Economy
Railways safety body gives final nod for Mizoram capital’s first rail link- Indian Express
The Commission of Railway Safety (CRS) has granted operational clearance for the Hortoki to Sairang railway line in Mizoram.
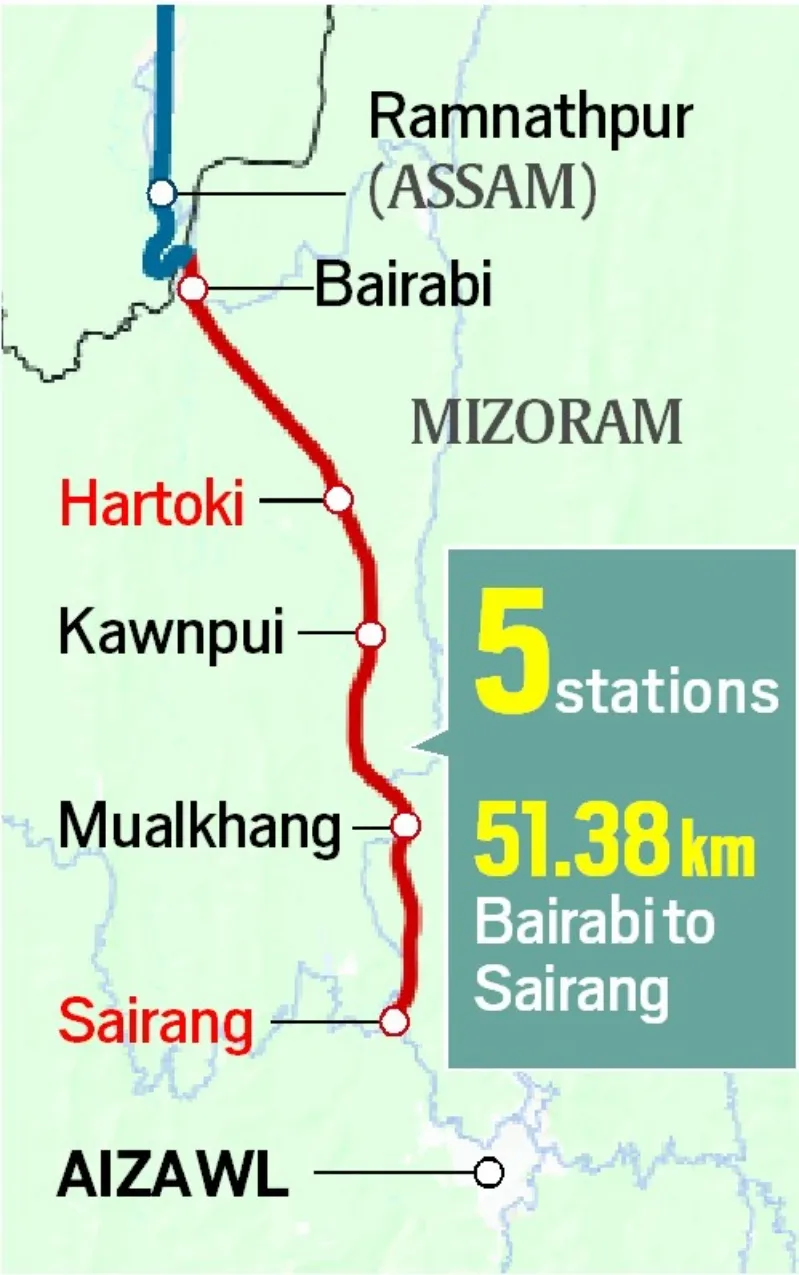
About
- The Hortoki–Sairang section (33.86 km) marks the final leg of the Bairabi–Sairang railway project in Mizoram, paving the way for Aizawl's first-ever railway connectivity.
- This stretch traverses challenging hilly terrain, featuring 32 tunnels and 35 major bridges.
- Sairang, a satellite town located about 20 km from Aizawl, will serve as the railhead connecting the capital city.
- Until now, Bairabi in the Kolasib district, close to the Assam border, was Mizoram’s only rail station.
Strategic Importance:
- The project is part of the Ministry of Railways' initiative to link all northeastern state capitals by rail.
- It includes multiple new line and doubling projects across states such as Assam, Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Manipur, and Tripura.
This railway expansion is a crucial component of the Centre’s Act East Policy, aimed at boosting connectivity and fostering economic integration across the Northeast region.
"Why a majority of aviation accidents occur during takeoff & landin- Plane Crash in Ahmedabad - Indian Express
A Boeing 787 Dreamliner (Air India) flying from Ahmedabad to London Gatwick with 242 passengers crashed shortly after takeoff. While the cause is still under investigation, it brings attention to the global trend that most aviation accidents occur during takeoff and landing phases.
Major Highlights:
1. Data Findings (Boeing Report, 2015–2024):
- Takeoff & Initial Climb: Account for 20% of accidents and 20% of fatalities, despite just 2% of flight time exposure.
- Final Approach & Landing: Account for 47% of accidents and 37% of fatalities, with only 4% of flight time exposure.
- Descent Phase: 3% of accidents and 7% of fatalities.
- Cruise Phase: Despite 57% of flight exposure, only 10% of accidents and less than 10% of fatalities occur here.
2. Reasons for Higher Risk during Takeoff & Landing:
- Aircraft fly closer to ground, with less time and space to recover in emergencies.
- Planes are under maximum stress, and pilot error is more likely.
- Environmental threats such as bird strikes, turbulence, and bad weather are more frequent.
- Course correction is harder at low altitude.
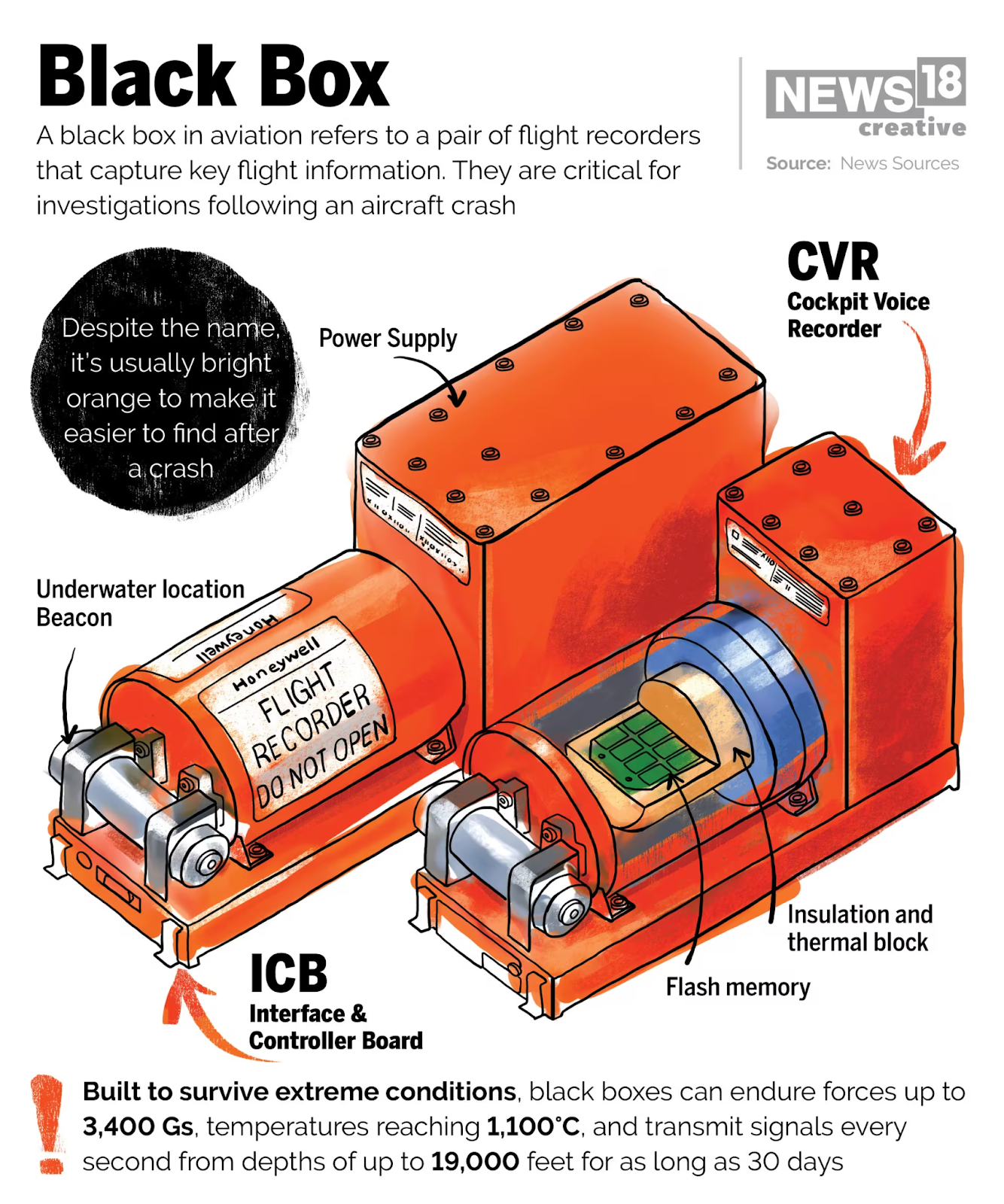
About Black Box
- It refers to two flight recorders: the Cockpit Voice Recorder (CVR) and the Flight Data Recorder (FDR).
- CVR captures cockpit conversations, alarms, and ambient sounds.
- FDR records 80+ flight parameters like altitude, airspeed, heading, engine data, etc.
- Housed in durable steel or titanium casings to withstand high-impact crashes and fire.
- Usually placed in the tail section of the aircraft, where damage is least likely.
- Designed to withstand extreme temperatures, pressure, and impact.
- Emit ultrasonic locator beacons (pingers) for up to 30 days if submerged underwater.
- Crucial for post-crash investigations and aviation safety improvements.
- Despite their name, black boxes are bright orange for visibility during recovery.
- Recovery is not always guaranteed, especially in deep or remote waters.
Challenges in the Indian Aviation Sector
- Market Concentration: Dominated by a duopoly — IndiGo (~60%) and Tata Group airlines (~30%) control ~90% of the domestic market.
- Barriers to Entry: High operating costs, predatory pricing, opaque slot allocation, and algorithmic coordination deter new entrants.
- Financial Instability:Chronic losses persist; Air India alone reported a ₹9,556 crore loss in FY22.
- Safety Concerns:
- IndiGo fined ₹1.2 crore (2023) for security violations.
Akasa Air and Air India penalised for lapses in safety and engineering protocols.
- Anti-Competitive Practices: Issues like collusive pricing, slot misuse, and gun-jumping remain under-regulated.
- Institutional Weakness:
Regulators like DGCA, AAIB, and BCAS face:
- Staff shortages
- Lack of technical expertise
- Leadership often without aviation backgrounds
- Slow and ineffective decision-making
India’s aviation sector is expanding rapidly, but financial stress, safety lapses, regulatory inefficiencies, and market distortion hinder sustainable, world-class growth. Comprehensive reforms are essential.
Income Tax Department investigating evasion from crypto assets - Indian Express
The Income Tax Department is probing tax evasion and money laundering by high-risk individuals using virtual digital assets (VDAs) like cryptocurrencies and NFTs.
Virtual Digital Assets
According to the Finance Act 2022 (India), a Virtual Digital Asset (VDA) refers to any digitally represented value that is created using cryptographic techniques, serves as a store of value or medium of exchange, and is transferred electronically.
It includes cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and stablecoins.
Taxation Provisions for Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs)
- Flat 30% tax on gains from VDAs under Section 115BBH, with no deductions permitted except for the cost of acquisition.
- A 1% TDS is applicable on all crypto transactions from July 1, 2022, under Section 194S.
- The CBDT is implementing a “NUDGE” approach (Non-intrusive Usage of Data to Guide and Enable) to encourage voluntary tax compliance, following a “trust-first” philosophy.
Science and Technology
New scheme to study crops using AI: What is CROPIC- Indian Express
The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare is set to launch CROPIC, an AI-powered study for real-time crop monitoring through field photographs, starting from Kharif 2025 and Rabi 2025–26 seasons.
What is CROPIC?
CROPIC stands for Collection of Real Time Observations & Photo of Crops. Under this initiative, crops will be photographed four to five times during their growth cycle, and the images will be analysed to evaluate crop health and identify any mid-season losses.
The study will initially be implemented for two agricultural seasons — Kharif 2025 and Rabi 2025–26.
How Will It Work?
- Mobile App developed by the Agriculture Ministry will be used for crowdsourced photo collection, directly from farmers.
- The AI-based cloud platform will:
- Analyze images to identify crop type, stage, damage, and extent.
- A web-based dashboard will provide visual insights for policymakers.
- During insurance/compensation assessments, officials will collect field evidence using the CROPIC app.
Purpose of the CROPIC Study
- To support Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) with accurate crop monitoring.
- To create a digital directory of crop signatures for future reference.
- To enable automated crop loss assessment using AI and computer vision.
To ensure timely and transparent compensation to eligible farmers.
- To promote digital innovation and financial resilience in Indian agriculture.
Society
India slips to 131st position in Global Gender Gap Index 2025 - The Hindu
India has ranked 131 out of 148 countries in the World Economic Forum’s Global Gender Gap Report 2025, released on June 12, 2025, with a parity score of just 64.1% — making it one of the lowest-ranked countries in South Asia.
India has slipped two places from its 2024 position, highlighting persistent gender inequality across key dimensions.
Global Overview
- Overall Gender Parity: The world has closed 68.5% of the gender gap, showing only marginal improvement from last year.
- Top Performers:
- Iceland remains the most gender-equal country for the 16th consecutive year, with over 90% parity.
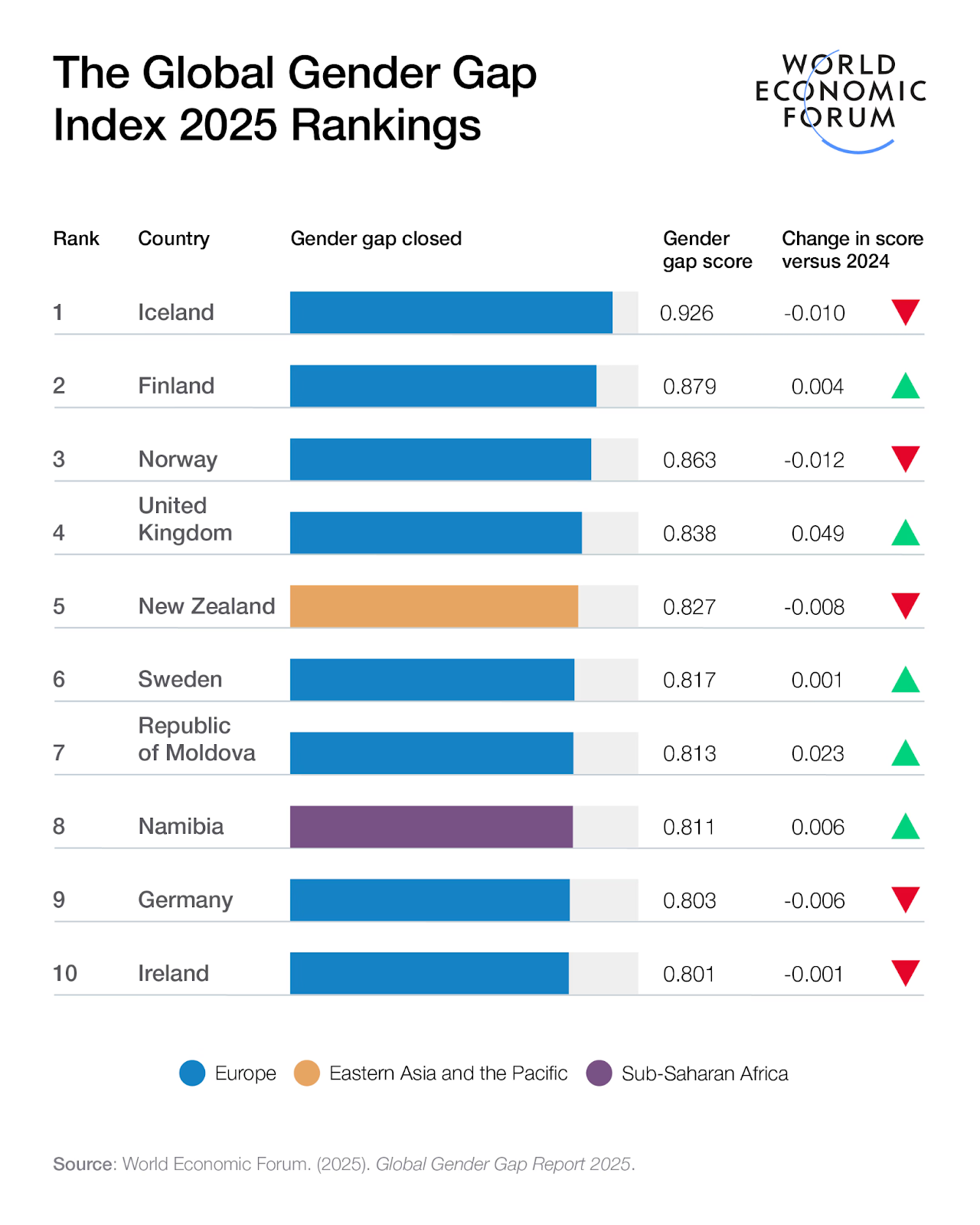
-
- Other high-ranking nations include Finland, Norway, and the United Kingdom
India’s Performance
- Overall Rank: India ranks 131 out of 148 countries, down two places from 2024, with a parity score of 64.1%.
- Economic Participation:Slight improvement to 40.7%, with estimated earned income parity rising from 28.6% to 29.9%.
- Educational Attainment:Strong performance with a score of 97.1%, indicating significant gains in literacy and higher education enrollment.

- Health and Survival:Modest progress seen in sex ratio at birth and healthy life expectancy.
- Political Empowerment: Continued decline in Women’s representation in Parliament fell from 14.7% to 13.8% as well as Ministerial roles dropped from 6.5% to 5.6%, far below the 2019 peak of 30%.
Key Concerns Highlighted in the Report
- Time to Parity: At the current rate, it will take 123 years to close the global gender gap.
- Economic Disparities:Women continue to earn significantly less than men, with persistent wage gaps across sectors.
- Regional Inequality:South Asia and the Middle East remain among the lowest-performing regions due to deep-rooted structural and cultural barriers.