Art and Culture
C. RAJAGOPALACHARI - PIB
Lok Sabha Speaker Shri Om Birla paid floral tributes to Bharat Ratna Shri Chakravarti Rajagopalachari in Central Hall of Samvidhan Sadan on his Birth Anniversary, recently.
C. Rajagopalachari (Rajaji)
- Birth: 10 December 1878, Thorapalli, Tamil Nadu.

- Role in India’s Independence Movement: Inspired by Mahatma Gandhi in 1919, he left his legal career to join the independence struggle.
- Participated in:
- Rowlatt Act protests
- Non-Cooperation Movement
- Vaikom Satyagraha
- Civil Disobedience Movement
- Award: Awarded the Bharat Ratna (1954) for contributions to politics and literature.
- Key Writings:
- Renowned for retelling Mahabharata and Ramayana in English.
- Ramayana – Chakravarti Thirumagan in Tamil.
Society
Yuva Sahakar Scheme - PIB
“Yuva Sahakar – Cooperative Enterprise Support and Innovation Scheme” is being implemented by National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC).
Yuva Sahakar Scheme
- Objective:
- Supports newly formed cooperative societies with innovative ideas.
- Focuses on young entrepreneur cooperatives operational for at least 3 months.
- Loan Features:
- Long-term loan: Up to 5 years.
- Interest Subvention: 2% on applicable term loan rate.
- Can be combined with subsidies from other Government of India schemes.
- Funding is project-based.
- Implementation: Executed by the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC).
- Key Features:
- Dedicated Rs. 1000 crore Cooperative Start-up and Innovation Fund under NCDC.
- Incentives for cooperatives in the North-East and aspirational districts.
- Special benefits for women, Scheduled Caste, and Scheduled Tribe candidates.
- Mission Link: Part of Sahakar 22, aiming to double farmers' income by 2022.
Polity
1991 Act: What SC stopped, why - Indian Express
The Supreme Court recently barred civil courts across the country from registering fresh suits challenging the ownership and title of any place of worship, and from ordering surveys of disputed religious places until further orders.
Case Before the Court
- Matter: Hearing petitions challenging the constitutional validity of the Places of Worship Act, 1991.
- Key Provisions:
- Prohibits conversion of any place of worship.
- Mandates maintenance of religious character as it existed on August 15, 1947.
- Exception: The Ram Janmabhoomi-Babri Masjid dispute was excluded since it was already under judicial consideration.
Impact of the Order
- Scope: Applies to both pending civil suits and those filed in the future.
- Restrictions on Courts:
- Bars civil courts from registering such cases.
- Prohibits courts from ordering surveys or seeking reports from the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
- Nature of Civil Cases: Challenges raised about the title of mosques, alleging they were built on razed Hindu religious structures.
- Supreme Court's Observation: Court orders in such cases can be challenged for violating constitutional principles of secularism and rule of law, irrespective of the Places of Worship Act.

Places of Worship Act, 1991
- Historical Context: Enacted during the Ram Janmabhoomi movement to prevent future religious disputes.
- Objective:
- Prohibit conversion of places of worship to maintain their religious character as of August 15, 1947.
- Prevent conversions within or between religions.
Economy
India's first Hyperloop train test track completed by IIT Madras - The Hindu
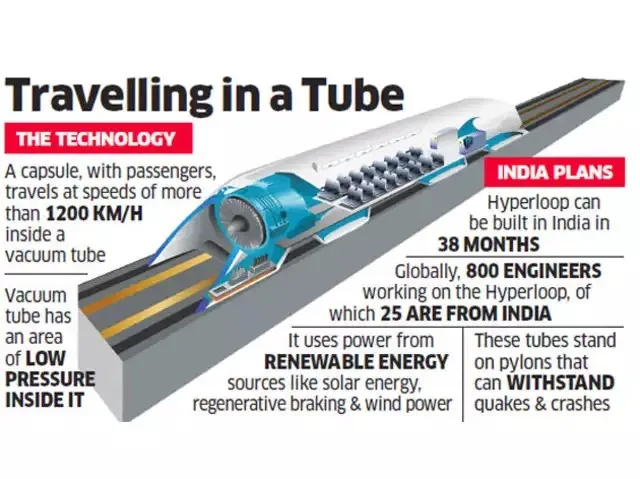
In a major leap forward for transportation technology, IIT Madras has completed a 410-meter Hyperloop test track, marking a significant milestone in India’s journey toward futuristic transport systems.
Hyperloop Track
- Concept: High-speed transport system with pods traveling in low-pressure tubes introduced by Elon Musk in 2012.
- Working Mechanism: Pods operate in vacuum-sealed tubes, reducing friction.
- Speeds: Up to 1,100 kmph; cruising speed: 360 kmph.
- Key Components:
- Low-Pressure Tubes: Minimize air resistance.
- Magnetic Levitation (Maglev): Eliminates friction by "floating" on magnets.
- Linear Electric Motors: Ensure smooth and efficient propulsion.
- Environmental Advantage: Zero direct emissions; promotes sustainable and green transit.
- India’s Hyperloop Project: Collaboration among Indian Railways, IIT-Madras (Avishkar Hyperloop team), and TuTr startup.
- Significance to India: Addresses growing demand for efficient, high-speed, and sustainable transportation.
Environment
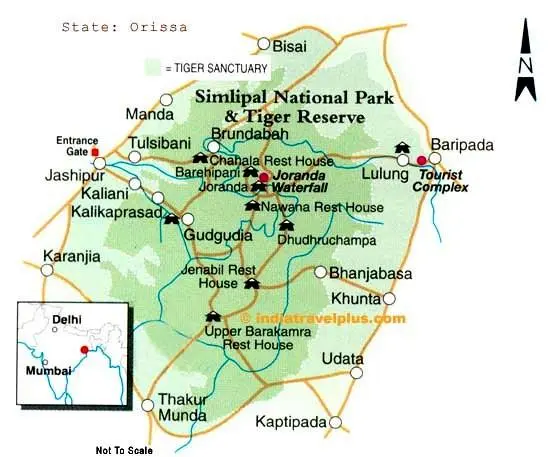
Similipal Tiger Reserve - The Hindu
- Location: Mayurbhanj District, in the Northernmost part of Odisha.
- Landscape: Surrounded by high plateaus and hills (highest peak - Khairiburu and Meghashini twin peaks (1515m)).
- Designation: Declared a 'Tiger Reserve' in 1956 and included under the national conservation programme 'Project Tiger' in 1973.
- Transitional area: 2250 sq. km
- Significance: Included as a part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves by UNESCO in the year 2009.
- Terrain: Udulating and hilly interspersed with open grasslands and wooded areas.
- Vegetation: Northern tropical moist deciduous dominating some semi-evergreen patches.
- Feature: Only landscape in the world that is home to melanistic tigers.
- Tribes: Kolha, Santhala, Bhumija, Bhatudi, Gondas, Khadia, Mankadia and Sahara.
- Flora: Sal is the dominant tree species.
- Fauna: Leopard, Gaur, Elephant, Langur, Barking and Spotted Deer, Sloth Bear Mongoose, Flying Squirrel, Porcupine, Turtle, Monitor Lizard, Python, Sambar, Pangolin etc.
Indian rock python - The Hindu
Capable of growing up to nine-feet in length and taking down large prey, including deer and cattle, the Indian rock python (Python molurus), used to be a common sight across Tamil Nadu, especially in agricultural areas and rocky foothills. However, due to habitat loss, the species is believed to have declined across the State, except in the Moyar Valley, where the pythons seem to be thriving.
Indian Rock Python

- Overview: Large, nonvenomous python species.
- Common names: Black-tailed python, Asian rock python.
- Appearance: Whitish or yellowish with blotched patterns (tan to dark brown).
- Variation:
- Darker: Western Ghats, Assam.
- Lighter: Deccan Plateau, Eastern Ghats.
- Habitat: Found in grasslands, savannas, swamps, marshes, rocky foothills, woodlands, open forests, and river valleys.
- Distribution: India, southern Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Bhutan, Bangladesh, northern Myanmar.
- Behavior: Nocturnal, terrestrial, skilled climber, and excellent swimmer.
- IUCN: Near Threatened.
- CITES: Appendix II.
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I.
- Threats: Habitat destruction and illegal trade.
Science and Technology
What is Disease X and why the world should prepare for it - The Hindu
The recent outbreak reported in the first week of December 2024 in the Democratic Republic of Congo, which has claimed over 400 lives and remains unclassified, has raised concerns that it could be an instance of Disease X.
Disease X
- Definition: A hypothetical global health threat representing an unknown pathogen capable of causing epidemics or pandemics, coined by WHO in 2018.
- Significance: Highlights preparedness needs, demonstrated by recent outbreaks like the unclassified epidemic in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) with over 400 deaths.
- Origin: Emerged after the 2014–2016 West African Ebola epidemic exposed global readiness gaps.
- Scope: Includes "known unknowns" (anticipated threats without specifics) and "unknown unknowns" (unanticipated threats).
- Purpose: Emphasizes the inevitability of new pathogens and the necessity for proactive measures.
Patterns in Emerging Diseases
- Link to Ecological Disruptions: New diseases like HIV, SARS, MERS, and Ebola often emerge due to deforestation, urbanisation, and climate change.
- Undiscovered Viruses: An estimated 1.7 million undiscovered viruses exist in wildlife, with hundreds of thousands potentially infecting humans.
- Rising Outbreak Frequency: Novel outbreaks have grown since the mid-20th century due to environmental, demographic, and global factors.
- Vulnerable Regions: Areas with high biodiversity and weak healthcare systems, e.g., Congo Basin, face higher risks.
- Global Interconnectedness: International travel and trade can turn local outbreaks into pandemics, as seen with COVID-19.
- Epidemiological Insights: High-risk regions and behaviours can be identified, though exact emergence of Disease X remains unpredictable.
Need for Global Collaboration
- Unified Global Response: WHO initiatives like the priority pathogens list and the proposed Pandemic Treaty aim to foster global cooperation against pandemics.
- Key Actions for Governments: Share data, pool resources, and ensure equitable access to diagnostics, treatments, and vaccines. Strengthen public health systems and invest in research and innovation.
- Frameworks for Collaboration: Expand agreements like the Nagoya Protocol to include biological materials like pathogens.
- Global Solidarity: Emphasises that a novel disease in one region is a threat to all, necessitating collective action.
Willow, Google's quantum computing chip - Indian Express
Google has announced a significant advancement in quantum computing as it unveiled its next-generation chip called 'Willow'.
Willow Chip
- About: A quantum computing chip developed by Google.
- Components:
- Single and two-qubit gates.
- Qubit reset and readout.
- Engineered to prevent lag between components for optimal performance.
- Performance:
- Solved a complex mathematical problem in 5 minutes, which classical computers would take longer than the history of the universe to complete.
- Completed a benchmark computation in under 5 minutes, compared to 10 septillion years for current supercomputers.
- Technology:
- Operates with superconducting transmon qubits.
- Uses tiny electrical circuits exhibiting quantum behavior at extremely low temperatures.
- Circuits function as artificial atoms in a quantum state.