Polity
The Collegium and Changes, It May Still Be Early Days - The Hindu
Two interesting nuggets of information have emanated in recent days about the functioning of the Supreme Court of India’s Collegium. As is often the case with the body’s processes, reports in the media attribute the news of these decisions to unnamed sources. The collegium, the accounts say, will now conduct interviews of candidates who have been recommended for elevation as judges to the High Courts. The panel will also, to the extent possible, exclude from selection those whose close relatives have served or continue to serve as judges of the High Courts or the Supreme Court.
Evolution of the Collegium System
- Origin: Created through judicial interpretations.
- Evolution: From the Second Judges Case (1993), where the SC interpreted ‘consultation’ in Article 124 as ‘concurrence’ by a Collegium.
- Composition: Chief Justice of India (CJI) and senior judges.
- Purpose: To protect judicial independence and shield judicial appointments from executive influence.
Challenges to Collegium’s Effectiveness
- Opacity in Functioning: Decision-making is secretive, with no formal records of deliberations.
- Absence of clear candidate evaluation: Leads to subjectivity and inconsistency.
- Executive Interference: The executive can delay or obstruct Collegium recommendations.
- Tactics: Stalling recommendations indefinitely and selectively accepting or returning them without justification.
- Nepotism: Judges are often accused of favouring candidates with familial or professional ties.
- Absence of Binding Rules: No formal rules, relying on informal practices.
Proposals to Reform the Collegium System
- Candidate Interviews: Interviews for High Court judgeships ensures merit-based appointments.
- Addressing Nepotism: Discouraging selection of candidates with familial ties to serving judges.
- Codification of Processes: Formalizing Collegium functioning with clear rules on eligibility, selection, and timelines.
- Time-Bound Approvals: Implementing fixed timelines for government action on Collegium recommendations.
- Transparency: Publishing justifications for appointments and rejections to enhance public trust.
- Independent Oversight Mechanism: Establishing a body to oversee Collegium recommendations.
Economy
PM to open Z-Morh tunnel, a key part of Kashmir-Ladakh corridor - The Hindu
The Z-Morh tunnel is set to become the first major milestone in the effort to build a strategic corridor between Kashmir and Ladakh which is open all through the year, with Prime Minister Narendra Modi slated to inaugurate it on January 13.
Z-Morh Tunnel
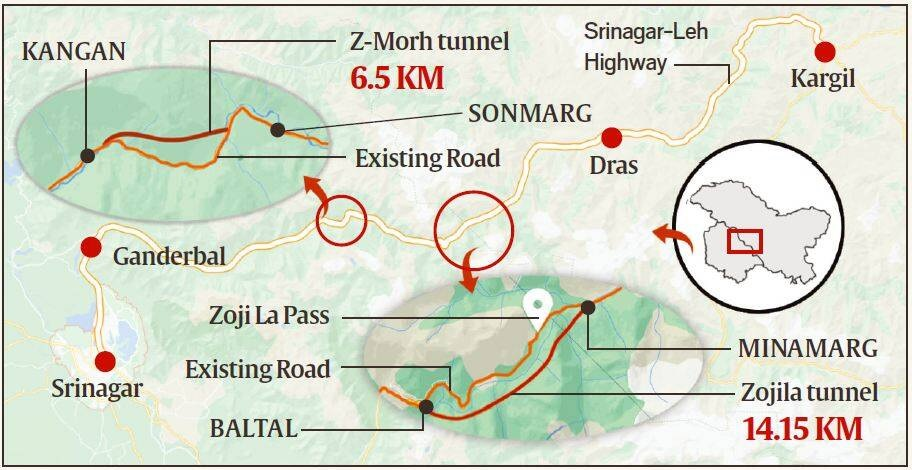
- Importance: Part of the strategic corridor connecting Kashmir and Ladakh, enabling year-round access.
- Location: Ganderbal district
- Length: 6.5 km, 2 -lane main tunnel with auxiliary escape & ventilation tunnels.
- Intelligent traffic management system: For vehicle flow and safety.
- Strategic Importance:
- Bypasses avalanche-prone areas, ensuring winter accessibility to Sonamarg.
- Integral to the Zojila tunnel project.
- Enhances defense preparedness with quicker access to border areas in Ladakh.
Decoding India’s growth slowdown - The Hindu
The first advance estimates of India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in 2024-25, released by the National Statistics Office (NSO) this week, shows a decline in the real GDP growth rate to 6.4% from 8.2% registered in 2023-24. This is lower than the 6.5 to 7% range projected by the Economic Survey in July 2024. The growth rate of nominal GDP, which is the sum of the real GDP growth rate and the overall inflation rate, is estimated at 9.7% in 2024–25—significantly lower than the 10.5% growth rate projected in the last Union Budget.
Data Discrepancies in India's GDP Estimates
- IMF Observations: Flaws in India's GDP estimates due to the use of WPI as a deflator instead of the more appropriate PPI (under development).
- Challenges with GDP Deflator: WPI volatility over the past decade has caused divergences between WPI and CPI inflation rates.
- Contradictory Trends:
- Nominal GDP growth declined from 14.2% (2022-23) to 9.6% (2023-24).
- Real GDP growth showed an increase from 7.0% to 8.2%, implying a deflator of only 1.4% in 2023-24 despite 5.4% retail inflation.
- Implications:
- High WPI volatility leads to misleading macroeconomic data.
- Creates risks of policy errors and challenges in accurately monitoring economic trends.
Fiscal Strains
- Economic Slowdown: GVA growth has been declining since 2023-24.
- Public Sector Growth: Public administration, defense, and other services are expected to show higher GVA growth in 2024-25.
- Revenue and Expenditure Gaps: Non-tax revenues reached 78% of the target due to a ₹2.11 trillion surplus from RBI transfers.
- Impact of Economic Slowdown on Budget: Slow tax revenue growth has disrupted the fiscal plan.
- Required Adjustments: A balance between fiscal rectitude and economic growth is needed.

Artificial intelligence, Big Data among top 10 fastest growing jobs by 2030: Report - Indian Express
The World Economic Forum's 'Future of Jobs' report 2025 presented results based on data gathered from more than 1,000 leading global companies.
Future of Jobs Report 2025
- Published By: World Economic Forum (WEF).
- Data Source: Insights from 1,000+ global companies, representing 14 million workers across 22 sectors and 55 economies.
Key Highlights
- Job Disruption:
- 22% of jobs disrupted by 2030.
- Net job increase of 78 million by 2030 (170 million new jobs, 92 million displaced).
- Drivers of Change:
- Technological advancements, geoeconomic fragmentation, demographic shifts, green transition, and economic uncertainty.
- Fastest-Growing Jobs:
- AI and machine learning experts, software developers, FinTech engineers (percentage growth).
- Frontline roles: farmworkers, delivery drivers, construction workers, salespersons, nursing professionals, and social workers.
- Declining Roles:
- Traditional jobs like graphic designers and administrative assistants impacted by automation.
- Skill Gap:
- 40% of future job skills will be new or evolving.
- 59% of the global workforce needs reskilling or upskilling by 2030.
- Top Skills by 2030:
- AI and big data.
- Networks and cybersecurity.
- Technological literacy, creativity, and resilience.
- Automation Impact:
- AI-driven tools reshaping routine tasks.
- 41% of companies plan workforce reductions due to automation.
Environment
Two rare Neuroptera species found for the first time from Kerala - The Hindu
Researchers have found two rare Order Neuroptera species, Glenochrysa zeylanica and Indophanes barbara from Kerala.
Neuroptera
- About: Insects commonly called lacewings due to intricate wing vein patterns.
- Nature: Adults are terrestrial, found on plants for settling or hunting prey.
- Ecological Significance:
- Predatory behavior aids in agriculture.
- Larvae act as biological control agents against major agricultural and horticultural pests.
|
Glenochrysa zeylanica
|
Indophanes barbara
|
- About: A green lacewing belonging to the Chrysopidae family in Order Neuroptera.
- Rediscovery: Wayanad district, Kerala.
- Location: Considered endemic to Sri Lanka; reported in India for the first time.
|
- About: A species of antlion belonging to the Myrmeleontidae family.
- Habitat: Under loose soil, shielded from sunlight, wind, and rain.
- Identification: Adults resemble damselflies but have long, distinct antennae.
|
Science and Technology
India releases compilation of 10,000 human genomes from 83 population groups - The Hindu
India has completed and made available a year-long compilation of 10,000 human genomes representing 83 population groups, making up about 2% of the country’s 4,600 population groups, as a database. This collection will serve as a template of future investigations into disease and drug therapy.
Genome India Database
- Location: Indian Biological Data Centre (IBDC), Faridabad, Haryana.
- Genomic Findings:
- 27 million low-frequency variants, with 7 million not found in global databases.
- Specific population groups exhibit higher frequencies of certain gene variants.
- Purpose: To study diseases, advance precision medicine, and enable targeted clinical interventions.
- Data Access: Data will be coded numerically, not by caste or tribe.
Genome India Project (GIP)
- Launch: By the DBT on 3rd January 2020.
- Research: By Centre for Brain Research, Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru, in collaboration with 20 institutions.
- Objective: Whole-genome sequencing of 10,000 individuals to study diseases and develop diagnostic markers for the Indian population.
- Genetic Diversity: India’s population has over 4,600 ethnic groups.
- Data Storage: The 8 petabyte dataset stored at IBDC, Faridabad, India’s first national life science data repository, inaugurated in 2022.
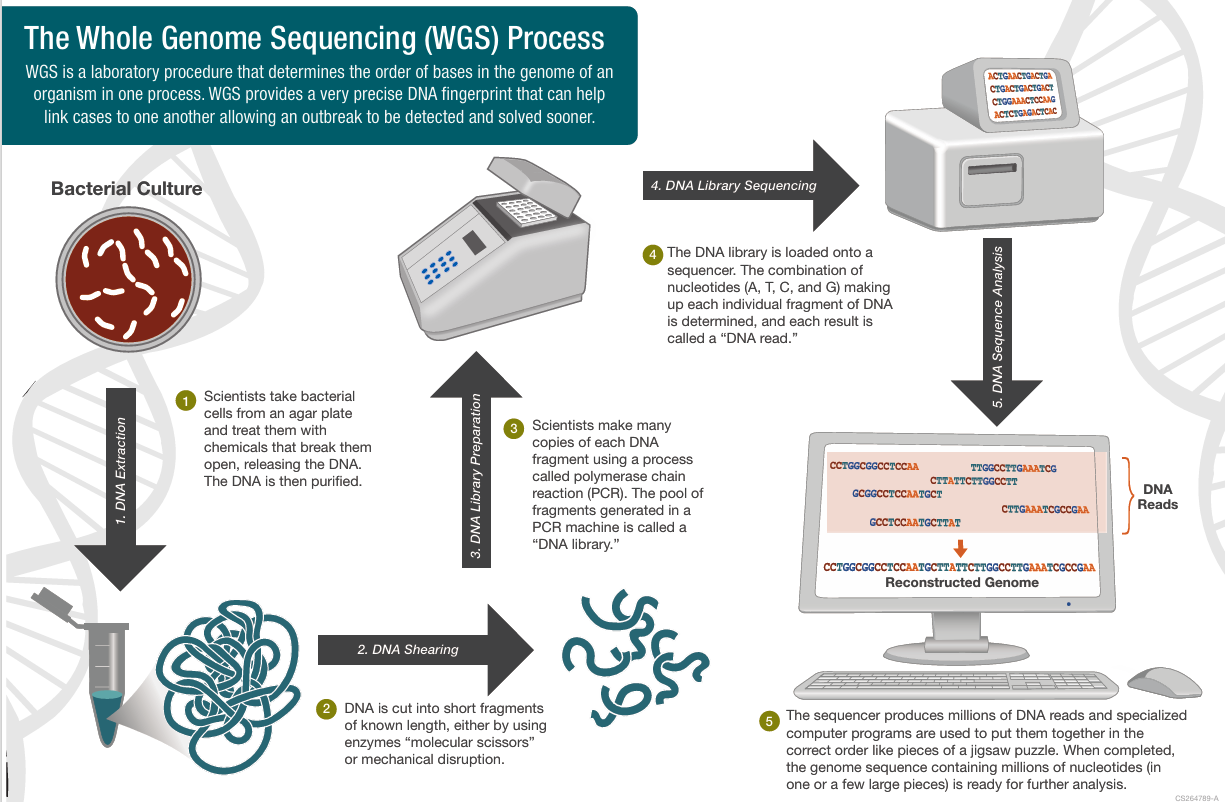
Genome Sequencing
Accessible, affordable technology to detect anaemia transferred to ICMR - The Hindu
AnemiaPhone, a technology developed by Cornell University researchers to accurately, quickly, and cheaply, assess iron deficiency, has been transferred to the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) for integration into its programmes for anaemia, women’s health, and maternal and child health throughout the country.
AnemiaPhone
Development: Cornell University, USA.
Key Features:
- Enables rapid screening and diagnosis of iron deficiency.
- Targets anemia, affecting 50%-70% of pregnant women in India.
Working:
- Requires a finger stick and a drop of blood on a test strip.
- Results are assessed within minutes.
- Data is uploaded to a clinical database via mobile or computer.
- Facilitates on-spot guidance, triage, and referrals by healthcare workers.