Polity
Manipur Naga body urges Governor to reinstate Free Movement Regime - The Hindu
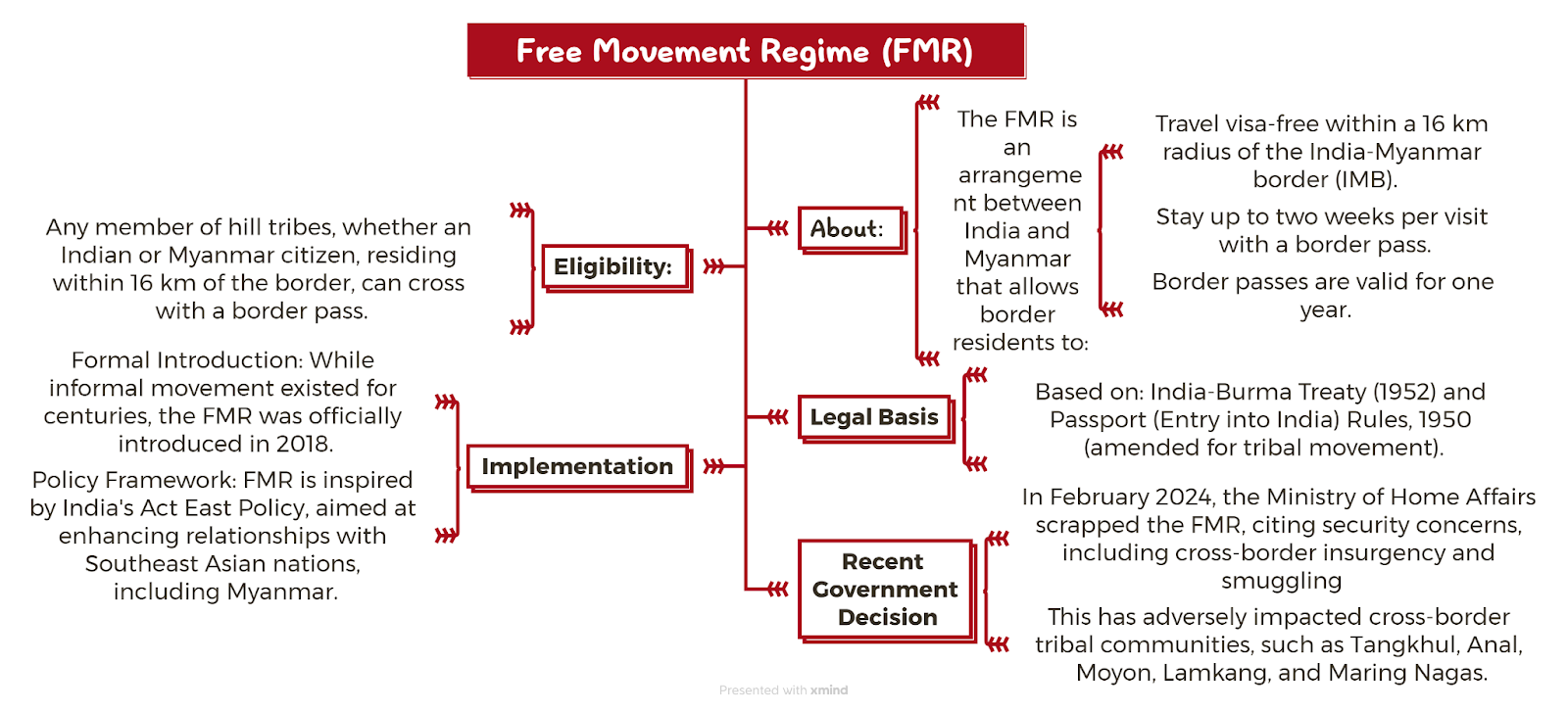
The United Naga Council (UNC) submitted a memorandum on May 2, 2025, to the Manipur Governor demanding Reinstatement of the Free Movement Regime (FMR) along the India–Myanmar border, and Rollback of the seven new districts created in Manipur in 2016.
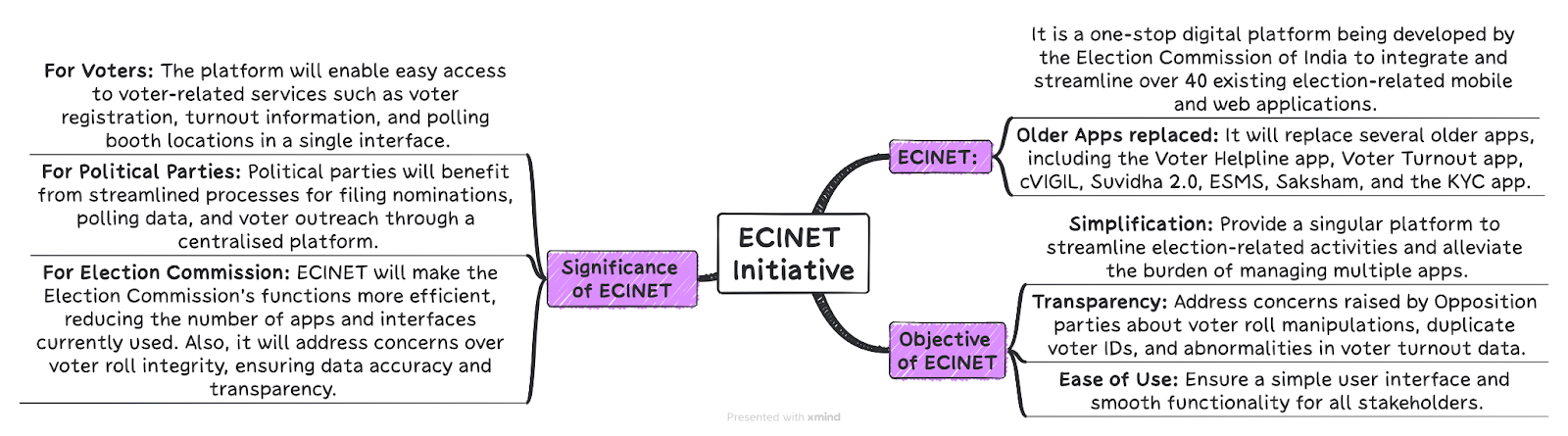
EC developing common digital platform for voters, officials - The Hindu
The Election Commission of India (ECI) recently announced the development of a user-friendly digital platform, ECINET, aimed at enhancing accessibility and simplifying electoral processes for voters, political parties, election officials, and civil society.
Economy
Angola invites Indian businesses to explore opportunities in export - The Hindu
During his official visit to India, Angola President Joao Manuel Goncalves Lourenco addressed the India-Angola Business Forum in New Delhi (May 2025), inviting Indian businesses to invest in Angola and explore strategic export and cooperation opportunities in key sectors.
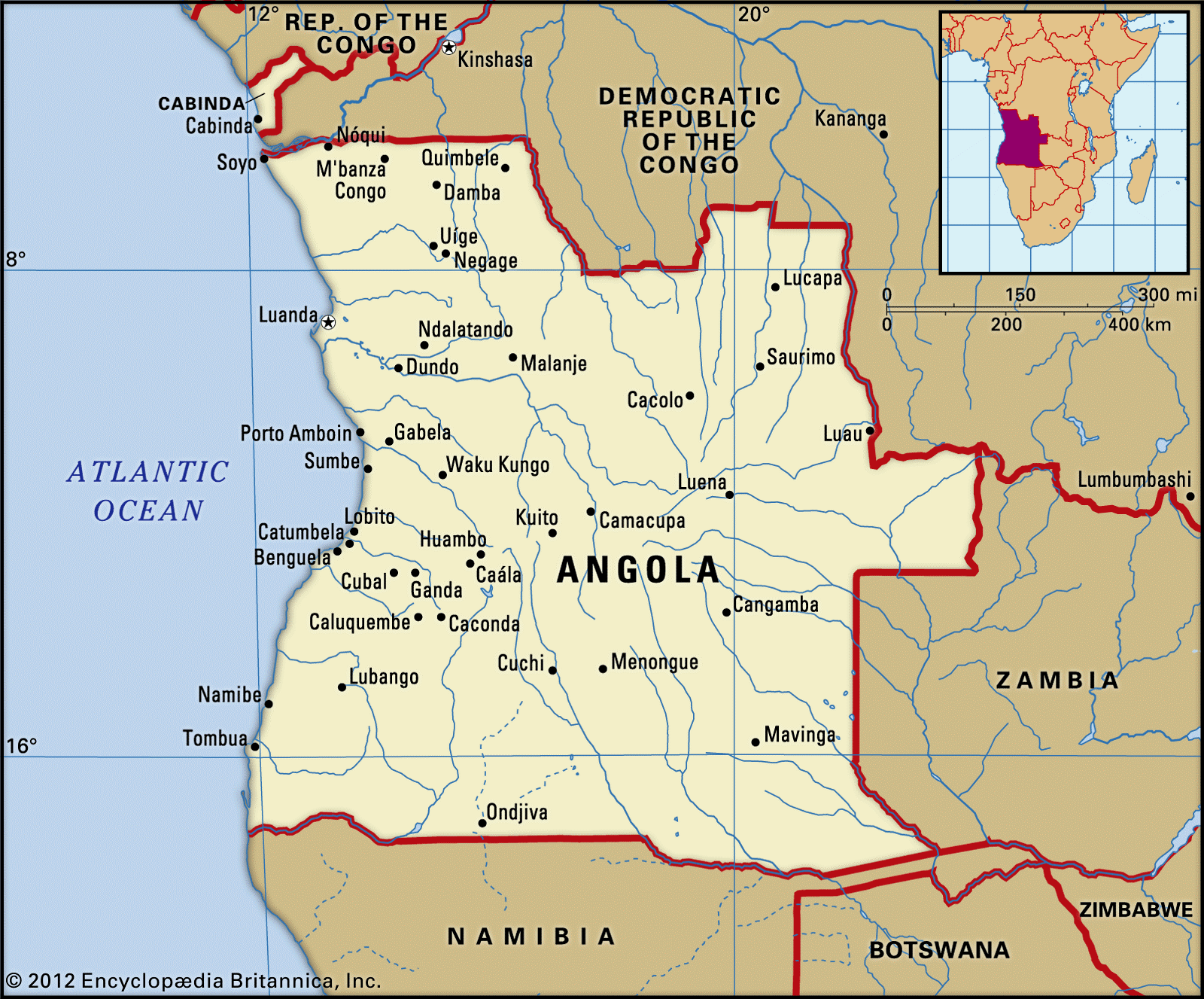
Angola
- Location: Angola is located in southwestern Africa, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west.
- Capital: Luanda, a coastal port city.
- Neighbouring countries: Republic of the Congo, DR Congo, Zambia, Namibia.
- Exclave: Cabinda, located north of Angola, separated by DR Congo.
- Major Plateaus: Bié Plateau (~2,600 m), Huíla Plateau (~2,300 m), Malanje Highlands.
- Highest Point: Mount Moco (2,620 m / 8,596 ft) near Huambo.
- Major Rivers:
- Cuanza (Kwanza) – largest river entirely in Angola.
- Cunene – forms part of the border with Namibia.
- Cuango – tributary of the Congo River.
- Other rivers drain into Zambezi and Okavango basins.
- Desert: Southwest Angola is part of the Namib Desert.
- Demographics & Culture: Ethnically diverse with major Bantu-speaking groups: Ovimbundu, Kimbundu, Bakongo.
- Economic Significance
- Among Africa’s top oil producers.
- Rich in diamonds, iron ore, copper, and gold.
- Northeast Angola has significant diamond reserves in alluvial river gravels.
Environment
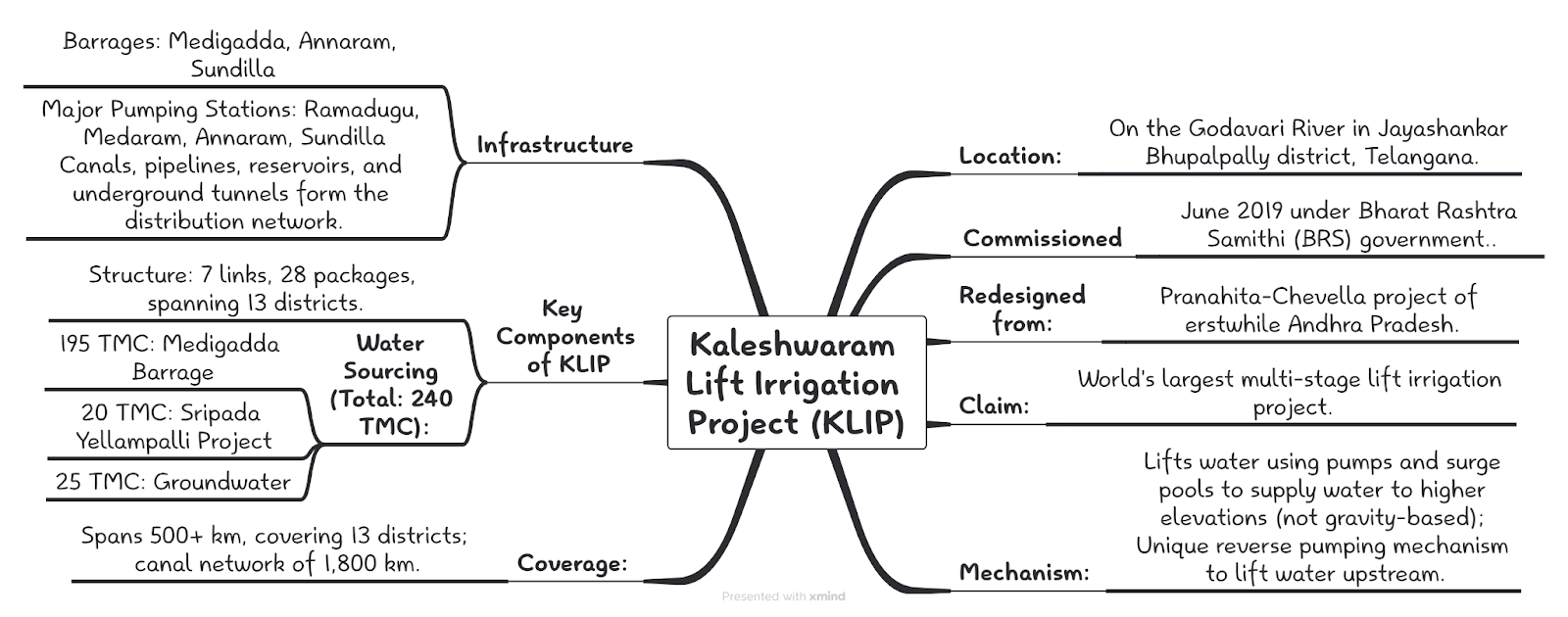
Crisis at Kaleshwaram — why Telangana’s massive irrigation project is distressed - Indian Express
The National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA) has found “irreparable damage” in the structure of three barrages of the Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP) in Telangana. The findings were made public by the Telangana government in April 2025 after a detailed inspection was conducted post the collapse of a pillar at Medigadda Barrage in October 2023.
Science and Tech
Mithridatism: poison against poison - The Hindu
Recently, US researchers reported in the journal Cell a breakthrough involving a man who voluntarily exposed himself to hundreds of snakebites and venom injections to build immunity — an ancient practice known as mithridatism. The findings may pave the way for developing broadly neutralising antivenoms.
What is Mithridatism?
- Definition: Mithridatism is the practice of protecting oneself against poison by gradually ingesting non-lethal doses of the poison over time.
- Origin: Named after Mithridates VI, the King of Pontus (135–63 BC), who allegedly used this method to immunise himself against assassination by poisoning.
- Modern Relevance: Rarely practised today due to the development of scientific and safer alternatives like vaccines and antivenoms.
- Significance
- Snakebite in India: India sees the highest number of snakebite deaths globally — estimated over 50,000 per year.
- Causes:
- Limited access to healthcare and antivenoms
- Species-specific venom: each snake requires a different antibody response
|
Aspect
|
Mithridatism
|
Vaccination
|
|
Method
|
Ingest small doses of poison/venom
|
Introduce weakened/inactive pathogen
|
|
Risk
|
High (can cause death/injury)
|
Low (clinically tested)
|
|
Scientific Basis
|
Historical/empirical
|
Modern immunology
|
|
Common Use Today
|
Rare
|
Widespread (global immunisation programs)
|
Defence
DRDO conducts maiden flight-trials of Stratospheric Airship Platform -PIB
Recently, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted the maiden flight trial of a Stratospheric Airship Platform from Sheopur, Madhya Pradesh.
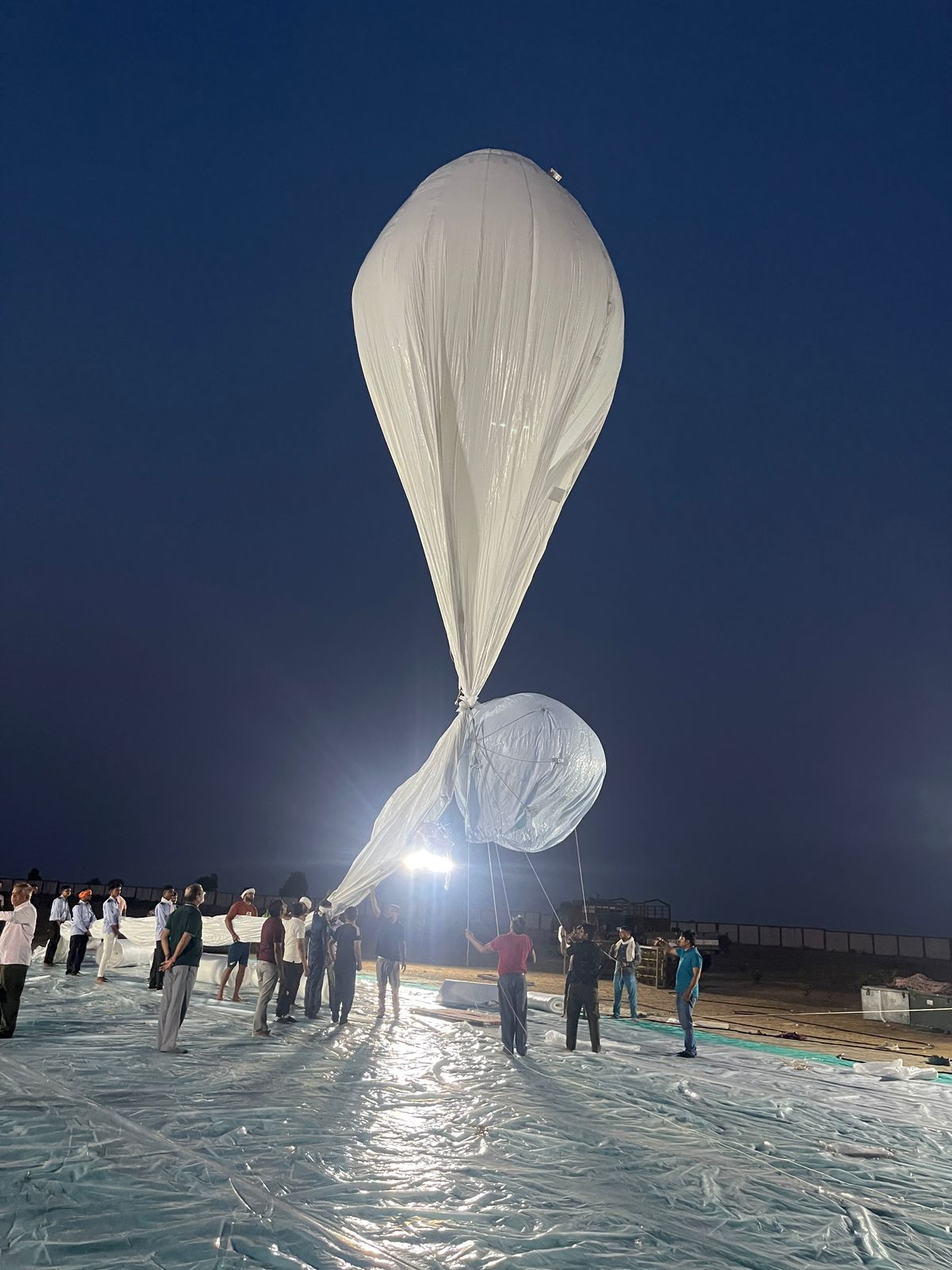

Stratospheric Airship Platform
- Developed by: Aerial Delivery Research and Development Establishment (ADRDE), Agra
- Altitude Achieved: ~17 km (stratosphere level)
- Flight Duration: ~62 minutes
- Purpose: To evaluate:
- Envelope Pressure Control System
- Emergency Deflation System
- Sensor data collection for simulation models
- Recovery: Entire airship system successfully recovered post-flight for analysis.
- Strategic & Technological Significance
- Indigenous Capability: India becomes one of the few countries with homegrown high-altitude lighter-than-air (LTA) platform technology.
- Enhanced ISR Capacity
- Strengthens Intelligence, Surveillance & Reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities.
- Supports persistent Earth observation for defence and strategic application
- Defence Readiness: Can serve as a strategic asset for border surveillance, especially in high-altitude and remote terrains.