Geography
New AI model ‘GenCast’ can beat the best traditional weather forecasts - The Hindu
A new machine-learning weather prediction model called GenCast can outperform the best traditional forecasting systems in at least some situations, according to a paper by Google DeepMind researchers published today in Nature.
GenCast Model
- About: Machine-learning weather prediction model by Google which uses a diffusion model approach similar to AI image generators.
- Role: Predicts weather for 15 days in 8 minutes, compared to hours in traditional methods.
- Working Mechanism:
- Trained on four decades of historical data (up to 2018) from ECMWF archives.
- Predicts variables like temperature, pressure, humidity, and wind speed at surface and 13 different heights.
- Divides the world into 0.25-degree latitude and longitude regions for precise forecasting.
- Significance:
- Outperforms existing systems with probabilistic ensemble forecasting for multiple weather scenarios.
- Offers a faster and more comprehensive understanding of atmospheric conditions.
Society
‘IndiaAI Future Skills’ initiative - PIB
Union Minister for Electronics and Information Technology Ashwini Vaishnaw has announced that 8.6 lakh candidates have enrolled in the IndiaAI Future Skills platform, a program aimed at democratizing Artificial Intelligence (AI) education and skilling.
IndiaAI Future Skills Platform
- Overview: A key pillar of the IndiaAI Mission to enhance AI workforce readiness.
- Focus: Mitigating barriers to AI education and advancing the AI talent pipeline.
- Objectives:
- Expand AI courses at undergraduate, postgraduate, and Ph.D. levels.
- Establish Data and AI Labs in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities for foundational AI education.
- Ensure inclusive access to AI education beyond urban hubs.
- Implementation: Developed in collaboration with industry partners for cutting-edge, industry-aligned training.
- AI Data Labs: Established in cities like Gorakhpur, Lucknow, Shimla, Aurangabad, Patna, Buxar, and Muzaffarpur.

Polity
The missing spotlight on urban local government elections - The Hindu
Urban local governments (ULGs) function as units of decentralised local self-governance, and are responsible for delivering civic services at the first mile, ensuring quality of life for citizens.
ULGs and Simultaneous Elections (ONOE)
- Socio-Economic Importance of ULGs:
- 4,800+ ULGs serve nearly 40% of India’s population, projected to exceed 50% by 2050.
- Contribute 60% to GDP, making their governance critical for economic and social development.
- Synchronised ULG elections can streamline governance at all levels.
- One Nation One Election (ONOE):
- Proposes synchronising elections for legislative bodies to reduce costs, voter fatigue, and disruptions.
- Focus has been on Lok Sabha and State Assemblies, with limited attention to ULG elections.
- Advantages of Synchronising ULG Elections:
- Cost and Efficiency: Reduces financial and administrative burden of frequent elections.
- Continuous Governance: Minimises interruptions caused by staggered election schedules.
- Enhanced Participation: Aligning ULG elections with state/national polls could boost voter turnout by leveraging larger campaigns.
Historical Exclusion of ULGs
- Partial treatment: ULG elections treated as distinct due to their status as State subjects under the Constitution.
- Exclusion from ONOE deliberations by:
- 79th Parliamentary Standing Committee Report (2015).
- NITI Aayog Discussion Paper (2017).
- Law Commission Draft Report (2018).
- Reasons cited: Logistical challenges and the large number of ULGs.
Challenges in ULG Elections
- Delays in ULG Elections: Over 60% of ULG elections delayed, as per the CAG report (2024) which may span over years, leaving ULGs under State government control, violating the spirit of local self-governance.
- Disempowerment of State Election Commissions (SECs): SECs lack autonomy for critical tasks like ward delimitation.
Implications of Delayed ULG Elections
- Administrative Inefficiency: Delays in ward delimitation and reservation exercises, often by State governments, hinder timely election schedules.
- Political Interference: State governments delay elections for political advantage, consolidating power or avoiding elections during unfavourable conditions.
- Citizen Disengagement: Delayed elections erode public trust in the democratic process & leads to reduced civic participation and engagement in governance.
Measures to Address Delayed ULG Elections
- Empowering SECs and Enforcing Timelines: Provide greater autonomy and resources to SECs for conducting elections timely.
- Mandate on the issue: Enforce the constitutional mandate of elections every five years with strict penalties for delays.
- Judicial scrutiny: Judiciary to ensure adherence to timelines.
- Decentralised Governance: Strengthen ULGs’ capacity and promote citizen participation in governance.
- Focus on ONOE: Align ULG elections with national and state elections to streamline processes and reduce delays.
World Affairs
National Dope Testing Laboratory (NDTL), New Delhi, receives approval from World Anti – Doping Agency (WADA) to manage Athlete Biological Passport (ABP) as a WADA approved unit - PIB
The World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) has granted approval for the NDTL, New Delhi on 6th December 2024, as an Athlete Passport Management Unit (APMU) to manage the Athlete Biological Passport (ABP).
Athlete Biological Passport (ABP)
- About: Advanced anti-doping tool that tracks an athlete's biological markers over time & ensures fair play and protects clean athletes by analyzing variations in blood and steroid profiles.
- Functions:
- Enables targeted testing and investigations for doping.
- Provides indirect evidence for the use of prohibited substances or methods.
- Serves as corroborating evidence in anti-doping rule violation cases.
- Modules in ABP:
- Haematological Module:
- Tracks markers of blood doping.
- Identifies prohibited substances/methods enhancing oxygen transport.
- Steroidal Module:
- Analyzes markers of steroid doping in urine/serum.
- Detects exogenous administration of Endogenous Anabolic Androgenic Steroids (EAAS).
- Endocrine Module:
- Monitors markers of human growth hormone (hGH) doping.
- Detects the use of hGH analogs.
Environment
Zero safe zones: No Indian city meets WHO air quality standards, says Lancet study - Indian Express
No one in India lives in areas where the yearly average pollution levels are below the levels recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO), with the high levels of PM2.5 associated with 1.5 million deaths a year, according to a study recently published in Lancet Planet Health.
Air Quality and Standards
- High vulnerability: 81.9% of Indians live in areas exceeding NAAQS limit of 40 µg/m³ PM2.5 (much higher than WHO’s standard of 5 µg/m³).
- Health Impacts of PM2.5:
- Affects respiratory system, increases risks of heart attacks, strokes, high blood pressure, and developmental delays in children.
- Every 10 µg/m³ increase in PM2.5 raises risk of death by 8.6%.
- Regional Pollution Levels:
- Lowest: 11.2 µg/m³ in Lower Subansiri, Arunachal Pradesh (2019).
- Highest: 119 µg/m³ in Ghaziabad and Delhi (2016).
- Study Findings:
- 1.5 million deaths (25%) linked to PM2.5 exposure during 2009-2019.
- Estimates higher than Global Burden of Disease report due to population growth and updated methodology.
WHO’s revised air quality guidelines 2021
- In September 2021, WHO updated its air quality guidelines (AQGs) to reflect the serious health impacts of air pollution
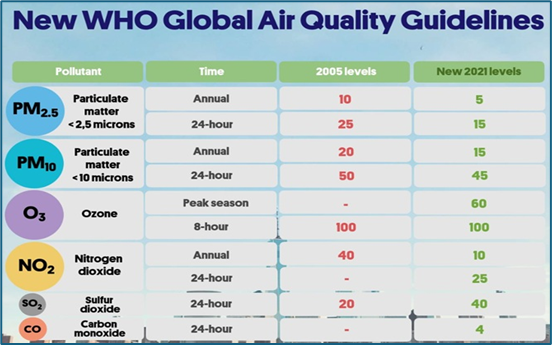
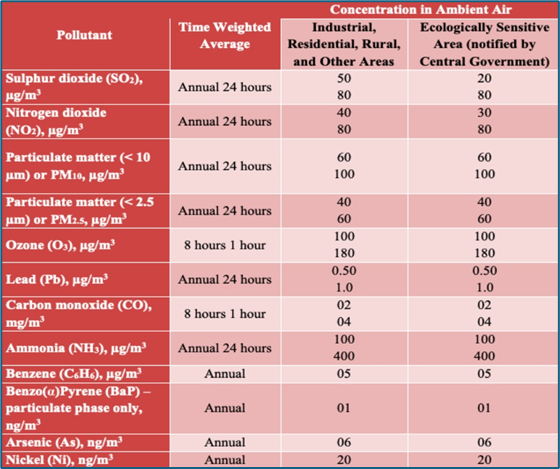
India’s National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS)
- Definition: Ambient air quality refers to the quality of outdoor air surrounding us.
- Legal Framework:
- Established under the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981.
- Set by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
- Pollutants Covered:
D. Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary - The Hindu
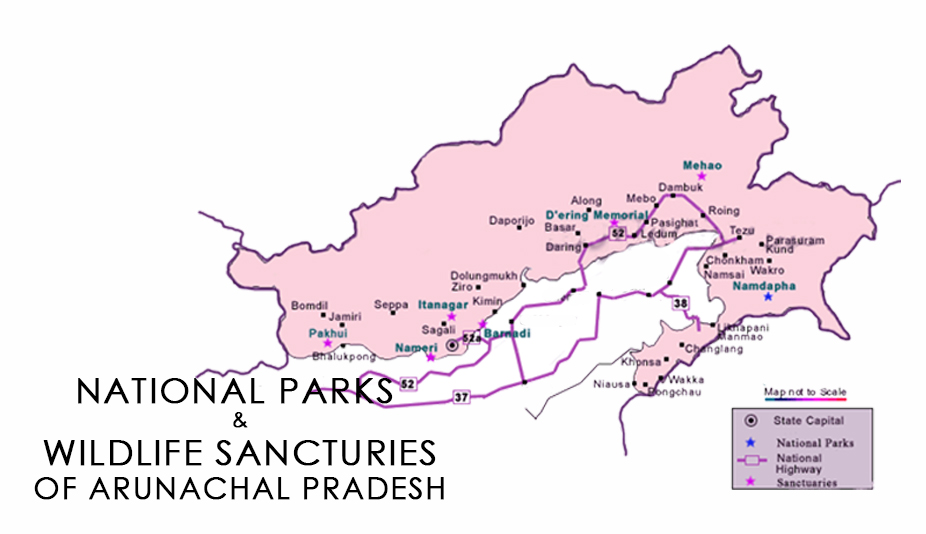
- Location: Situated in East Siang district, Arunachal Pradesh.
- Establishment: Established in 1976; renamed from Lali Wildlife Sanctuary in 1986.
- Climate: Tropical climate with rainfall from north-east and south-west monsoons.
- River: Traversed by the Siang River, a major river in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Flora: Dominated by riverine plains with thatch and grasses, Termenelia myriocarpa, Dillenia indica, Albizia spp., Bombax ceiba.
- Fauna: Hog Deer, Wild Pig, Tiger, and Elephant & over 150 bird species, including endangered ones like the White-Winged Wood Duck and Bengal Florican.
Malayan Night Heron - Indian Express
The Malayan Night Heron, a migratory bird from Southeast Asia, has been recently officially recorded in Madurai for the first time, near the Alagar Kovil hills.
Malayan Night Heron/ Malaysian night heron/ Tiger bittern
- Appearance: Medium-sized, nocturnal bird.
- Features: Rufous neck, barred chestnut back, black cap with crest, and white-tipped primaries.
- Habitat: Dense subtropical forests, including wetlands (streams, marshes, swamps) and evergreen forests at moderate elevations.
- Distribution: India, Southeast Asia, Philippines, and East Indies.
- Pattern: Native to Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia; migrates to India during winter (Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka).
- Diet: Feeds on earthworms and beetles.
- IUCN: Least Concern.
Defence
US unveils new anti-missile system Dark Eagle - The Hindu
The United States has developed a new anti-missile system called Dark Eagle, which is capable of intercepting enemy missiles in mid-air.
Dark Eagle Anti-Missile System
- About: Long-range hypersonic anti-missile system developed by the USA which can intercept ballistic, cruise, and hypersonic missiles mid-air.
- Range: Over 2,775 km; can strike deep within adversary territory.
- Capabilities: Features a two-stage ballistic missile with a C-HGB hypersonic glide warhead.
- Warhead speed: Mach 17 (3,000-3,700 m/s) at altitudes below 50 km.
- Prowess: Designed to surpass Russia’s S-300V4, S-400, and S-500 air defense systems.