World Affair
India and Croatia to make long-term plans for deepening defence ties: PM-The Hindu
India and Croatia have agreed to deepen their defence partnership, collaborate on coastal infrastructure and space ventures, following Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Zagreb. Croatia also expressed solidarity with India after the April 22 Pahalgam terror attack.
About Croatia
- Location: Lies at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, along the eastern Adriatic Sea.
- Capital: Zagreb.
- Neighbouring Countries: Borders Slovenia, Hungary, Serbia, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Montenegro, and shares maritime access with Italy.
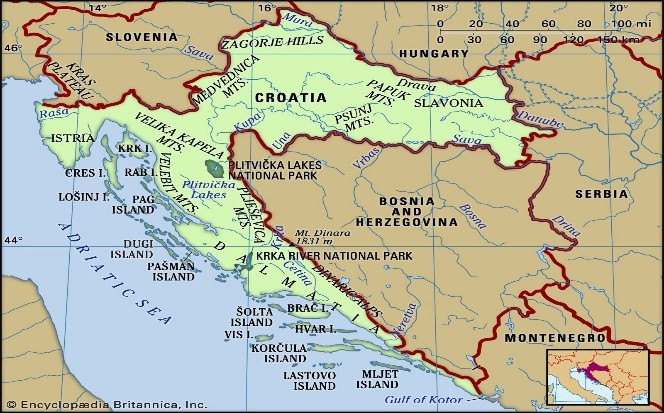
Geographical Features of Croatia
- Major Rivers:
- Sava River: Passes Zagreb; borders Bosnia & Herzegovina.
- Drava River: Forms part of the border with Hungary and joins the Danube.
- Kupa & Una Rivers: Tributaries of the Sava.
Krka & Cetina Rivers: Flow into the Adriatic Sea; important for hydropower.
- Valleys & Plains:
- Pannonian Plains: Fertile agricultural zone.
Zagorje Hills: Known for vineyards and orchards north of Zagreb.
- Mountains:
- Dinaric Alps: Extend inland from the Dalmatian coast.
- Dinara Peak: Croatia’s highest mountain at 1,831 meters.
India–Croatia Relations
- Diplomatic Ties: Established in 1992 following Croatia’s independence from Yugoslavia.
- Political Engagement: Regular bilateral visits; 2025 marked the first-ever Indian Prime Ministerial visit to Croatia.
- Economic Links: Active trade in pharmaceuticals, chemicals, engineering goods; expanding ties in IT, shipbuilding, and renewable energy.
Geography
Humid phases once turned Arabian desert into a lush paradise - The Hindu
Recent studies challenge the long-held view of Arabia as a biogeographical barrier, showing it may have served as a key migration corridor for early humans moving out of Africa during humid interglacial periods, when the desert transformed into a green, habitable landscape.
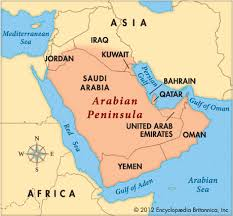
Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, located in southwestern Asia, is the ancestral homeland of the Arab people and the birthplace of Islam. It comprises countries like Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, the UAE, Yemen, Bahrain, and parts of Jordan and Iraq.
Surrounded by the Red Sea, Gulf of Aden, Arabian Sea, Gulf of Oman, and Persian Gulf, the region is largely covered by the Arabian Desert.
Recent discoveries challenge the long-standing belief that Arabia was always an arid wasteland. Instead, evidence suggests it once supported human habitation and played a critical role in early human migration and evolution. These findings also highlight the influence of climate change on human history—past and future.
Environment
Cooking oils can help recover silver from e-waste - The Hindu
Silver is in focus due to its surging industrial demand in India, particularly in solar energy and electronics. It's crucial for rooftop solar panels generating over 108 GW of power and is widely used in mobile phones and laptops—key sectors driving India's clean energy and digital growth.
What is E-Waste?
E-waste refers to discarded electrical and electronic devices that are obsolete or non-functional—such as computers, smartphones, televisions, and other gadgets—mainly due to rapid technological advancement.
India’s E-Waste Scenario:
- India is the third-largest producer of electronic waste globally, after China and the U.S.
- Industrial use accounts for over 50% of global silver demand (World Silver Survey 2024), yet only 15% of silver is currently recycled, leading to a significant loss of this non-renewable resource.
Challenges in E-Waste Management:
- Lack of Consumer Incentives: Most users lack financial or logistical motivation to dispose of e-waste responsibly.
- Poor Collection Infrastructure: Authorised collection centres are scarce, especially in Tier-II and Tier-III cities.
- Dominance of Informal Sector: About 90–95% of e-waste is handled by informal workers using hazardous methods like acid leaching and open burning.
- Grey Market Imports: Used electronics often enter India as "donations" or "refurbished items," eventually adding to domestic e-waste volumes.
Green Method for Silver Recovery from E-Waste:
- Traditional methods produce toxic byproducts and pose environmental and health risks.
- A new eco-friendly technique uses unsaturated fatty acids (linolenic and oleic acids) found in cooking oils like sunflower, groundnut, and olive oil.
- These acids are combined with 30% hydrogen peroxide to create a green solvent that dissolves silver under mild conditions.
- In a second step, ethyl acetate (a safer chemical) is used to isolate and recover the silver, replacing toxic alternatives.
Science and Technology
Hydraulic systems: their functioning and myriad applications - The Hindu
Hydraulics is in focus due to its critical role in modern machinery—from construction and aerospace to industrial automation—driven by innovations improving energy efficiency, precision, and sustainability in mechanical power systems.
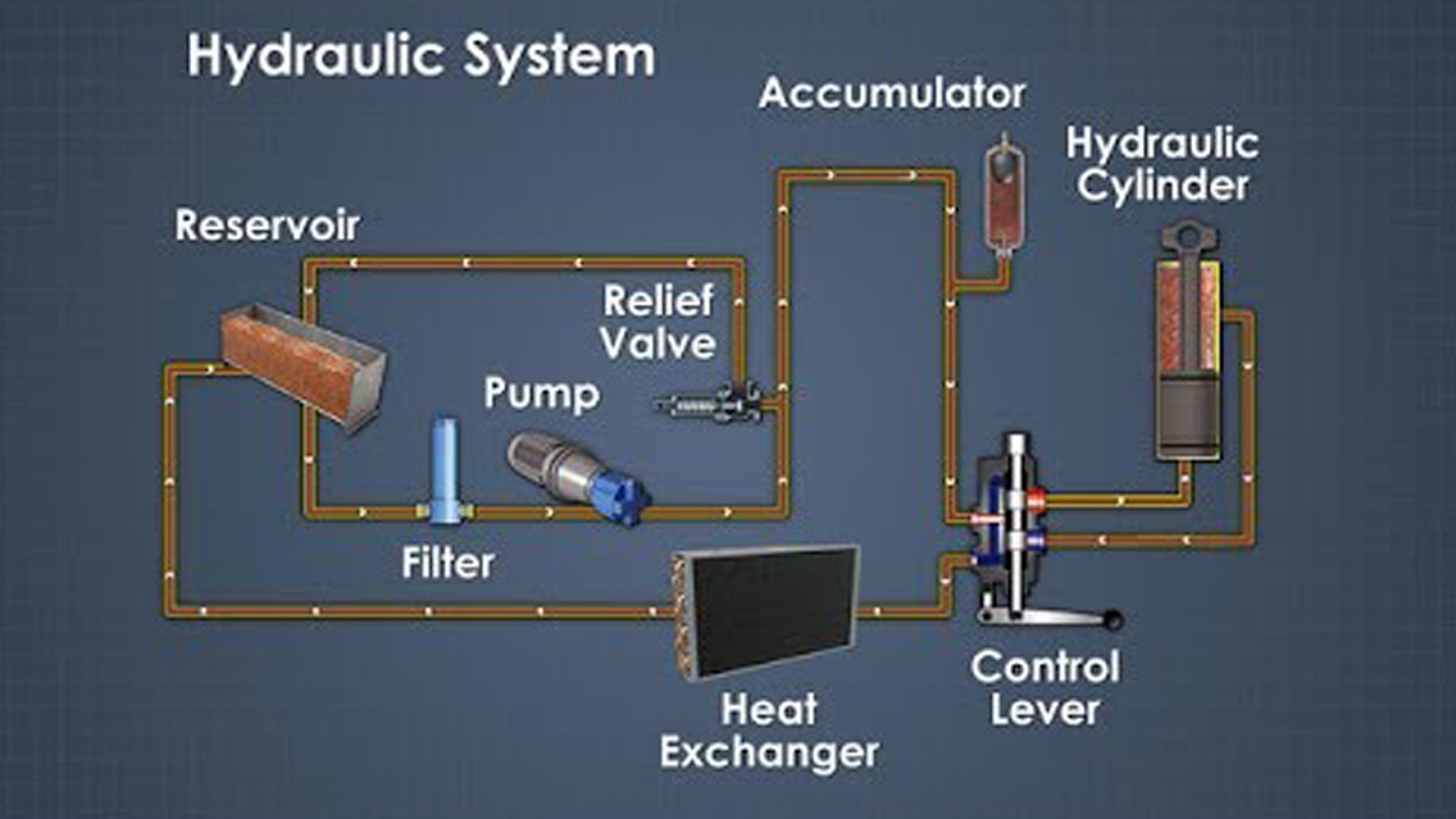
Components of a Hydraulic System
- Pump: Converts mechanical energy into hydraulic pressure and generates oil flow.
- Pipes: Transport hydraulic fluid to and from components.
- Valves: Control flow, pressure, and direction of hydraulic fluid.
- Actuators:
- Linear (Hydraulic Cylinders): Provide push-pull motion.
- Rotary (Hydraulic Motors): Deliver rotational output.
- Tank (with Filters): Stores hydraulic oil and filters contaminants.
- Sensors/Switches: Monitor and control parameters for safety and automation.
Applications of Hydraulics
- Mobile Equipment: Cranes, excavators, dump trucks.
- Stationary Equipment: Hydraulic presses, injection molding machines, wind turbines.
- Sectors: Agriculture, automation, waste management, construction, energy.
- Market Size: ~$45–50 billion globally and steadily growing.
Technological Advancements
- Integration with sensors for real-time monitoring (pressure, temperature, contamination).
- Enables predictive maintenance and improved performance and safety.
- Efforts underway to improve energy efficiency (currently 30–40%).
Electrical alternatives exist but hydraulics remains superior in large-scale and complex operations.
Economy
Union Minister of Commerce & Industry Reviews Progress of NICDC-led Industrial Nodes- Indian Express
The Union Minister of Commerce & Industry recently chaired a high-level review meeting to evaluate the progress of NICDC-led industrial nodes in Andhra Pradesh under various industrial corridor projects.
About NICDC:
The National Industrial Corridor Development Corporation (NICDC), operating under the Ministry of Commerce & Industry, is tasked with developing world-class industrial smart cities to drive manufacturing growth, attract investments, create employment opportunities, and enhance India’s global economic competitiveness.
NICDC focuses on integrated planning, offering plug-and-play infrastructure, sustainable urban development, and seamless multimodal connectivity.
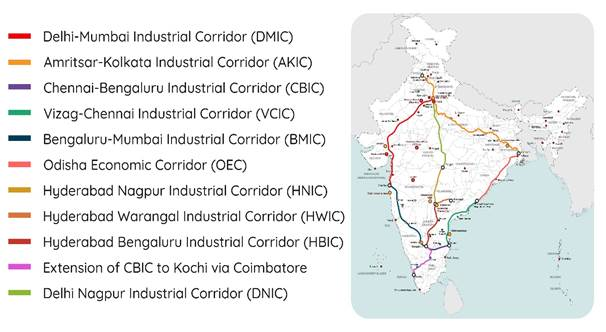
Notably, Andhra Pradesh is the only state in India to host industrial nodes under three different industrial corridors, making it a unique hub for corridor-based industrial development.
Global Drought Outlook 2025 -
The OECD released its “Global Drought Outlook 2025” warning that 40% of the world is now facing more frequent and intense droughts, posing a systemic risk to water, food, energy, and ecosystem security due to worsening climate change.
About the Report
- Published by the OECD to assess global drought trends, impacts, and adaptive policy needs.
Highlights drought as a systemic risk affecting water, food, energy, and ecosystems.
What is Drought?
- A hydrological imbalance due to prolonged below-average rainfall.
- Types:
- Meteorological – Rainfall deficiency
- Agricultural – Soil moisture deficit
- Hydrological – Low river/lake/groundwater levels
Global Drought Trends
- Global land affected by drought doubled since 1900.
- In 2023, 48% of Earth faced at least one month of extreme drought.
- 62% of aquifers show declining levels; major rivers drying up.
- +4°C warming could make droughts 7 times more frequent/severe by 2100.
Impact of Drought
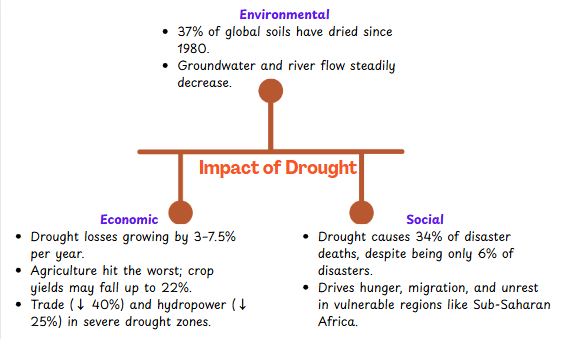
Solutions to Mitigate Drought
- Integrated Water Resource Management (IWRM) for efficient water use.
- Nature-Based Solutions (NbS) like reforestation and urban de-sealing.
- Drought-tolerant crops and smart irrigation (can save up to 76% water).
- Urban planning to recharge aquifers through permeable surfaces.
- Early Warning Systems for real-time drought monitoring.
- Cross-sector collaboration across agriculture, health, energy, and infrastructure.
- Investment in resilience offers 2–10 times return in long-term benefits.