Polity and Governance
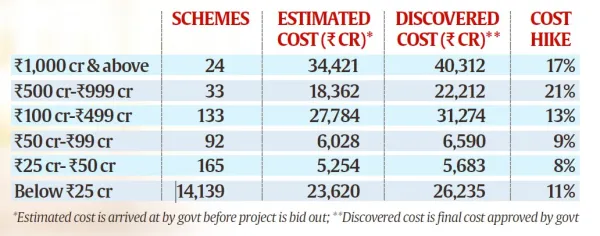
Tweak in Jal Jeevan tender rule removed cap on expense, led to Rs 16,000-crore extra cost
The Government has deployed 100 inspection teams across 135 districts in 29 states and Union Territories to review implementation of the Jal Jeevan Mission, following concerns over cost overruns and irregularities in tender processes.
About the News
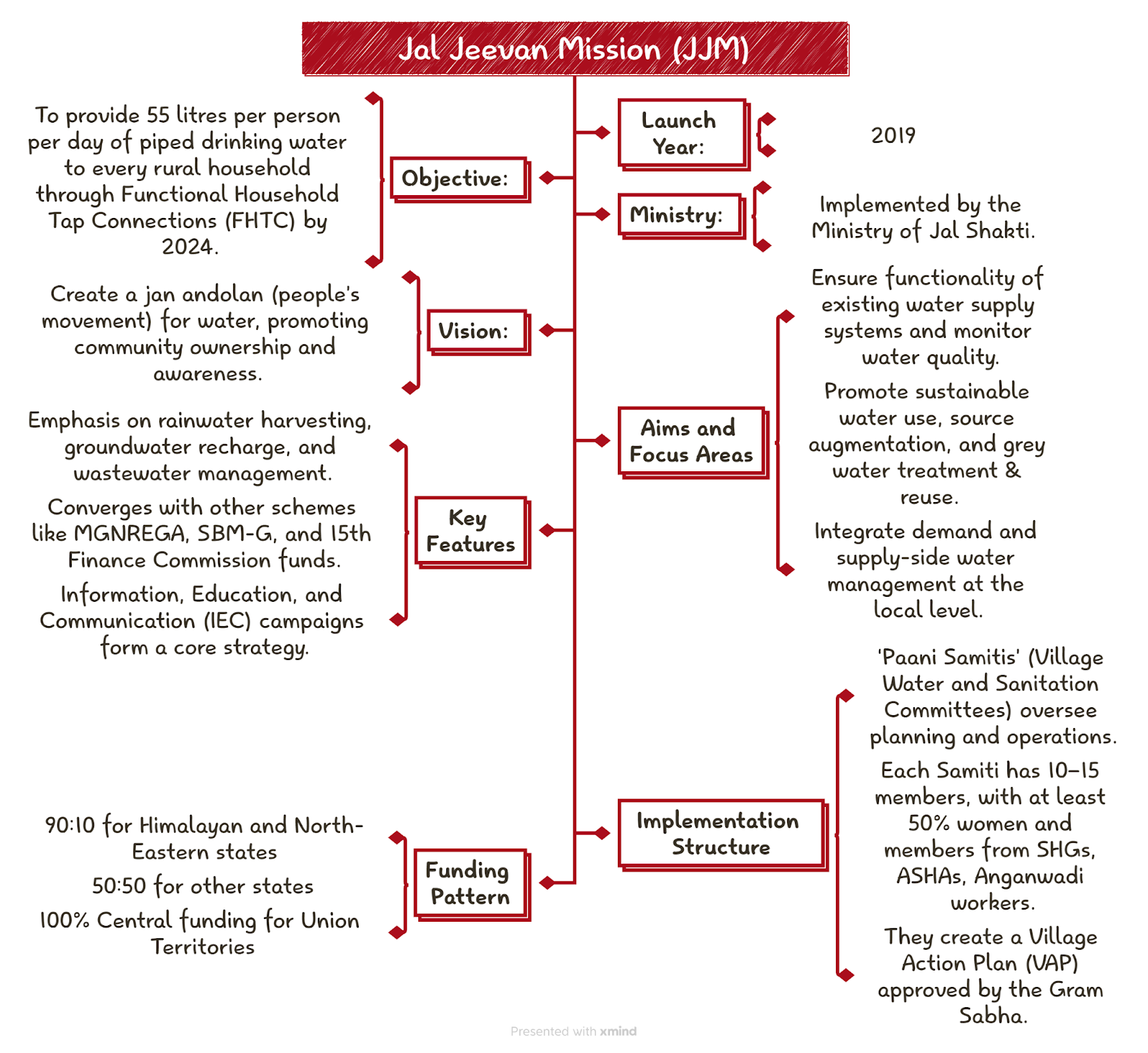
- Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) was launched in 2019 with the aim of providing tap water connections to every rural household.
- Initially, the operational guidelines (2019) clearly stated that cost escalation beyond the approved amount would have to be borne by the State Governments and “tender premium” (bidding higher than estimated cost) was listed as inadmissible expense under Central funding.
- However, on June 21, 2022, the Ministry of Jal Shakti amended the guidelines, removing “tender premium” from inadmissible expenses and allowing "discovered costs" (actual cost post-bidding) to be considered as the approved cost.
The role of the Internet in spreading misinformation- The Hindu
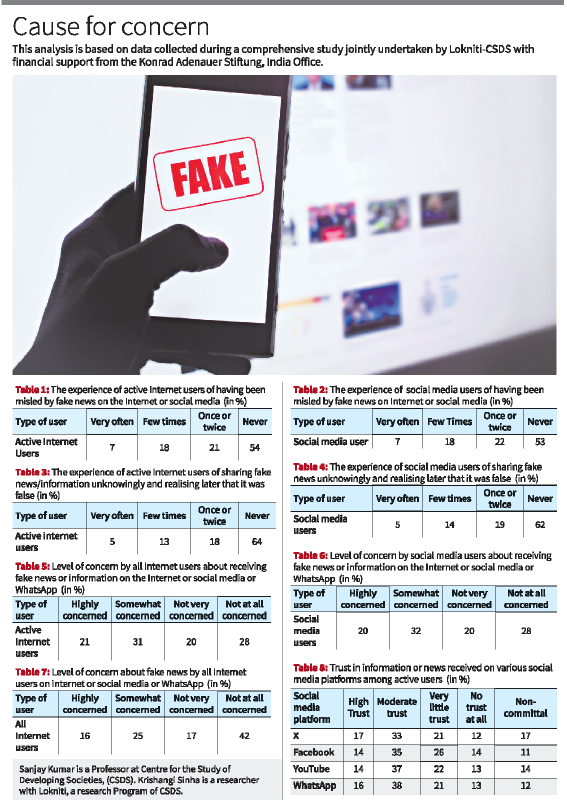
A study shows that a substantial share of users on social media platforms reported very little or no trust at all in the news and information they encounter
- 88% of social media users who unknowingly shared fake news expressed concern about misinformation.
- Even among those who never shared or were misled, 44% and 39% respectively reported concern, showing growing awareness.
- Many users reported low trust in online news; on X (formerly Twitter), 21% had very little trust and 12% complete distrust.
- According to the Reuters Institute’s 2024 report, over 70% of Indians prefer online media, mainly YouTube (54%) and WhatsApp (48%), indicating a major shift toward social media as the primary news source.
 i
i
What is Misnformation and Disinformation
- Misinformation is false or misleading information shared without intent to harm. Even though the sharer doesn’t aim to cause damage, it can still lead to confusion or harm.
- Disinformation is false or misleading information shared deliberately to deceive, often for political, economic, or other strategic reasons, which can cause significant public harm.
- The rapid spread of posts on social media worsens the problem and makes it hard to correct false information.
- With about half the world’s population having internet access, information is created, shared, and consumed at an unprecedented speed.
Environment
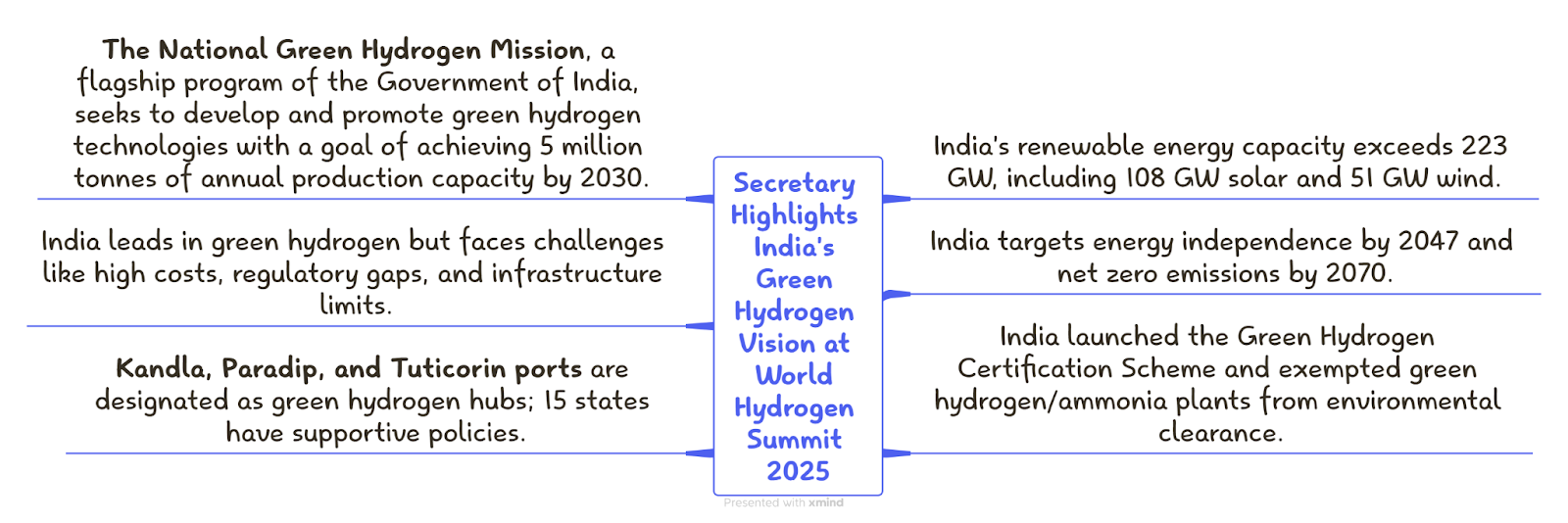
Ministry of New & Renewable Energy at World Hydrogen Summit 2025- PIB
Secretary, Ministry of New & Renewable Energy, Government of India, Shri Santosh Kumar Sarangi addressed the World Hydrogen Summit 2025 in Rotterdam, highlighting India's strategic vision and capabilities in the domain of renewable energy and green hydrogen production.
International Relations
Germany and India united in fight against terrorism: PM- The Hindu
Prime Minister Narendra Modi spoke with German Chancellor Friedrich Merz, congratulating him on assuming office and reaffirming the commitment to strengthen the India-Germany Strategic Partnership.
The leaders exchanged views on regional and global developments and emphasized that both countries stand united in combating terrorism. The External Affairs Ministry stated that they reiterated their shared commitment to fighting terrorism in all its forms.
India-Germany Partnership
- Trade & Investment: Germany is India's largest trading partner in Europe, with bilateral trade reaching USD 33.33 billion in 2023. It is the 9th largest FDI source, (April 2000–Dec 2023).
- Climate & Sustainability: Under the 2022 Green and Sustainable Development Partnership, Germany pledged €10 billion for solar and agro-ecology projects. It also supports India-led global initiatives like CDRI and ISA.
- Technology & Innovation: The Indo-German Science and Technology Centre (IGSTC) backs 49 priority projects, including the WISER program promoting women in STEM fields.
- Defence & Security: The 2006 Defence Cooperation Agreement has enabled collaboration in counter-terrorism, cybersecurity, and defence. Germany has shown interest in India’s Project 75I submarine programme and participates in joint exercises like MILAN, PASSEX, and TARANG SHAKTI-1.
- Strategic Diversification: Amid EU-China trade tensions and tariffs on Chinese EVs, Germany seeks stronger trade ties with India as part of a China+1 strategy.
FTA with UK marks India’s maturing global presence, readiness to lead growth
India-UK Free Trade Agreement (FTA): Key Highlights and Significance
- The India-UK FTA marks a major step in India’s global trade leadership and economic maturity.
- Nearly 99% of Indian tariff lines now get zero-duty access in the UK, benefitting sectors like apparel, textiles, leather, marine products, and toys.
- Tariff disadvantage against countries like Bangladesh and China is eliminated, boosting India’s global competitiveness.
- India offers phased duty-free access to 85% of UK goods over 10 years while protecting sensitive sectors like dairy, apples, edible oils, smartphones, and medical devices.
- The services sector gains significantly with better access for IT, telecom, education, and financial services.
- Professional mobility improves via mutual recognition of qualifications and the Double Contribution Convention, which waives UK social security for Indian professionals.
- The FTA enables joint innovation, tech transfer, and co-manufacturing with UK firms in R&D and advanced manufacturing.
- Includes chapters on labour rights, environment, consumer welfare, gender equity, and anti-corruption—signaling India’s commitment to values-based trade.
- Indian firms must adapt through market-specific strategies, regulatory compliance, certifications, and brand localisation.
- The FTA supports India's vision of Viksit Bharat, encouraging a shift from cost-driven exports to value-based global trade leadership.
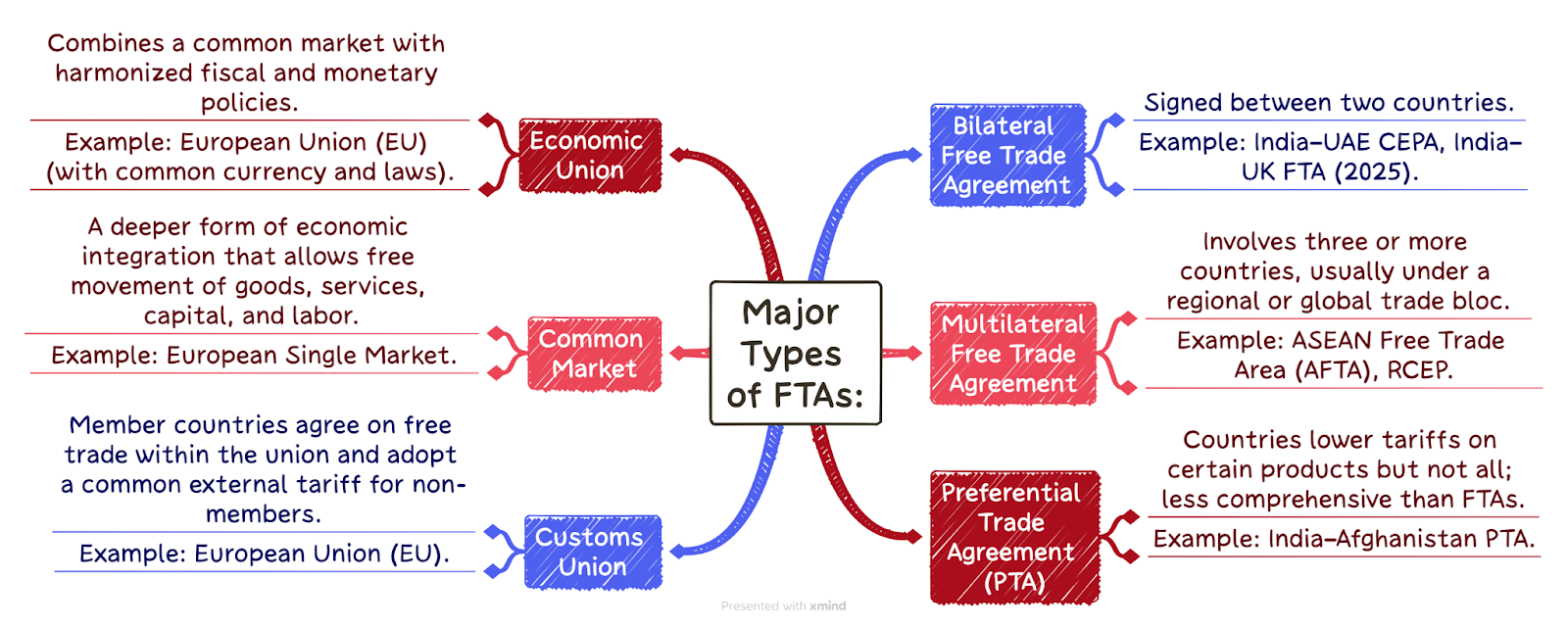
What is a Free Trade Agreement (FTA)?
A Free Trade Agreement (FTA) is a pact between two or more countries to reduce or eliminate barriers to trade, such as tariffs, import quotas, and export restrictions, to promote the free flow of goods and services across borders. The aim is to encourage trade and economic integration among the signatory nations.
i