciduous to tropical mixed deciduous.
- Flora: Rosewood, sandalwood, Indian kino tree, bamboo, etc.
- Fauna: Hosts largest population of wild Asian elephants in South Asia; Bengal tiger, gaur, sloth bear, golden jackal, dhole, four-horned antelope.
Science and Technology
ISRO executes satellite docking, places India in elite space club - The Hindu/ How ISRO achieved space ‘docking', and why it matters - Indian Express
The ISRO recently successfully demonstrated space docking — or the joining of two fast-moving satellites in space. Two small 220-kg satellites were brought within a distance of 3 metres from each other in orbit, their extended ring was joined with each other, retracted, and locked in space.

Docking Process
- Docking: Process of bringing two fast-moving spacecraft into the same orbit and joining them manually or autonomously.
- Significance:
- Essential for missions involving heavy spacecraft beyond the capacity of a single launch vehicle.
- Required for assembling space stations with multiple modules.
- Crucial for transporting crew and supplies to space stations.
First Docking Achievements
- United States: 1966: NASA’s Gemini VIII docked with Agena, crewed by Neil Armstrong.
- Soviet Union: 1967: Kosmos 186 and Kosmos 188 achieved the first uncrewed, automated docking.
- China:
- 2011: Unmanned Shenzhou 8 docked with Tiangong 1.
- 2012: Crewed Shenzhou 9 docked manually with Tiangong 1.
Significance
- Space Station: ISRO aims to set up a space station by 2035 and send humans to the Moon by 2040.
- Launch Vehicle Requirements: New heavy-lift launch vehicle (30 tonnes capacity) required for space station missions.
- Chandrayaan-4 Mission: Docking required for returning Moon samples.
Docking Experiment Process
- Maneuvers: ISRO conducted a series of maneuvers to bring SDX01 & SDX02 closer.
- Future Steps: Future plans include sharing electrical power and undocking for separate experiments.
- Final Steps: After drifting 5 km apart, satellites were brought to 3 meters by January 12. Data being analyzed before the actual docking occurs.
Bharatiya Docking System
- Docking Mechanism: India uses an androgynous docking system, where both Chaser and Target satellites have identical systems.
- New Sensors: Laser Range Finder, Rendezvous Sensor, and Proximity and Docking Sensor for precise measurements during docking.
Sriharikota to get third launch pad - The Hindu
ISRO on Thursday secured the Cabinet’s nod to set up the Third Launch Pad (TLP) at Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh, at an outlay of ₹3,985 crore.
Third Launch Pad (TLP) at Sriharikota
- Purpose: Will enhance launch capacity for future human spaceflight missions, including crewed lunar missions and space station development.
- Design: Designed to be universal and adaptable, supporting both NGLV and LVM3 vehicles with semi-cryogenic stages.
- Adaptability: Capable of scaling up configurations of NGLV.
Indian Launch Pads
- First Launch Pad (FLP): Operational for 30 years, supports PSLV and SSLV launches.
- Second Launch Pad (SLP): Established for GSLV & LVM3, operational for 20 years; is preparing for Gaganyaan human-rated launches.
- Third Launch Pad:
- Setting up the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) by 2035 and a Crewed Lunar Landing by 2040.
- Requires new, heavier launch vehicles with advanced propulsion systems, beyond the capacity of existing pads.
- Importance: Crucial to meet evolving space transportation needs for the next 25-30 years & serves as a backup for SLP.
Costly HPV vaccine needs to be part of national immunisation programme - The Hindu
January is Cervical Cancer Awareness Month, and doctors are urging women to get screened for this deadly disease. Cervical cancer develops in the cervix, or the wall of the cervix. The Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is responsible for 99.7% of cervical cancers worldwide and is among the leading causes of cancer in Indian women.
HPV Vaccine in India

- Introduction and Usage:
- Introduced in India in 2008; limited by high cost.
- States like Punjab and Sikkim have included it in immunization programs.
Target Group and Effectiveness:
- Most effective when given before virus exposure (recommended for children aged 12-13 years and high-risk individuals).
- Prevents over 90% of cancers linked to HPV.
- Does not treat existing infections but prevents future ones.
Protection and Benefits:
- Prevents genital warts and cancers (cervical, vaginal, vulvar, penile, anal, oral, throat, head, and neck cancers).
- Safe for immunocompromised or HIV-infected individuals.
- Vaccines in India: Gardasil (quadrivalent), Cervarix (bivalent), and Cervavac (Indian-developed).
Cervical Cancer in India
- Prevalence: Third most common cancer in India; second leading cause of death (GLOBOCAN 2020).
- Incidence: 123,907 cases, mortality: 9.1% (age-standardized incidence rate: 18 per 1 lakh).
- Impact: Cervical cancer contributes 6-29% of all cancers in women.
- Regional Data: Highest incidence in Papumpare district, Arunachal Pradesh (27.7).
Challenges to HPV Vaccination Uptake in India
- Key Challenges:
- High vaccine cost.
- Safety and effectiveness concerns due to lack of awareness.
- Cultural perceptions around reproductive health.
- Recommendations:
- HPV vaccine recommended for all males and females aged 9–26 years.
- Unvaccinated individuals aged 27–45 years should consider vaccination.
- Most effective before exposure to the virus.
How and why are plants grown in space: Takeaways from ISRO's success - Indian Express
The lobia (black-eyed pea) seeds that the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) sent to space on December 30 as a part of its Compact Research Module for Orbital Plant Studies (CROPS) germinated last week.
Why Grow Plants in Space?
- Sustainable food source: Reducea reliance on limited supplies.
- Nutrition benefits: Pre-packaged vitamins lose effectiveness over time.
- Air quality: Plants release oxygen during photosynthesis.
- Mental well-being: Taking care of plants can reduce stress.
Challenges of Growing Plants in Space
- Microgravity: Lack of gravity prevents roots from growing downwards and complicates nutrient delivery.
- Water distribution: Water clings to surfaces, hindering absorption by roots.
- Radiation and temperature: High radiation levels and extreme temperature fluctuations can damage plants and disrupt growth.
- Light conditions: Limited sunlight can halt photosynthesis, causing plants to consume more oxygen than they produce.
Methods of Growing Plants in Space
- Space garden: The "Veggie" system aboard the ISS.
- Hydroponics: Plants are grown using liquid solutions for water & nutrients.
- Aeroponics: No soil needed; reduces water (98%) and fertilizer (60%) usage.
- Soil-like media: Plants can also be grown in media resembling soil.
ISRO's Lobia Growth in Space
- CROPS box: A mini greenhouse with soil-like medium at 0.01 g gravity.
- Soil-like medium: Highly porous clay pellets with slow-release fertilizer.
- Photosynthesis: Warm and cool LEDs, simulating day-night cycle.
- Environmental control: Temperature maintained between 20-30°C.
- Watering system: Electric valve from Earth injected water.
- Growth progress: Seeds sprouted on day 4, leaves appeared by day 5.
Ideal Plants for Growing in Space
- Criteria: Growth rate, nutrient content, & compatibility with space farming.
- Leafy greens: Lettuce, spinach, and kale, which grow quickly.
- Legumes: Beans and peas, protein-dense and nitrogen-fixing.
- Root vegetables: Radishes and carrots.
- Cereals: Wheat and rice, grown for long-term sustenance.
- Fruits: Tomatoes and strawberries.
Defence
Three cheers for Indian Navy - Indian Express
Three frontline combatants — INS Nilgiri, lead ship of the Project 17A stealth frigate class, INS Surat, fourth and final ship of the Project 15B stealth destroyer class, and INS Vaghsheer, sixth and final submarine of the Scorpene-class project were commissioned in the Indian Navy at the Naval Dockyard in Mumbai recently.
INS Nilgiri
- About: Nilgiri-class stealth frigate, part of Project 17A, follow-on to Shivalik-class.
- Construction: By Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders (MDL), Mumbai, and Garden Reach Shipbuilders (GRSE), Kolkata.
- Design: "Integrated construction" for reduced building periods.
- Capability: Suitable for blue water operations, dealing with conventional and non-conventional threats.
- Weapons: Supersonic surface-to-surface missile, MRSAM, 76mm gun, rapid-fire close-in weapon systems.
INS Surat
- Abour: Fourth and final destroyer under Project 15B, following INS Visakhapatnam, INS Mormugao, and INS Imphal.
- AI-enabled: First Indian Navy warship with AI.
- Construction: Built by MDL, designed by the Warship Design Bureau.
- Capabilities: High speed, manoeuvrability, strike capability, and endurance.
- Network-centric warfare: Equipped with modern sensors and communication for integrated operations.
- Specifications: Displacement of 7,400 tonnes, length of 164 metres
- Weaponry: Armed with surface-to-air missiles, anti-ship missiles, & torpedoes.
- Speed: Powered by four gas turbines, speeds over 30 knots (56 km/h).
INS Vaghsheer
- About: Sixth and final submarine of Kalvari class, built under Project 75.
- Design: Based on the Scorpene class by Naval Group (France) and Navantia (Spain).
- Capabilities: Diesel-electric transmission, designed for attack and hunter-killer missions.
- Versatility: Silent, versatile, for anti-surface, anti-submarine warfare, intelligence, surveillance, and special operations.
- Armament: Wire-guided torpedoes, anti-ship missiles, and advanced sonar systems.
- Naming: Named after decommissioned Kalvari and Vela classes.
- Significance: Named after a type of sandfish found in the Indian Ocean.