Geography
Krishna River Floods - Indian Express
Context
The recent surge in the Krishna River has resulted in boats being washed downstream, with some colliding with the gates of the Prakasam Barrage.
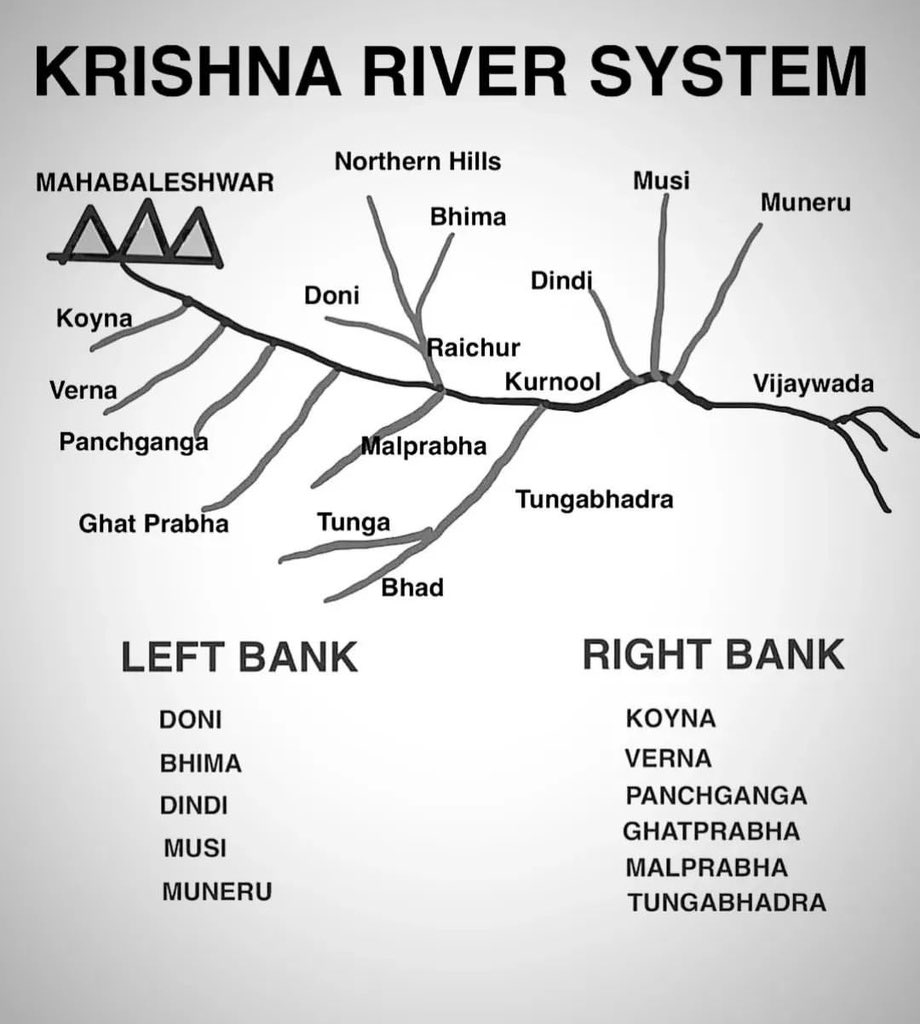
Krishna River
- About: The fourth biggest river after Ganga, Godavari and Brahmaputra in terms of water inflows and river basin.
- Origin: Western Maharashtra state in the Western Ghats range near the Mahabaleshwar.
- Drainage: Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana, and Andhra Pradesh
- Mouth: Bay of Bengal at Hamasaladeevi in Andhra Pradesh.
- Total Length: 1300 km
- Basin area: ~ 258,948 sq. km.
- Boundaries:
- North: Balaghat range
- South & East: Eastern Ghats
- West: Western Ghats
- Right bank tributaries: Ghatprabha, Malprabha, and Tungabhadra,
- Left bank tributaries: Bhima, Musi and Munneru.
Polity
What do we know about ANIIDCO? - The Hindu
Context
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDCO) is the project proponent for the NITI Aayog-promoted ₹72,000 crore mega infrastructure project in Great Nicobar, the southernmost island in the Andaman and Nicobar archipelago.
ANIIDCO
- Incorporation: June 28, 1988 under the Companies Act.
- Objective: To develop and commercially exploit natural resources for the balanced and environment friendly development of the territory.
- Main activities:
- Trading of petroleum products, Indian made foreign liquor and milk
- Managing tourism resorts
- Infrastructure development for tourism and fisheries
- Issues with ANIIDCO:
- It neither had an environment policy nor an environment cell.
- It did not even have the human resources needed to oversee.
- It recently started a process for recruiting people with relevant expertise such as urban planners, environmental planners, architects, infrastructure specialists, and legal and financial experts.
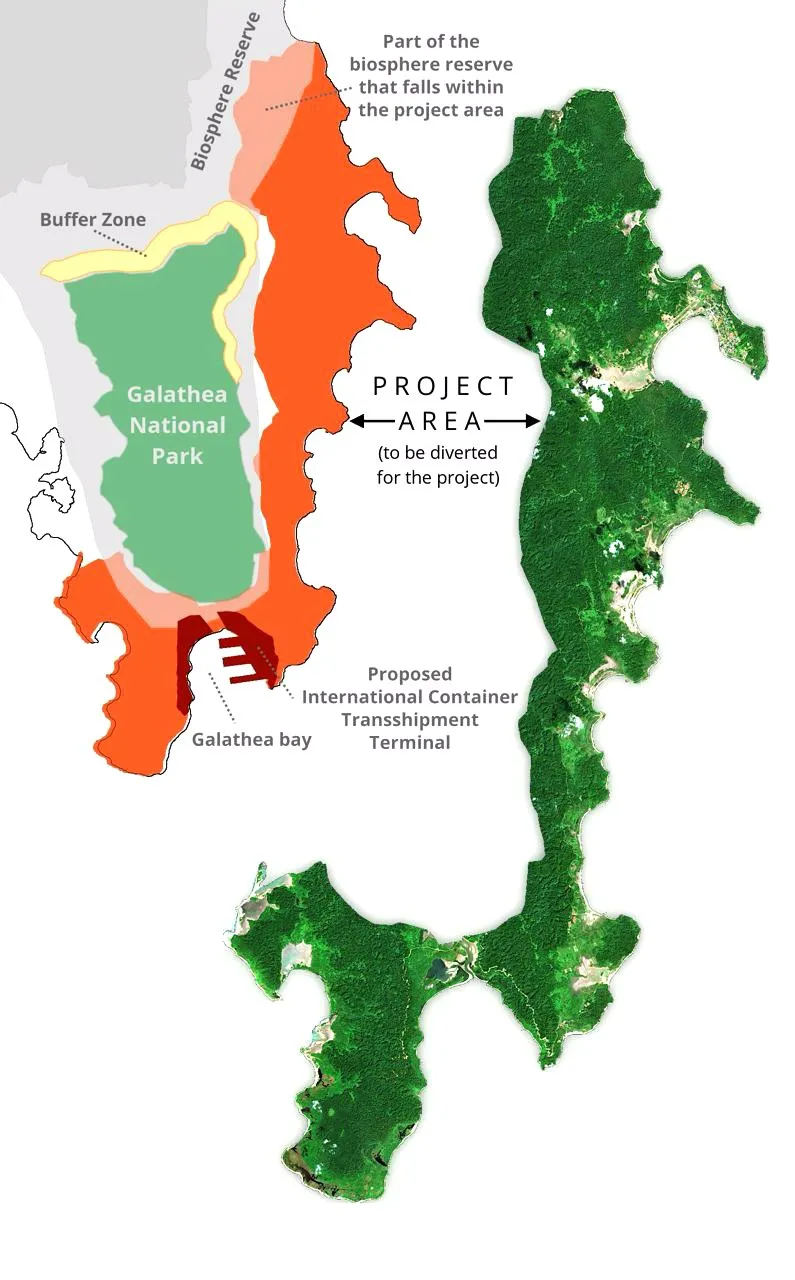
Great Nicobar Island Project
- Launch: 2021
- About: A mega project to be implemented at the southern end of the Andaman and Nicobar islands.
- Components:
- An International Container Trans-shipment Terminal (ICTT)
- A greenfield airport
- A tourism and township project
- A 450 MVA solar and gas based power plant in Great Nicobar
- Implementation: Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDCO)
- Location: Close to the Malacca Strait, the main waterway that connects the Indian Ocean to the Pacific.
Pros and Cons of the project
|
Pros
|
Cons
|
- Strategic significance: Great Nicobar is equidistant from Colombo to the southwest and Port Klang and Singapore to the southeast & is also close to the significant East-West international shipping corridor.
- Economic significance: The proposed port will allow Great Nicobar to participate in the regional and global maritime economy by becoming a major player in cargo transshipment.
- Security significance: Increasing Chinese influence in the Bay of Bengal & china building a military facility at Coco Islands (Myanmar) lying just 55 km to the north of the Andaman & Nicobar Islands has made this project more important.
|
- Threat to Island Ecology: The loss of tree cover will affect the flora and fauna, increase runoff and sediment deposits in the ocean, impact the coral reefs & mangroves in the area and threaten the Nicobar Megapode bird and leatherback turtles in the Galathea Bay area.
- Impact on tribes: There may be devastating impact on the Shompen, a PVTG of hunter-gatherers with an estimated population of a few hundred individuals.
- Seismic issues: The proposed port is located in a seismically volatile zone, which experienced a permanent subsidence of about 15 ft during the 2004 tsunami.
|
Why has H.P. raised the marriageable age for women? - The Hindu
Context
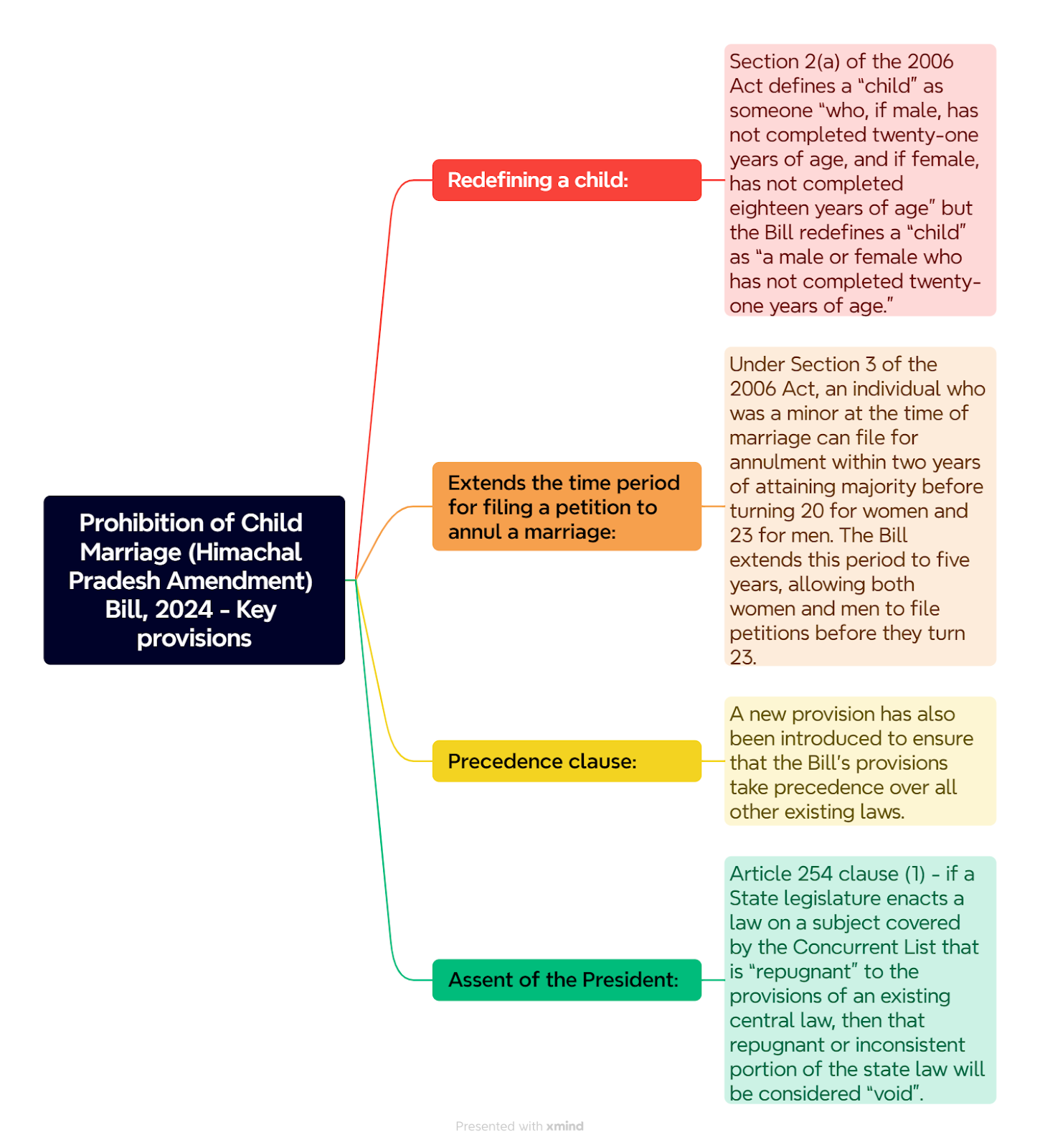
Recently, the Himachal Pradesh Assembly passed a Prohibition of Child Marriage (Himachal Pradesh Amendment) Bill, 2024 raising the minimum marriageable age for women from 18 to 21 years.
Reason behind the passage of the will
- Welfare of women: HP is the first State in the country to enact the legislation to increase the marriage age of girls to 21.
- Issues with early marriage: It obstructs girls’ education and limits their potential for progress in life.
- Health concerns: It reduces instances of early pregnancies and motherhood, which adversely affect women’s health.
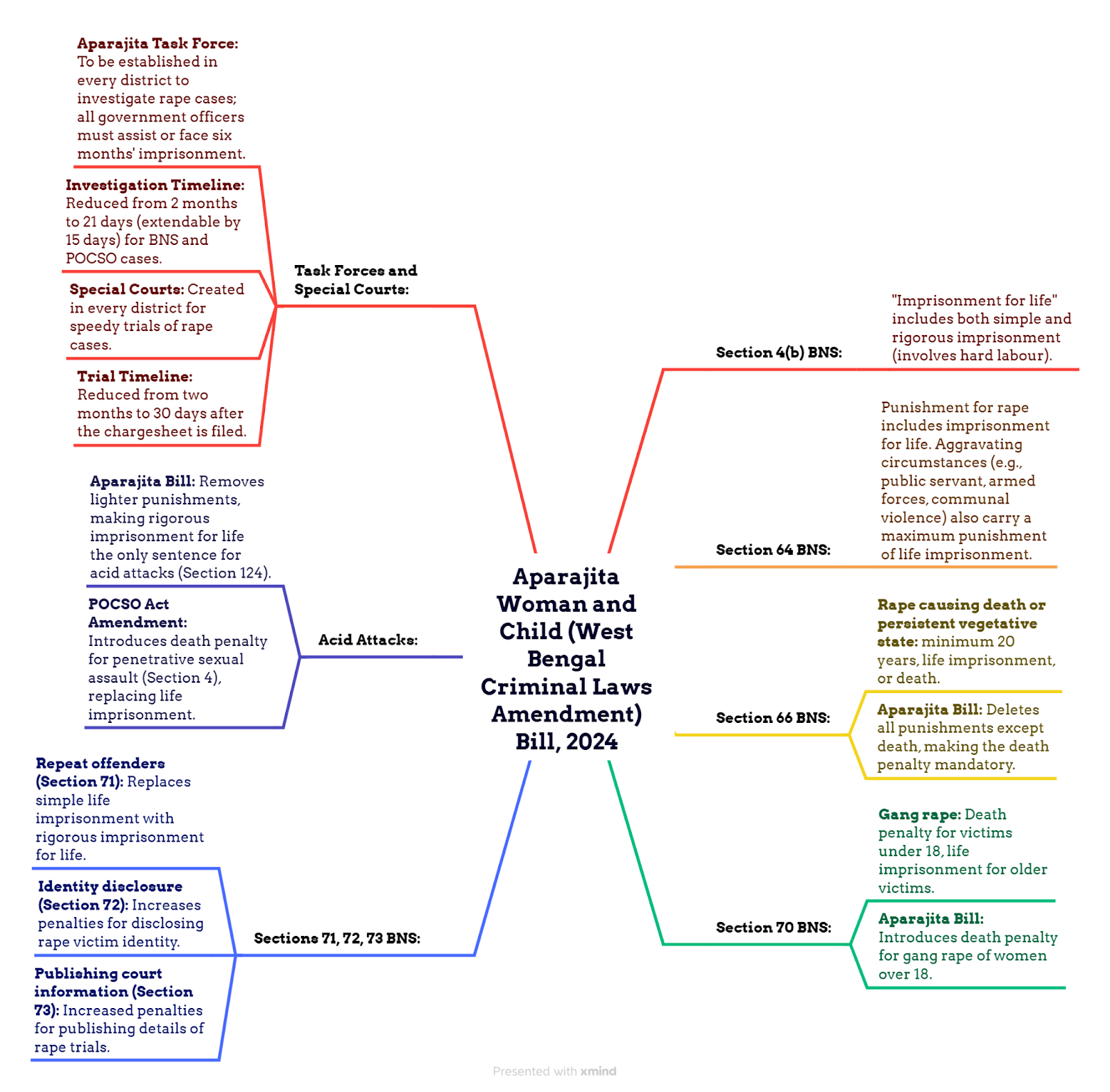
State changes in rape law - Indian Express
Context
The Bengal state Assembly recently unanimously passed a Bill providing for mandatory death penalty in cases of rape where the victim dies or is left in a permanent vegetative state.

|
Andhra Pradesh: Disha Bills
|
Maharashtra: Shakti Bill
|
- Background: Triggered by the gang rape and murder of a 26-year-old veterinary doctor in Hyderabad in November 2019 in which 4 accused were killed in a police encounter in December 2019.
- December 2019: Andhra Pradesh Assembly passed two bills:
- Andhra Pradesh Disha Act – Criminal Law (Andhra Pradesh Amendment) Bill, 2019
- Andhra Pradesh Disha (Special Courts for Specified Offences against Women and Children) Bill, 2019
- The bills amended the IPC, 1860, and CrPC, 1973, for Andhra Pradesh.
- Death Penalty for Rape:
- IPC Section 376: Death penalty introduced for rape, including cases involving minors under 16.
- Section 376D: Death penalty for gang rape.
- Section 376E: Death penalty for repeat offenders.
- Special Police Teams and Courts:
- Creation of Special Police Teams and Exclusive Special Courts in every district.
- Shortened timelines for investigation and trial of crimes against women.
- Women and Children Offenders Registry:
- Proposed creation of a registry with full details of individuals involved in offences against women.
- Registry to be available to law enforcement agencies.
- Current Status: Both Disha Bills are pending at the Centre, awaiting President’s assent.
|
- Introduction: Maharashtra legislature passed the Shakti Criminal Laws (Maharashtra Amendment) Bill, 2020 which introduced death penalty for rape cases and expedited timelines for investigation and trial.
- Obligation on Web Platforms: Punishes social media platforms, internet, and mobile providers with up to 1 month imprisonment for failing to share requested data or electronic records with Investigation Officers in crimes against women.
- Death Penalty for Acid Attacks: Introduces the death penalty for heinous acid attacks where conclusive evidence warrants exemplary punishment.
- POCSO Act Amendment: Similar to Aparajita, Shakti amends the POCSO Act to introduce the death penalty for penetrative sexual assault (Section 4).
- Current Status: Presidential assent is pending.
|
Economy
Latest ILO study links AI to dip in labour income - The Hindu
Context
Inequality is on the rise as the share of labour income has stagnated worldwide and a large share of youth remain out of employment, education, or training, according to the International Labour Organisation’s (ILO) World Employment and Social Outlook: released in Geneva recently.
Findings of the report
- Impact of technological innovations: While these innovations have produced persistent increases in labour productivity and output, they can also reduce the labour income share.
- Absence of a stronger policy response: It could push the labour income share still further down.
- Slow progress on key Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- Income share: The global labour income share, which represents the portion of total income earned by workers, fell by 0.6% points from 2019 to 2022.
- Impact of pandemic: Nearly 40% of the reduction in the labour income share occurred during the pandemic years of 2020 to 2022 which exacerbated existing inequalities.
Way forward
- Mandate on countries: Countries must take action to counter the risk of declining labour income share.
- Policy legislation: Policies that promote an equitable distribution of economic benefits need to be formulated.
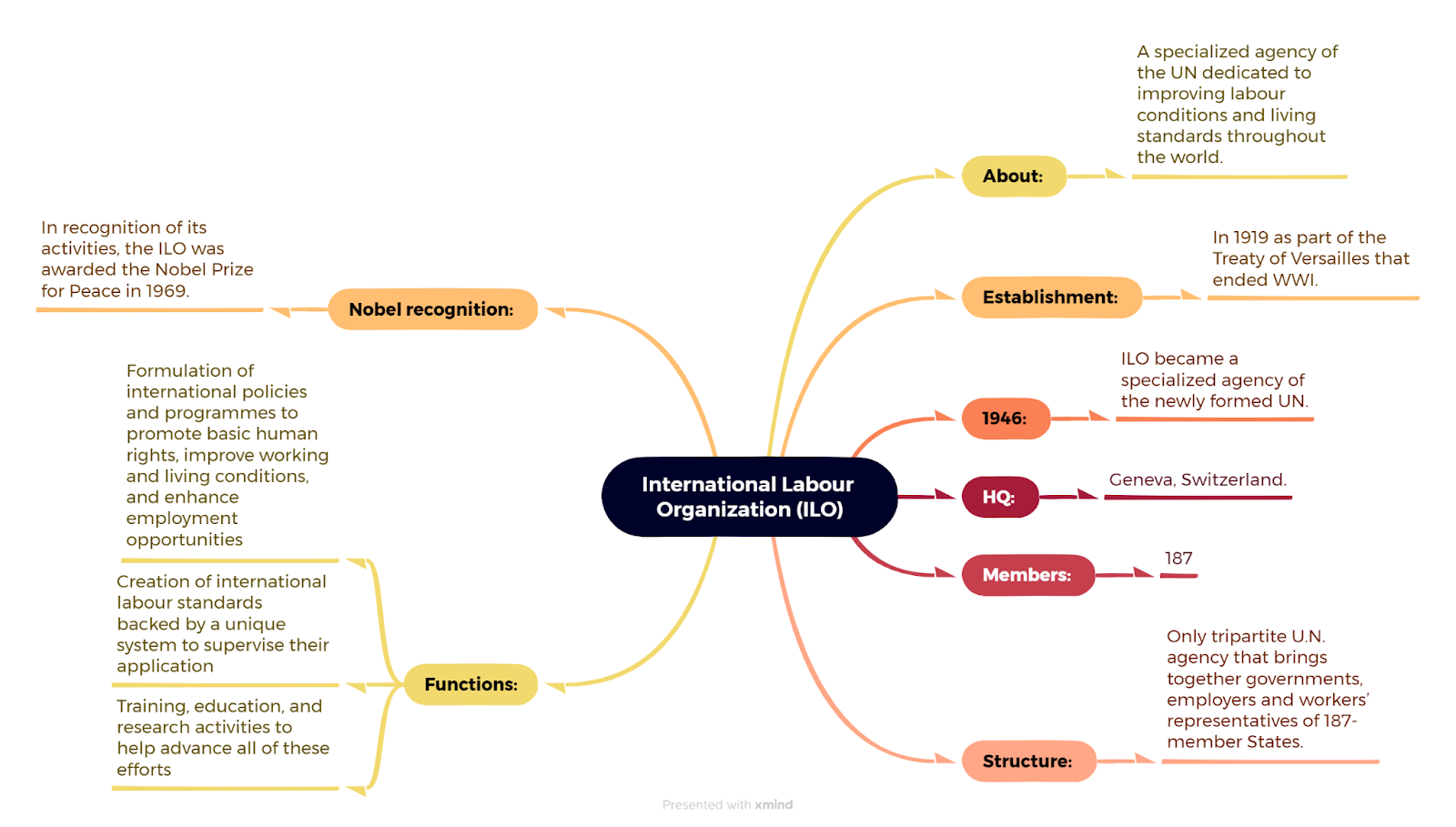
SATELLITE-BASED HIGHWAY TOLL COLLECTION: HOW WILL IT WORK? - Indian Express
Context
After the announcement for the implementation of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) based Electronic Toll collection in India, Ministry of Road Transport & Highways (MoRTH) said that it has developed a GIS based software for Real-time monitoring’ of the waiting time at the Toll Plazas.
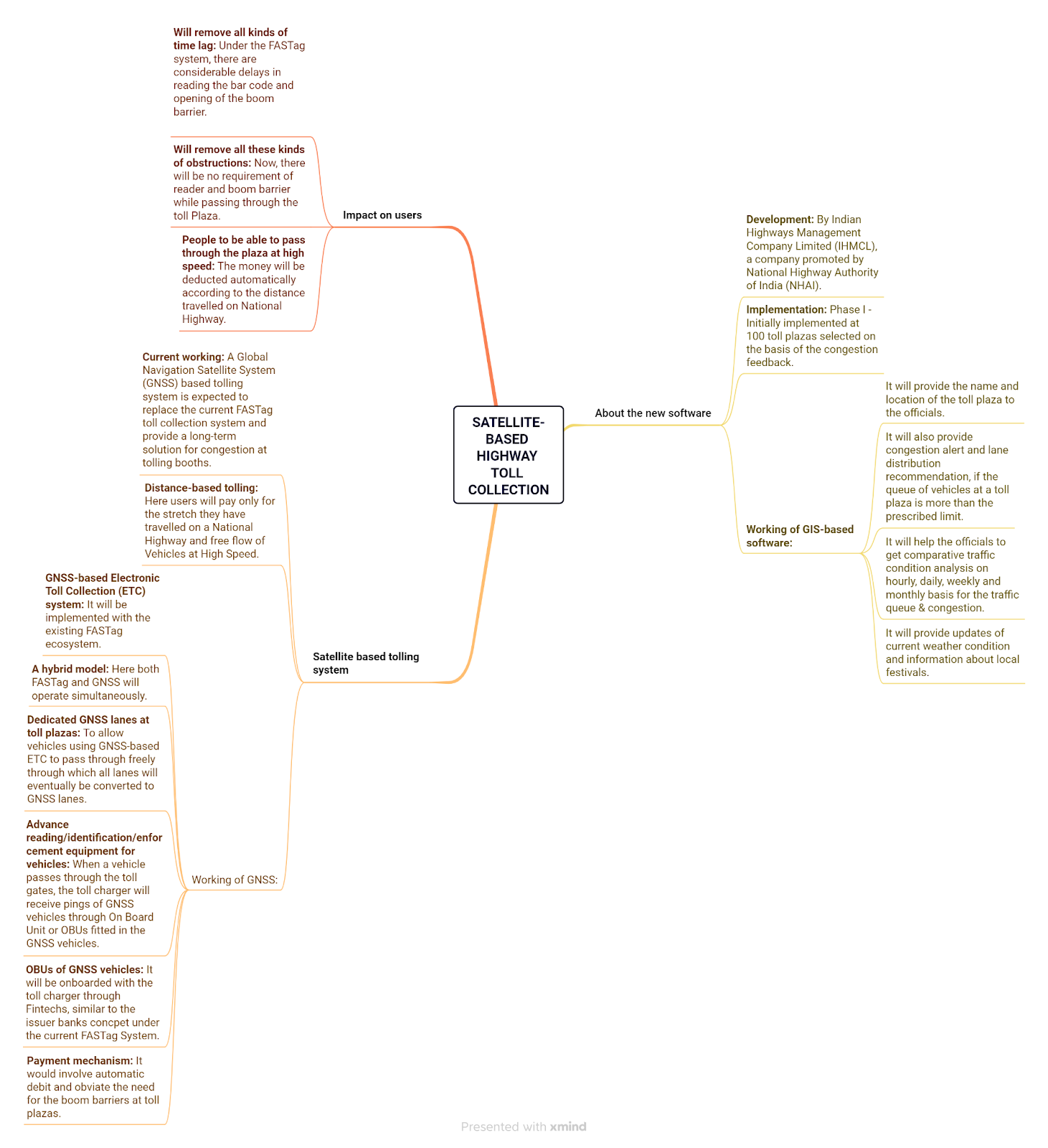
How to ensure food safety and reduce waste - Indian Express
Context
The importance of food goes far beyond basic sustenance.
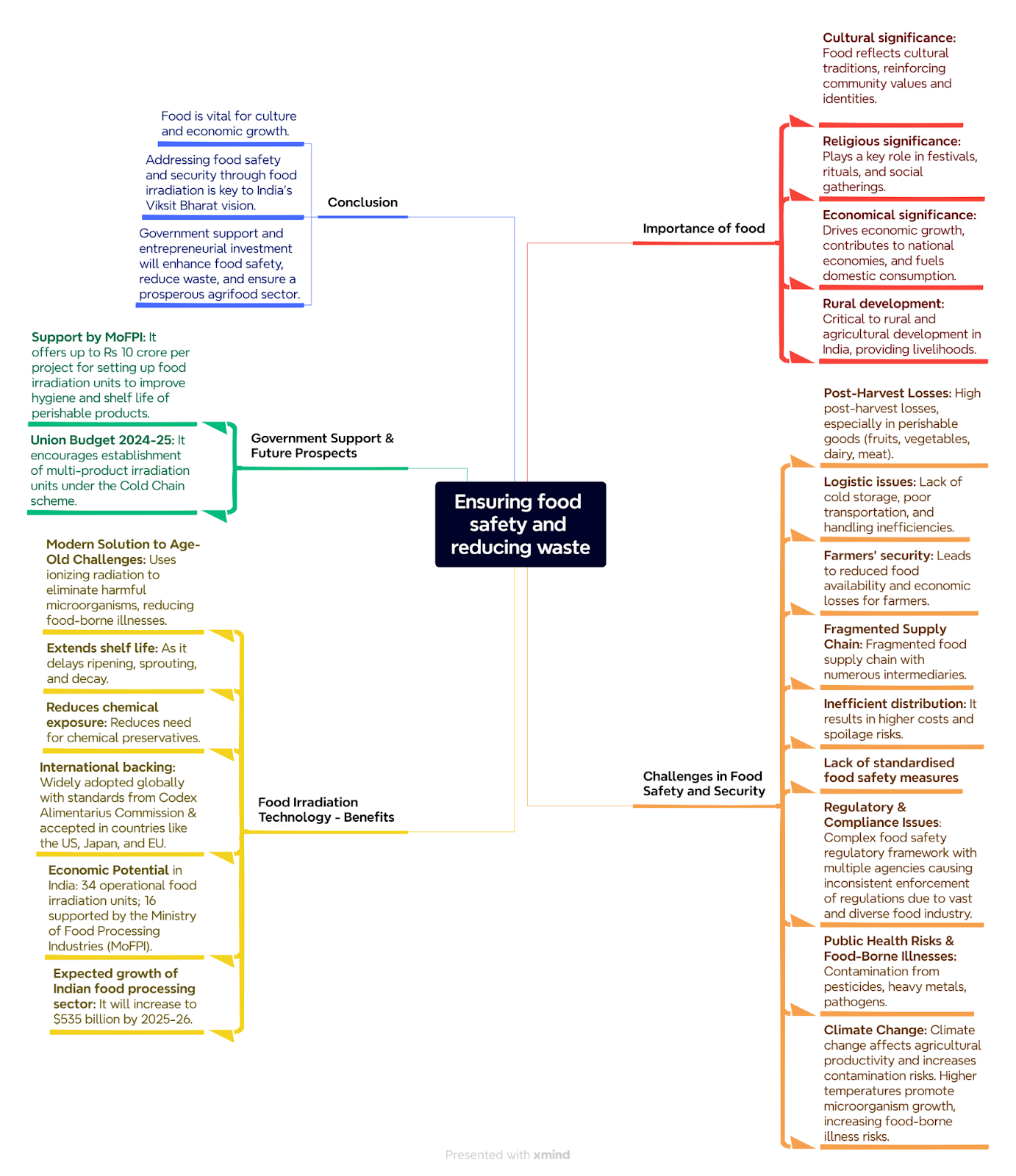
AgriSURE Fund - PIB
Context
In a significant development for the agricultural sector, Union Minister for Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare and Rural Development recently launched the AgriSURE Scheme in New Delhi.
The Centre for Marine Living Resources and Ecology (CMLRE) organises national-level workshop on IndOBIS - PIB
Context
The Centre for Marine Living Resources and Ecology (CMLRE), an attached office of the Ministry of Earth Sciences, conducted a national-level workshop on the Indian Ocean Biodiversity Information System (IndOBIS) recently at its Kochi campus.
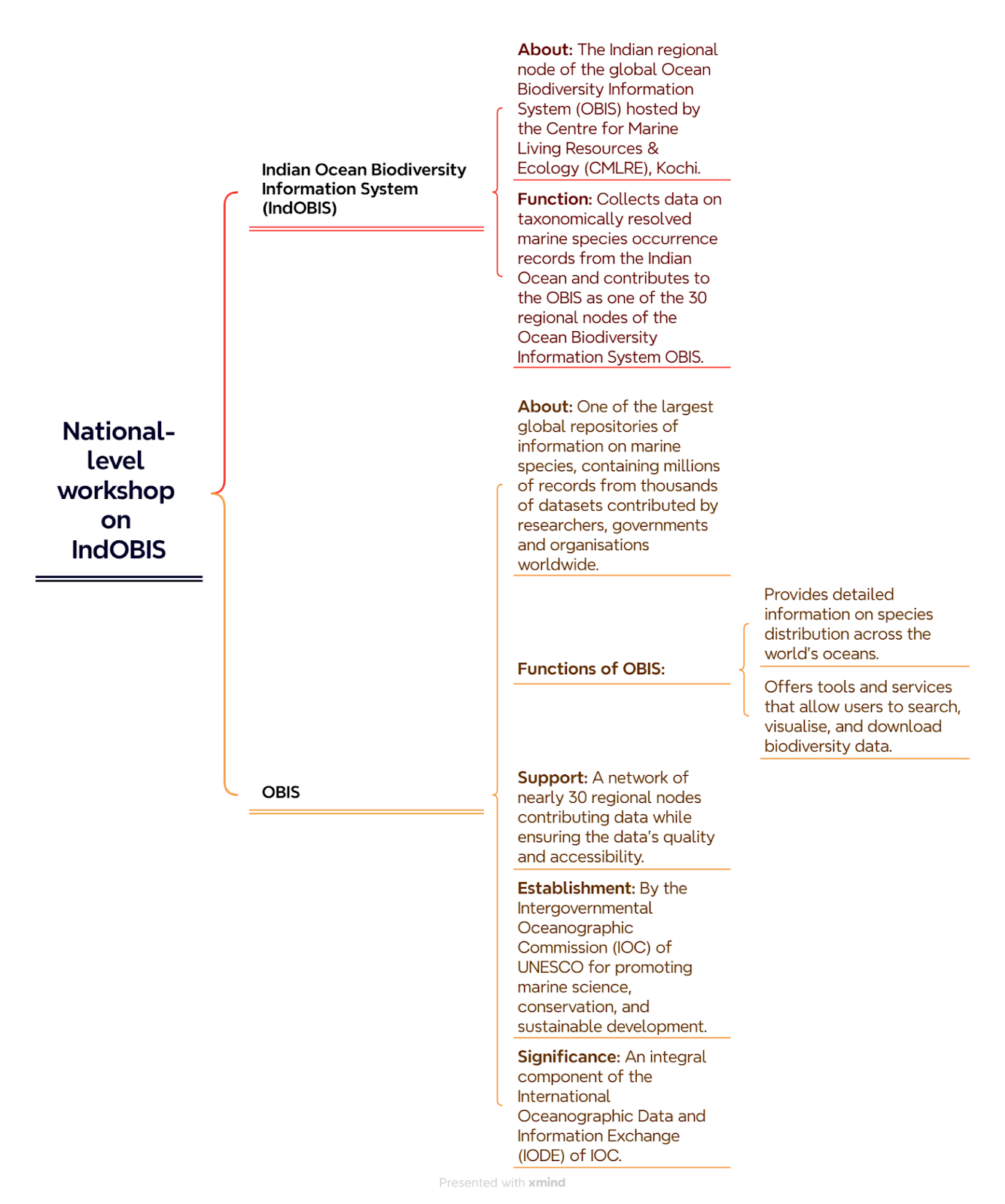
Environment
Bandipur Tiger Reserve - Indian Express
Context
An alert elephant patrolling team rescued a tusker that was stuck in a rail barricade in the Maddur range of Bandipur Tiger Reserve. They took less than 15 minutes to remove the bolts and screws of the barricade, allowing the elephant to pass through without any injuries.
Bandipur Tiger Reserve
- Location: 2 districts (Mysore and Chamarajanagar) of Karnataka and in the tri-junction area of the States of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Kerala (“ecological confluence” of the Western and Eastern Ghats).
- Establishment: In 1931 as Venugopala Wildlife Park by the Maharaja of Mysore & then expanded with the name Bandipur Tiger Reserve under Project Tiger in 1973.
- Part of the larger Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve: The Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve is recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Surrounding reserves:
- Nagarahole Tiger Reserve (Tamil Nadu) in the North West (Kabini Reservoir separates the two).
- Mudumalai Tiger Reserve (Tamil Nadu) in the South.
- Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary (Kerala) in the South West.
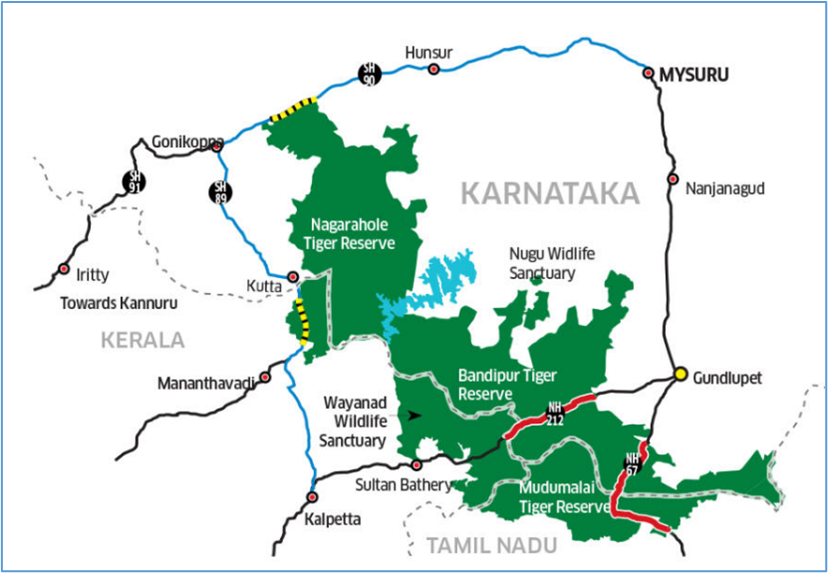
- Rivers: River Kabini (north) and River Moyar (south).
- Climate: Typical tropical climate with distinct wet and dry seasons.
- Vegetation: Dry deciduous to tropical mixed deciduous.
- Flora: Rosewood, Indian kino tree, sandalwood, Indian laurel, clumping bamboo, giant clumping bamboo, etc.
- Fauna: Wild Asian elephants in South Asia, Bengal tiger, gaur, sloth bear, golden jackal, dhole, four-horned antelope, etc.
Spider mimicking bird excreta found in Assam - The Hindu
Context
Assam has added a species of spider whose web mimics a bird’s excrement to India’s list of arachnids.
Phrynarachne decipiens/ Bird dung/ Bird-dropping crab spider
- Distribution: Malaysia and Indonesia’s Java and Sumatra.
- Presence in India: Recorded for the first time in the country from Assam’s Sonapur in the Kamrup (Metropolitan) district and the Chirang Reserve Forest in the Kokrajhar district.
- Appearance: Chalky white colour & whitish deposition (its web) on the leaves, looking like bird excreta
- Genus: Phrynarachne - it presently consists of 35 accepted species.
Sci and Tech
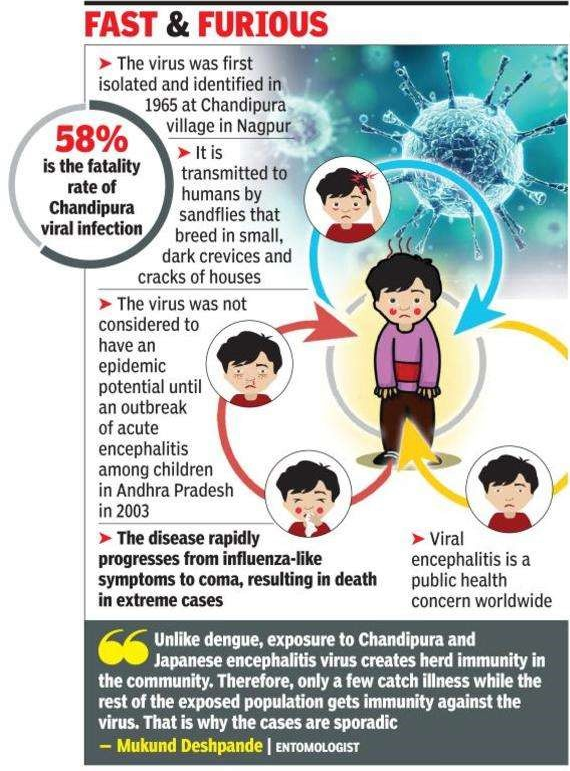
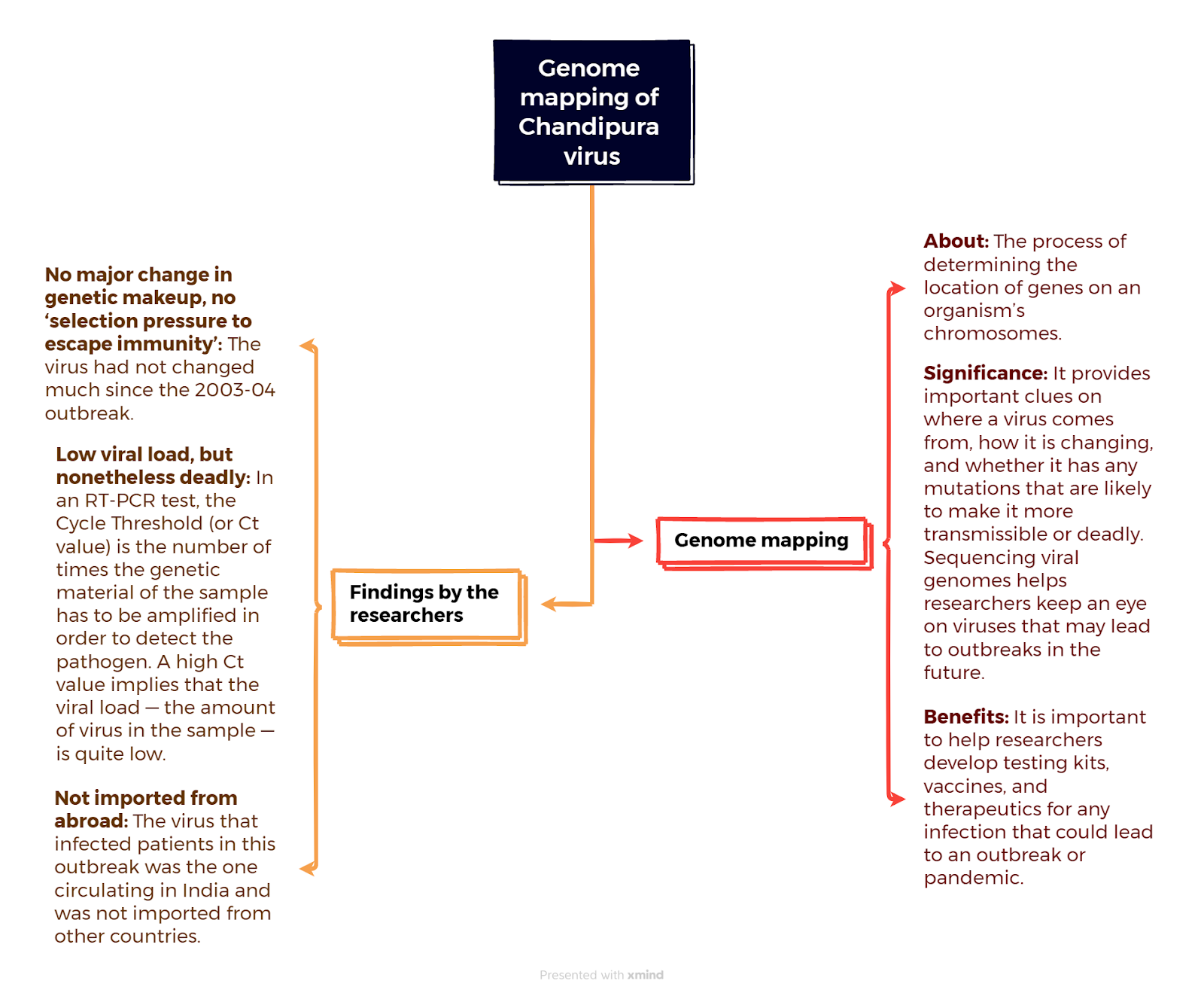
Genome mapping of Chandipura virus: findings - Indian Express
Context
The Gujarat Biotechnology Research Centre (GBRC) in Gandhinagar has published the only fully mapped genome of the Chandipura Vesiculovirus (CHPV) — the viral infection that caused at least a third of the encephalitis or brain swelling cases in Gujarat during the outbreak in July-August.
Chandipura
Defence
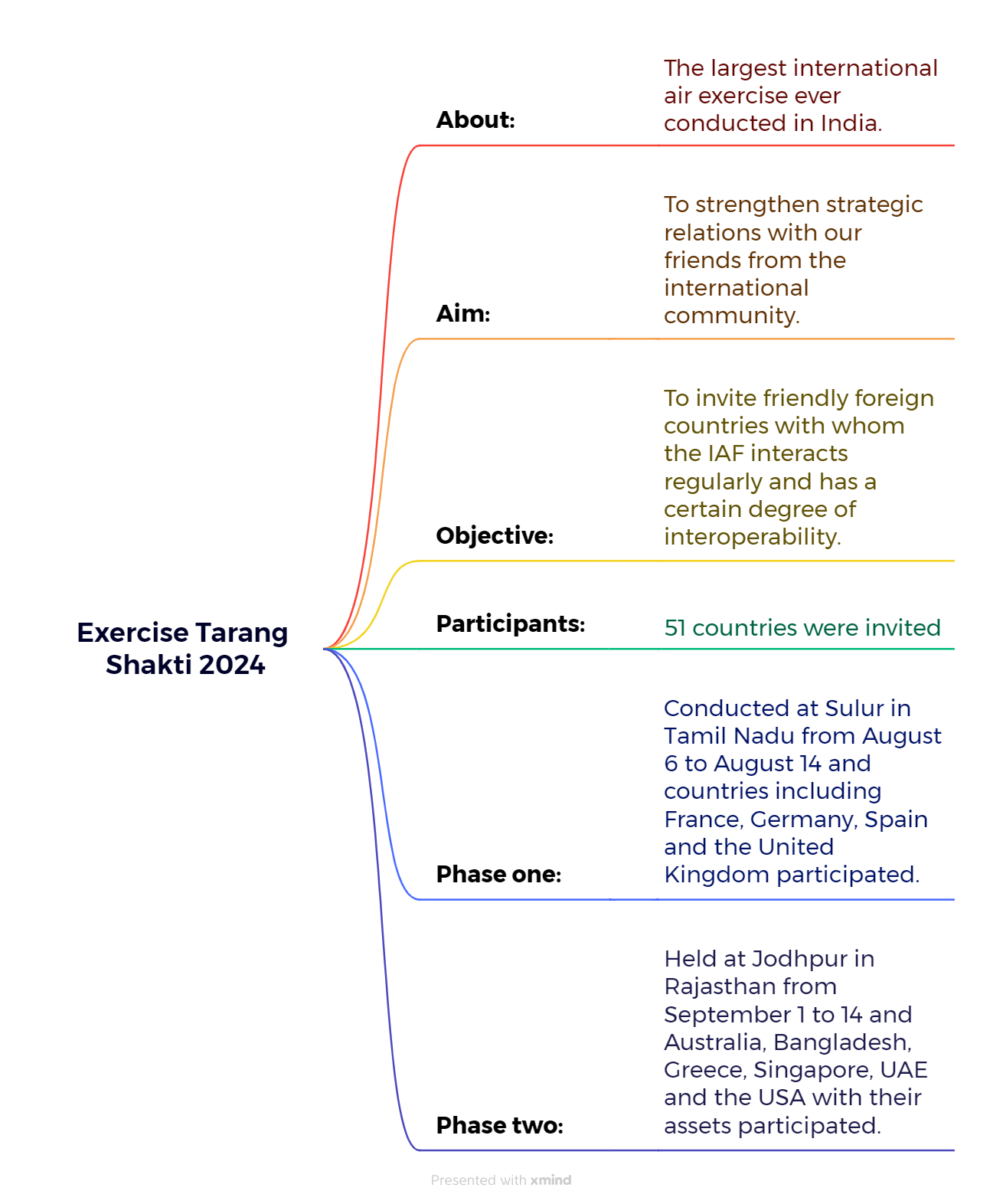
Exercise Tarang Shakti 2024 - The Hindu
Procurement of 240 Russian jet engines approved for IAF’s Su-30MKI fighter jets - The Hindu
Context
The Cabinet Committee on Security recently approved the proposal for the procurement of 240 aero-engines for Su-30MKI aircraft of the Indian Air Force (IAF) under the ‘Buy (Indian)‘ category from Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) at a cost of over ₹26,000 crore.
Su-30MKI Fighter Jet
- About: A multirole combat fighter aircraft jointly developed by the Sukhoi Design Bureau and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for IAF.
- Features: A fourth-generation fighter jet powered by two AL-31 FP aero engines & an air-launched version of BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles.
- AL-31FP: A high-temperature turbojet by-pass engine of modular design.
- Has a Tarang Radar Warning Receiver (RWR): It is indigenously developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- Maximum unrefuelled flight range: 3,000 km.
- Has an in-flight refuelling system: It provides a maximum range of 8,000km with two refuellings.
