World Affairs
War in Middle East: what next- Indian Express
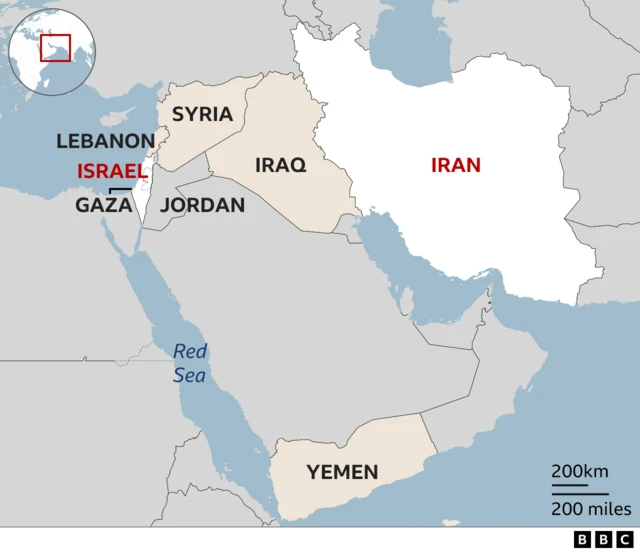
Israel and Iran have engaged in four waves of cross-border strikes, with the assassination of top Iranian generals, including Ali Shamkhani, a senior adviser to Iran’s Supreme Leader, marking a major escalation. The Israel Defense Forces (IDF) has also issued warnings in Persian to Iranian civilians, indicating further intensification of conflict.

Implications of the Iran-Israel Conflict
- Widening of Proxy Wars: Iran’s allies like Hezbollah, Hamas, Houthis, and PMF may retaliate, risking a multi-front conflict across the Middle East.
- Instability in Fragile States: Violence may surge in Lebanon, Syria, Iraq, and Yemen, deepening political instability and humanitarian crises.
- Threat to Maritime Trade: Strategic chokepoints like the Strait of Hormuz, Bab el-Mandeb, and Eastern Mediterranean may face disruption, impacting global trade and oil flow.
- Global Oil Price Volatility: A direct conflict with Iran could affect oil exports, triggering a global spike in prices and inflation.
- Collapse of Nuclear Talks: The conflict could derail JCPOA negotiations, ending prospects of a peaceful resolution on Iran’s nuclear ambitions.
- Acceleration of Iran’s Nuclear Program: Israeli attacks may push Iran to expedite nuclear weapons development citing national defense.
- Regional Nuclear Arms Race: Gulf nations like Saudi Arabia may seek nuclear capabilities, escalating an arms race in West Asia.
India’s Strategic and Economic Concerns
- Oil Supply Risk: Instability in West Asia threatens disruption of crude oil imports, impacting India’s energy security and current account deficit.
- Gulf Indian Diaspora at Risk: With millions of Indians in the Gulf, conflict may necessitate emergency evacuations and affect remittance inflows.
- Diplomatic Tightrope: India must balance ties with Israel, Iran, and Arab nations to safeguard its strategic and geopolitical interests.
- Export Disruption Threat: Escalating tensions may hinder India’s tea exports to the Middle East, affecting trade revenues.
India sends final batch of machinery to Suriname - The Hindu
The Ministry of External Affairs announced that the second and final consignment of passion fruit processing machinery has been dispatched to Suriname under the SEEDS (Supply of Equipment for Efficient Development of SMEs) initiative, aimed at boosting bilateral ties.
About SEEDS Initiative (Supply of Equipment for Efficient Development of SMEs)
- Objective: To support the growth and modernization of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in partner countries by providing critical equipment and technology.
- Launched by: Ministry of External Affairs, Government of India as part of its development partnership initiatives.
- Focus Areas: Enhancing industrial capacity, promoting value-added production, and strengthening bilateral ties through economic cooperation.
- Implementation: Equipment is supplied based on the needs of local industries, such as food processing, agriculture, textiles, etc.
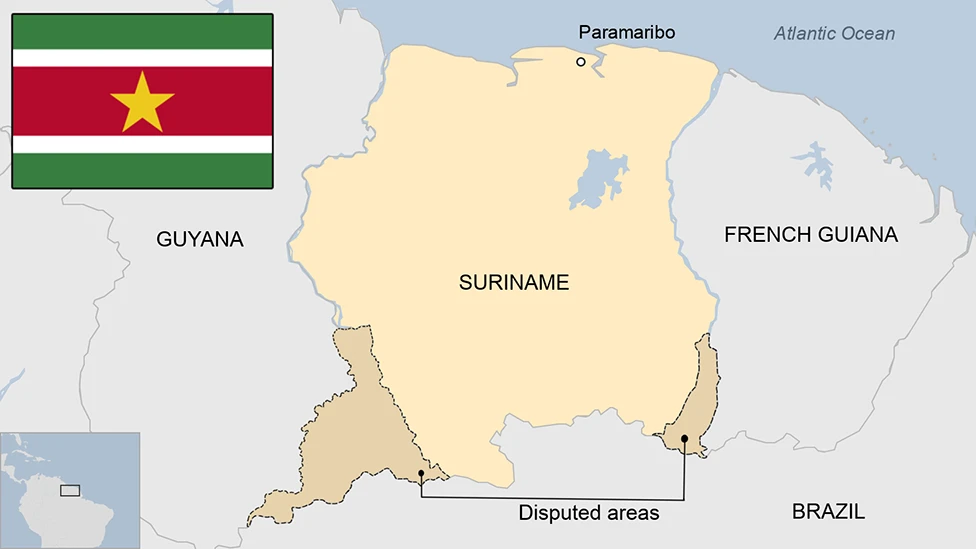
About Suriname –
- Location: Suriname is in northeastern South America, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean, French Guiana, Brazil, and Guyana.
- Capital: Paramaribo, located on the banks of the Suriname River.
- Governance: A democratic republic with a president and a multi-party system.
- Official Language: Dutch is the official language; other widely spoken languages include Sranan Tongo, Hindustani, Javanese, and English.
Independence: Gained independence from the Netherlands on November 25, 1975 (formerly Dutch Guiana).
- Economy: Resource-rich with key sectors like mining (gold, bauxite, oil), agriculture (rice, bananas, timber), and services.
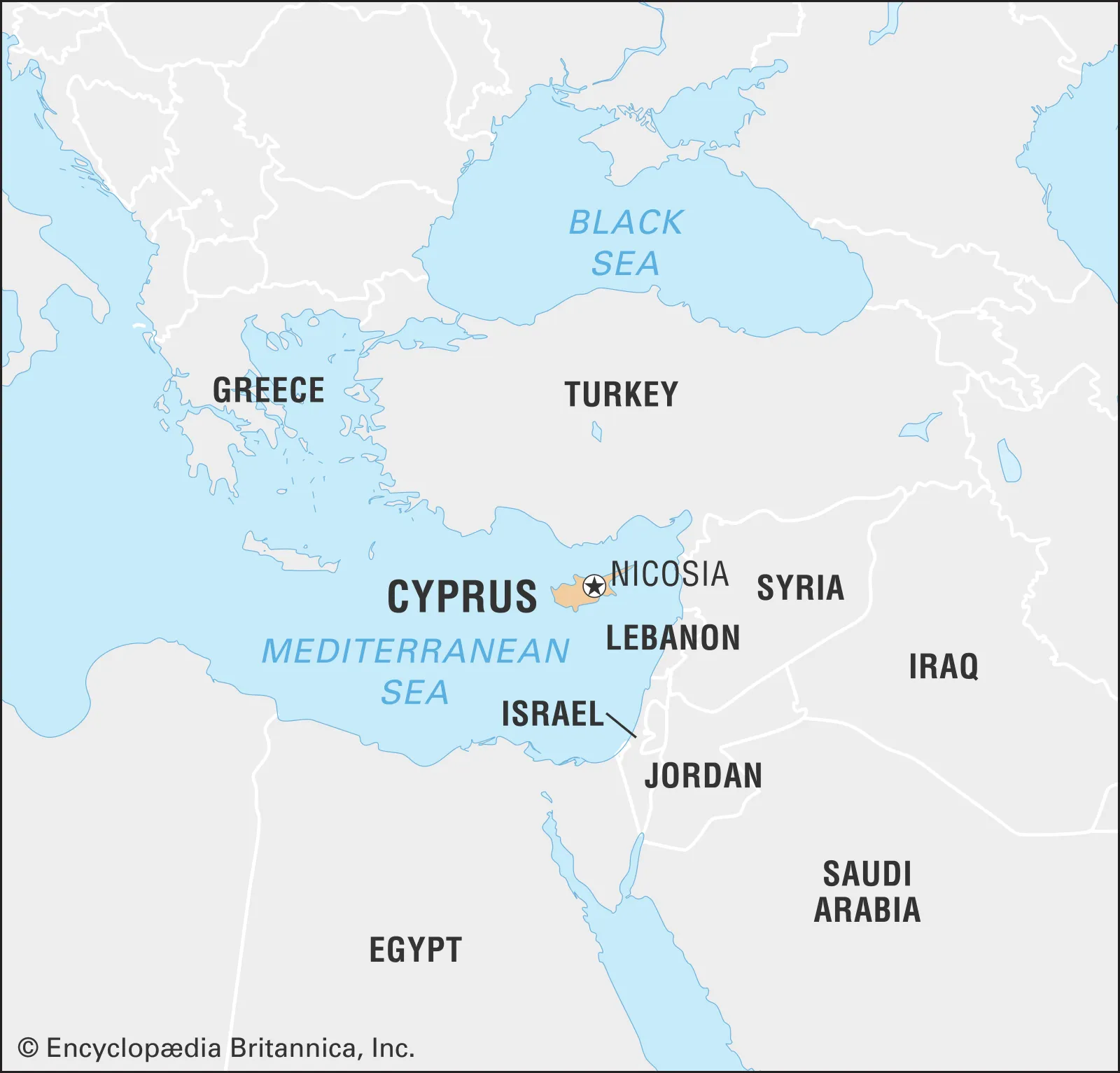
India will continue efforts to strengthen ties with Cyprus: PM- The Hindu
PM Narendra Modi arrived in Cyprus to deepen bilateral ties, marking a strategic visit amid the ongoing Israel-Iran conflict and ahead of the G7 summit.
India–Cyprus Relations:
- Dependable Partner: Cyprus is regarded as one of India’s consistent and reliable allies.
- UNSC Support: Strongly supports India’s bid for a permanent seat at the UN Security Council.
- Nuclear Cooperation: Backed the India-US Civil Nuclear Deal in the NSG and IAEA, aiding India’s energy security.
- Strategic Alignment: Endorses India on key global issues including cross-border terrorism.
India–Cyprus Defence Cooperation:
- MoU & BDCP Signed (2022, 2025): Agreements focus on joint training, defence exchanges, and structured cooperation, including drills and industry ties.
- AERO India 2025 Participation: Cypriot delegation explored maritime and defence trade, boosting India's Eastern Mediterranean footprint and "Make in India" initiative.
India–Cyprus Economic & Trade Relations:
- Growing Trade: Bilateral trade reached USD 137 million in 2023–24, recovering post-pandemic.
- Diverse Trade: India exports pharmaceuticals, textiles, steel, ceramics, and machinery; Cyprus exports beverages, pharma, and niche manufactured goods.
- Facilitating Mechanisms: Joint Economic Committee, Cyprus–India Business Association, and Invest India–Cyprus MoU (2021) promote dialogue, B2B ties, and investment.
- EU Gateway: Cyprus serves as a strategic bridge for Indian businesses entering the EU market.
Environment
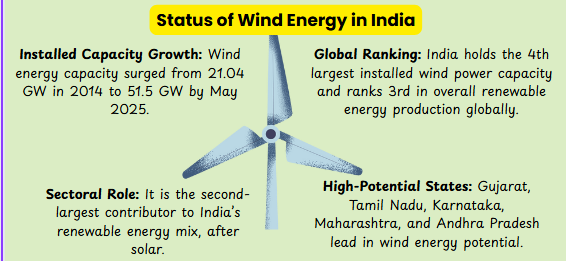
Wind Energy is at the centre of India’s strategy for the renewable energy sector:PIB
India observed Global Wind Day 2025 on June 15, with Union Minister Pralhad Joshi highlighting wind energy as the core of India’s renewable energy strategy at a national conference in Bengaluru.
Key Government Initiatives to Boost Wind Energy
- Centralized Data Collection and Coordination (CCDC) Initiative: Enhances wind resource mapping and site identification for project viability.
National Wind-Solar Hybrid Policy (2018): Promotes large-scale grid-connected hybrid projects to ensure efficient energy utilization.
- Viability Gap Funding (VGF) Scheme for Offshore Wind (2015): Supports offshore wind projects aligned with the National Offshore Wind Energy Policy.
- Additional Supportive Measures:
- Green Energy Open Access Rules (2022) – Facilitates easy access to renewable energy for consumers.
- Renewable Energy Purchase Obligations (RPO) – Mandates obligated entities to purchase a defined share of power from renewable sources.
Society
Centre’s rationale behind MGNREGS spending cap, the problems with it- Indian Express
The Union Finance Ministry has, for the first time, capped MGNREGS spending at 60% of the annual budget for the first half of FY 2025–26, aiming to control overspending and streamline fund utilization.
Rationale Behind the Spending Cap:
- Over 70% of MGNREGS budget is typically exhausted by September, leading to fund shortages in later months.
- Pending dues have ranged from ₹15,000 to ₹25,000 crore in the last five years.
- Around 20% of the next year’s budget is routinely used to clear past dues.
About MGNREGA
- MGNREGA stands for the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005.
- It provides a legal guarantee of 100 days of unskilled manual work to adult members of rural households.
- The scheme is designed to strengthen livelihood security in rural areas through wage employment.
- It enshrines the “Right to Work” as a statutory right under Indian law.
- MGNREGA was enacted to combat rural poverty and underemployment.
- It aims to create durable rural assets while ensuring economic relief to the poor.
- The Act was a result of sustained grassroots movements and civil society pressure.
- It also promotes transparency and accountability through social audits and public participation.