Polity and Governance
ED crossed all limits with a raid on T.N. govt. body: SC - The Hindu
The Supreme Court stayed the Enforcement Directorate’s investigation and raids on Tamil Nadu’s State-run TASMAC, criticising the agency for overstepping its mandate and violating the federal structure. Chief Justice B.R. Gavai questioned the legality of ED’s involvement despite the State already registering multiple FIRs.
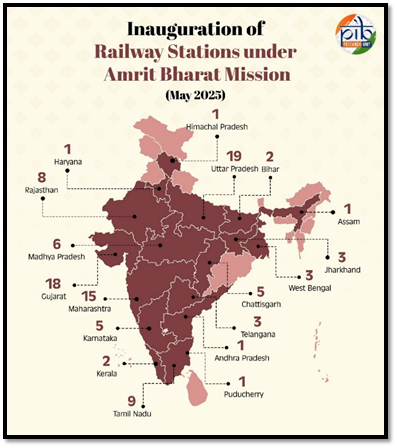
PM inaugurates 103 Amrit Bharat railway stations - The Hindu
Prime Minister Narendra Modi on Thursday inaugurated 103 Amrit Bharat railway stations through video conference from Rajasthan. These stations, in 86 districts across 18 States and UTs, cost of over ₹1,100 crore. He also flagged off a train connecting Bikaner to Mumbai.
Amrit Bharat Station Scheme (ABSS)
- Launch & Ministry: Launched by Ministry of Railways in February 2023.
- Objective: Long-term redevelopment of railway stations to transform them into modern city hubs.
- Scope: Applies to over 1,300 stations across India in a phased and holistic manner.
- Approach: Based on station-specific master plans with phased implementation, tailored to local needs.
- Key Features
- Modern Passenger Amenities:
- Clean waiting rooms, toilets, seating, drinking water.
- Divyang-friendly infrastructure.
- Food courts and retail outlets.
- Traffic Circulation:
- Separate entry/exit points for vehicles and pedestrians.
- Wider roads, footpaths, improved parking facilities.
- Inter-modal Integration:
- Seamless connectivity with bus depots, metro, taxis, autos.
- Enhanced Signage: Multilingual, visible signboards for ease of navigation.
- Sustainability Features:
- Energy-efficient lighting and appliances.
- Rainwater harvesting systems.
- Ballastless tracks for reduced noise and vibration.
- Green spaces and landscaping.
- Roof plazas for additional passenger and commercial space.
International Relation
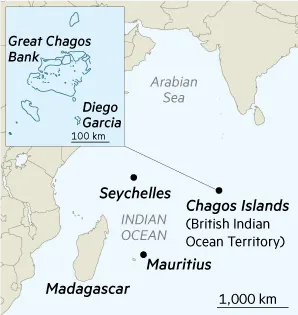
U.K. to hand sovereignty of Chagos Islands to Mauritius - The Hindu
Britain signed a sovereignty transfer agreement with Mauritius over the Chagos Islands, including Diego Garcia.The deal includes a £101 million annual lease for 99 years to maintain the U.S.-U.K. military base, which the U.K. calls crucial for national security and counterterrorism efforts.
About the Chagos Dispute:
- Colonial Origins: The Chagos Archipelago was acquired by Britain along with Mauritius in 1814. Just before Mauritius gained independence in 1968, the U.K. separated the Chagos Islands in 1965 to establish the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT).
- Military Use: In 1966, Britain leased Diego Garcia, the largest island in the archipelago, to the United States for a military base. This led to the forced displacement of the native Chagossian population.
- Legal Challenges: Displaced Chagossians have long pursued legal efforts to return to their homeland. Mauritius has consistently asserted sovereignty over the islands since 1968.
- International Verdicts: In 2019, the International Court of Justice (ICJ) ruled that the U.K.’s continued control over the Chagos Islands was unlawful and that the territory should be returned to Mauritius.
Geographical Context:
- Location: Situated in the central Indian Ocean, approximately 1,600 km south of the Indian subcontinent.
- Key Atolls: Includes significant islands such as Diego Garcia, Peros Banhos, and Danger Island.
- Climate: Features a tropical marine climate influenced by trade winds.
- Disputing Parties: The dispute primarily involves the United Kingdom (current administrator) and Mauritius (claimant), with the United States involved due to its military presence on Diego Garcia.
Environment
MoEFCC celebrates International Day for Biological Diversity 2025 - PIB
India celebrated the International Day for Biological Diversity (IDB) 2025 at a national-level event in Udaipur, Rajasthan.
Why India needs stable urban forests- The Hindu
The Supreme Court reprimanded the Telangana government for allotting 400 acres of Kancha Gachibowli—one of Hyderabad’s last urban forests—for industrial use, after over 100 acres of trees were felled. The move sparked protests and raised concerns over the destruction of urban green spaces and ecologically insensitive urban planning.
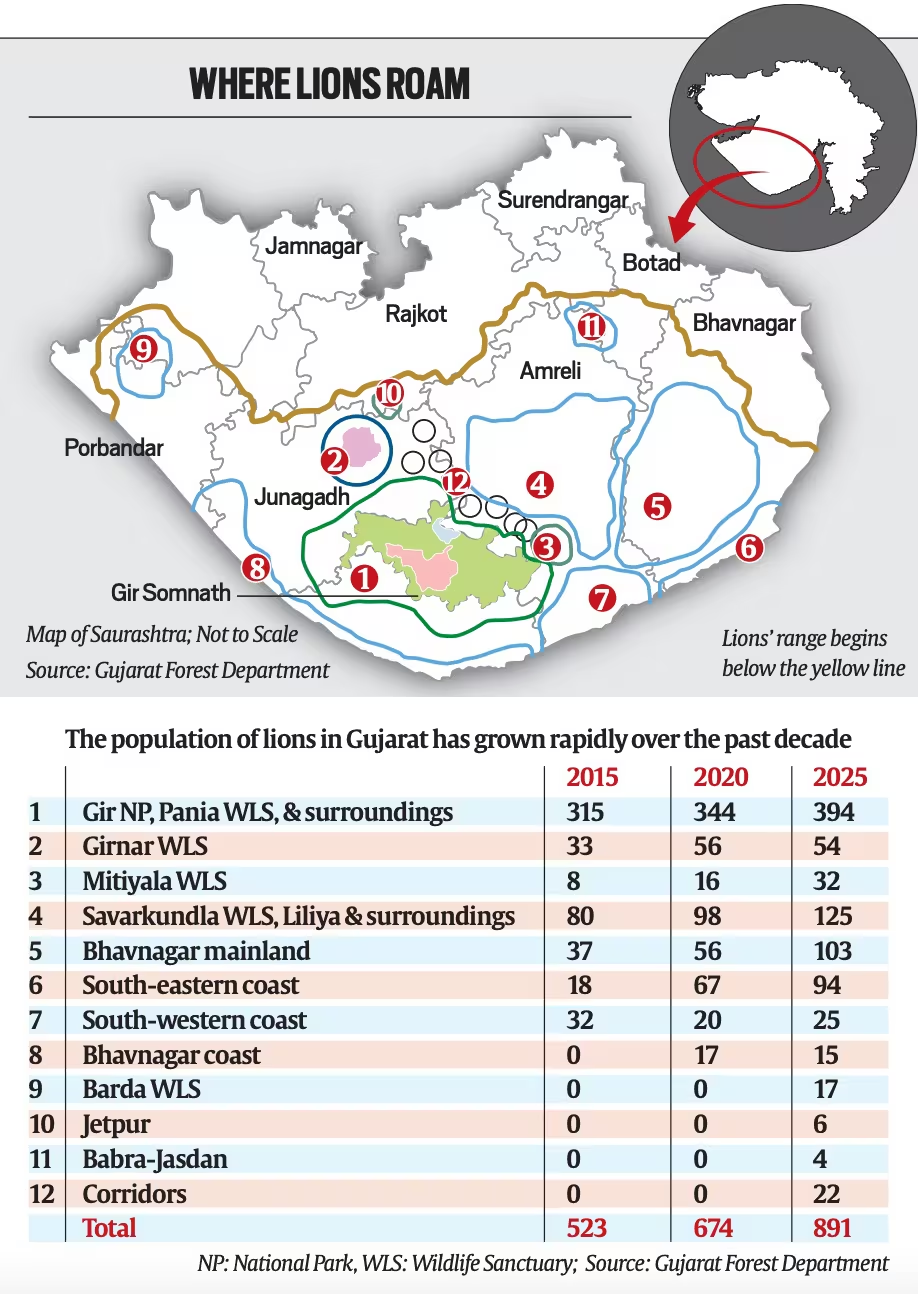
2025 Lion census shows 32% population rise: Why Asiatic lion’s future can’t be secured by numbers alone - Indian Express
The 2025 Asiatic Lion Census recorded 891 lions, showing a 32% increase from 2020. The lion population has also expanded its geographic range by 17% to cover 58 talukas in 11 districts of Gujarat. Despite numerical growth, conservationists highlight critical concerns about habitat quality, disease vulnerability, and human-animal conflict.
Historical Context and Significance
- The Asiatic lion (Panthera leo persica), once critically endangered, has made a steady recovery. From fewer than 200 individuals in the 1960s, the population has grown under the protection of Gir Forest National Park.
- This positive trend led the IUCN to reclassify it from “Critically Endangered” to “Endangered” in 2008.
Trend and Range Expansion
- 1960s–1995: Slow population rise; under 300 till 1995, confined mainly to Gir forest.
- 1990–2005: Range expanded from 6,600 to 13,000 sq km, but only 26% rise in lion numbers.
- 2005–2020: Range doubled again to 30,000 sq km, yielding 88% population increase.
- The 2025 figures: it affirms the trend, but also show the second instance (after 2015) where population growth outpaced range expansion.
Various Concerns
- Gujarat has few protected forest areas beyond Gir, Girnar, Mitiyala, Pania, Barda.
- Many lions now inhabit agricultural fields, plantations, and wastelands, lacking ideal conditions.
- Only 56% of lions live in forested areas (2020 data); density drops sharply in non-forested zones.
- Unprovoked attacks on humans are being reported due to lions losing natural fear of people
- Conflict risks such as Electrocution, well drownings, and retaliatory attacks exists.
- Disease vulnerability: Carcass feeding exposes lions to canine-borne infections (e.g., CDV).
- Delayed Interventions
- The Supreme Court (2013) ordered translocation to Kuno Wildlife Sanctuary, MP within 6 months.
- Project Lion (2020) proposed 7 new sites, including 3 in Madhya Pradesh and 3 in Rajasthan.
- However, the Gujarat government restricted relocation efforts within state boundaries, despite ecological unsuitability.
- Barda Sanctuary, newly colonised, spans under 200 sq km, inadequate for large-scale relocation.
Asiatic Lion
- Scientific Name: Panthera leo persica
- Common Names: Asiatic Lion, Indian Lion, Persian Lion
- Exclusive Habitat: Found only in India, primarily in Gir National Park, Gujarat.
- Historical Range: Once ranged from West Asia to Middle East; now extinct in those areas.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Downlisted from Endangered (2008) to Vulnerable (2025).
- CITES: Appendix I.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I of the (highest protection).