GEOGRAPHY
Mission Mausam: ₹ 2,000 crore fillip for weather forecasting - Indian Express
Context:
- The Union Cabinet has approved a mission to enhance the capabilities of India's weather department in forecasting, modelling, and information dissemination. Mission Mausam is allocated a budget of ₹2,000 crore for the first two years.
Aim:
-
To improve weather surveillance, forecasting, and modelling to benefit key sectors such as agriculture, aviation, defence, disaster management, tourism, and health.
Coverage:
Institutions Involved:
Objectives:
-
Provide accurate and timely weather forecasts and extreme weather alerts.
-
Introduce weather interventions for managing fog, hail, and rainfall.
-
Build personnel capacity and offer training.
Controversy over Mumbai's salt pans: Why do these lands matter? - Indian Express
Context
- The Centre recently approved the transfer of 256 acres of salt pan land in Mumbai to the Dharavi Redevelopment Project Pvt Ltd (DRPPL), a joint venture between Adani Realty Group and the Maharashtra government, for building rental housing for slum dwellers. The move has drawn criticism from opposition leaders and environmentalists.
Salt Pan Lands
-
About:
These comprise low-lying lands where seawater flows in, leaving behind salt and other minerals.
-
Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) Notification, 2011:
Salt pans fall under the ecologically sensitive CRZ-1B category, where no economic activity is allowed except for salt extraction and natural gas exploration.
-
Distribution:
India has around 60,000 acres of salt pan lands spread across Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Gujarat, and Karnataka.
-
Largest Salt Pan Area:
Andhra Pradesh (20,716 acres), followed by Tamil Nadu (17,095 acres) and Maharashtra (12,662 acres).
-
Significance:
Salt pans prevent flooding in Mumbai's eastern suburbs and support diverse species of birds, insects, flora, and fauna.
Rainfall in Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh raises water level in Ukai Dam - Indian Express
Context
Recent rainfall in the upper catchment areas of Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh caused the discharge of 1.19 lakh cusecs of water from the Ukai Dam, Gujarat's second-largest reservoir after Sardar Sarovar. The water level is now just five feet below the danger mark of 345 feet.
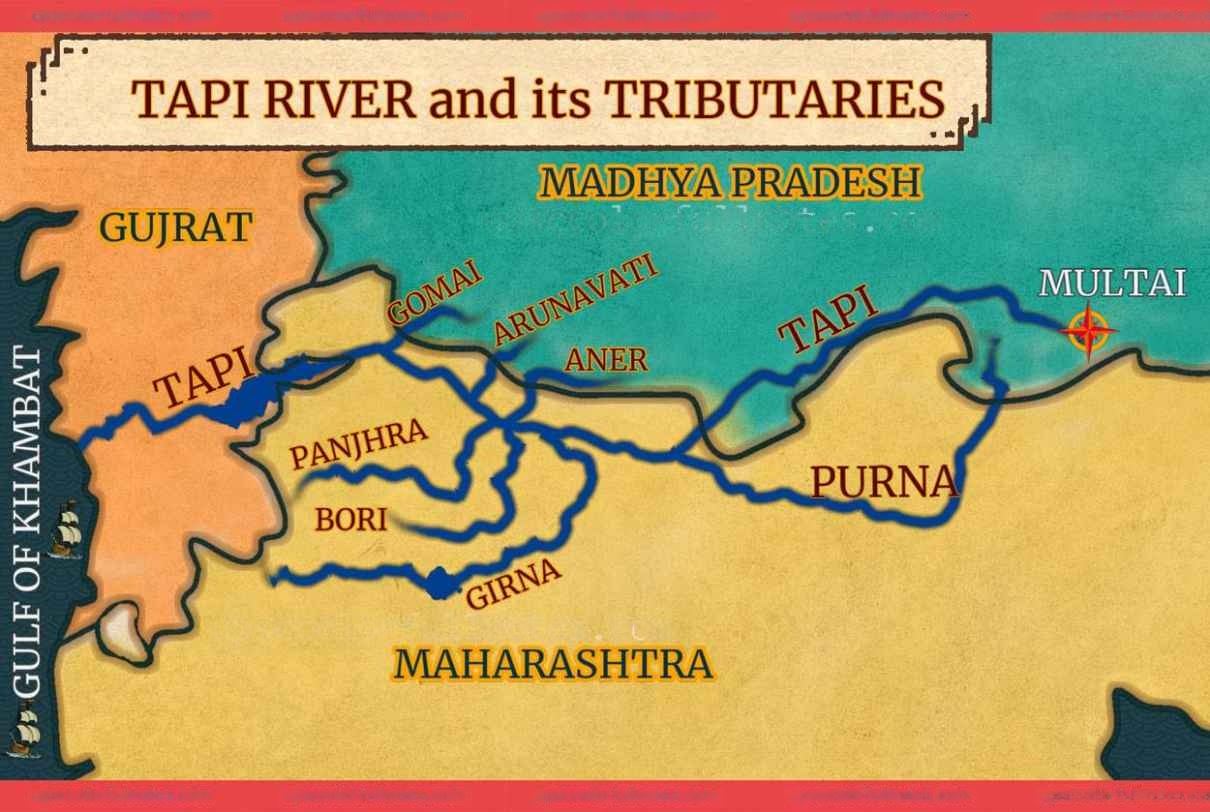
Ukai Dam/Vallabh Sagar Dam
- River: Built on the Tapti River.
- Construction: Completed in 1972.
- Usage: Irrigation, power generation, and flood control.
- Catchment Area: Approx. 62,255 km².
- Water Spread: 52,000 hectares.
- Type: Earth-cum-masonry dam.
- Dimensions: Earth dam is 80.77 meters high; masonry dam is 68.68 meters high.
Tapti River
- About: One of the three major rivers flowing east to west in peninsular India.
- Origin: Gawilgarh Hills, Madhya Pradesh.
- Mouth: Gulf of Khambhat (Arabian Sea).
- Length: 700 km (435 miles).
- Catchment Area: Approx. 65,145 sq. km (80% in Maharashtra).
SOCIETY
Cabinet clears health insurance cover of ₹5 lakh for all aged 70 years and above - Indian Express
Context
The Union Cabinet recently approved the expansion of the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY) to provide health coverage to all senior citizens aged 70 years and above, irrespective of their income.
New Provisions of PM-JAY
- Extended Coverage: ₹5 lakh annual coverage per family for citizens aged 70 years and above.
- Beneficiaries: An additional 6 crore senior citizens (from 4.5 crore families) are expected to benefit, with new cards issued under PM-JAY.
- Choice: Senior citizens availing of public health schemes like CGHS, ECHS, or private health insurance can choose to switch to PM-JAY if they prefer.
Ayushman Bharat-Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana
- About: The world’s largest health insurance scheme fully financed by the government.
- Launch: 2018
- Provision: It offers a sum insured of Rs.5 lakh per family for secondary care and tertiary care.
- Health Benefit Packages: They cover surgery, medical and day care treatments, cost of medicines and diagnostics.
- Beneficiaries: An entitlement-based scheme that targets the beneficiaries as identified by latest Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) data.
- Funding: 60:40 for all states and UTs with their own legislature, 90:10 in Northeast states and J&K, Himachal and Uttarakhand and 100% Central funding for UTs without legislature.
- Nodal Agency:
- National level: National Health Authority (NHA) (an autonomous entity under the Society Registration Act, 1860).
- State level: State Health Agency (SHA).
POLITY
National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) - The Hindu
- Constitution: Under the Commission for Protection of Child Rights (CPCR) Act, 2005.
- Mandates:
- To function for the protection and promotion of child rights.
- To monitor the proper and effective implementation of
- Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012
- Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015
- Right to Free and Compulsory Education (RTE) Act, 2009
- Composition:
- Chairperson: Person of eminence and has done outstanding work for promoting the welfare of children (3 years or till the age of 65 years/ Not more than 2 terms)
- 6 Members (atleast 2 women): Person of eminence in:
- Education
- Child health, care, welfare or child development
- Juvenile justice or care of neglected or marginalized children or children with disabilities
- Elimination of child labour or children in distress
- Child psychology or sociology
- Laws relating to children ( 3 years or till the age of 60 years/ Not more than 2 terms)
- Appointment: By the Central government.
- Appointment of chairperson: On the recommendation of 3 members committee constituted by the Central government under the chairmanship of the Minister of Education.
- Removal: By the Central Government if he:
- is adjudged insolvent.
- engages during his term of office in any paid employment outside the duties of his office.
- refuses to act or becomes incapable of acting.
- is of unsound mind and stands so declared by a competent court.
- has so abused his office as to render his continuance in office detrimental to the public interest.
- is convicted and sentenced to imprisonment for an offense, which in the opinion of the Central Government, involves moral turpitude.
Hindi should be generally accepted as the language of work with consensus: Shah - The Hindu
Context
Union Home Minister was unanimously re-elected the Chairperson of the Parliamentary Committee on Official Language recently.
Parliamentary Committee on Official Language
- Constitution: Under the provisions of Section 4 of the Official Languages Act, 1963, in the year 1976.
- Composition: Chairman: Union Home Minister
- Report: The panel submits its report to the President, who “shall [then] cause the report to be laid before each House of Parliament, and sent to all the State Governments”.
- Purpose: To review the progress made in the use of Hindi for official purposes, and to make recommendations to increase the use of Hindi in official communications.
- Members: 30 members of Parliament (20 from Lok Sabha and 10 from Rajya Sabha).
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Amit Shah Launches Four Key Cybersecurity Initiatives - The Hindu
Context
- Union home minister recently inaugurated four cybersecurity initiatives in Delhi: the Cyber Fraud Mitigation Centre (CFMC), Cyber Commandos, Samanvaya portal, and Suspect Registry.
New Cybersecurity Initiatives
|
Cyber Fraud Mitigation Centre (CFMC)
|
- Establishment: At the Indian Cybercrime Coordination Centre (14C) in New Delhi
- Representatives: Major banks, Financial Intermediaries, Payment Aggregators, Telecom Service Providers, IT Intermediaries, and States/UTs Law Enforcement Agencies (LEAs).
- Function: Immediate action and seamless cooperation to tackle online financial crimes.
|
|
Samanvaya Platform (Joint Cybercrime Investigation Facilitation System)
|
- About: A web-based module to act as a One Stop Portal for data repository of cybercrime, data sharing, crime mapping, data analytics, cooperation, and coordination platform for LEAs across the country.
|
|
'Cyber Commandos' Program
|
- About: Under it, a special wing of trained 'Cyber Commandos' in States/ UTs and Central Police Organizations (CPOs) will be established to counter threats of the cyber security landscape in the country.
- Proper training: Trained Cyber Commandos will assist States/UTs and Central Agencies in securing the digital space.
|
|
Suspect Registry
|
- About: A new initiative to strengthen fraud risk management by creating a registry of identifiers based on the National Cybercrime Reporting Portal in collaboration with banks and financial intermediaries.
|
Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA)
- Aim: To deal with cybercrime in the country in a coordinated and comprehensive manner.
- Focus: Tackling issues related to cybercrime for citizens, including improving coordination between various LEAs and stakeholders.
- Headquarter: New Delhi.
Functions:
- To act as a nodal pointin the fight against cybercrime.
- To identify the research problems and needs of LEAs and take up R&D activitiesin developing new technologies and forensic tools in collaboration with academia/research institutes within India and abroad.
- To prevent misuse of cyberspace for furthering the cause of extremist and terrorist groups.
- To suggest amendments, if required, in cyber lawsto keep pace with fast-changing technologies and international cooperation.
- To coordinate all activities related to the implementation of Mutual Legal Assistance Treaties (MLAT) with other countries related to cybercrimes in consultation with the concerned nodal authority in MHA.
Components:
- National Cybercrime Threat Analytics Unit (TAU): For reporting threats pertaining to cybercrimes at regular intervals.
- National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP): To report various cybercrime complaints by citizens at all India level on a common platform on a 24x7 basis from “anywhere, anytime”.
- National Cybercrime Training Centre (NCTC): To impart training to government officials, especially state law enforcement agencies.
- National Cybercrime Research and Innovation Centre: To carry out research for the development of indigenous tools for the prevention of cybercrimes.
- Platform for Joint Cyber Crime Coordination Team: For coordination, sharing of modus operandi of cybercrimes, data/information among states/UTs LEAs.
- Cybercrime Ecosystem Management Unit: For creating mass awareness in cyber hygiene for prevention of cybercrimes.
- National Cybercrime Forensic Laboratory (Investigation) Ecosystem: For helping LEAs in cyber forensics investigation.
India's 1st Silicon Carbide manufacturing facility - The Hindu
Context
Odisha Chief Minister recently graced the ground-breaking ceremony of India's first silicon carbide manufacturing facility to be set up in Odisha at an investment of Rs 620 crore. The project will be developed by RIR Power Electronics Limited, a leader in India's semiconductor power electronics technology at the EMC Park, Infovalley, Bhubaneswar.
Silicon Carbide
- Discovery: American inventor Edward G. Acheson (1891).
- Properties:
- Exceedingly hard, synthetically produced crystalline compound of silicon and carbon.
- Fractures that make them extremely useful in grinding wheels and in abrasive paper and cloth products.
- High thermal conductivity and high-temperature strength, low thermal expansion, and resistance to chemical reaction
- A semiconductor
- Applications:
- Used in the manufacture of high-temperature bricks and other refractories.
- Used in refractory linings and heating elements for industrial furnaces, in wear-resistant parts for pumps and rocket engines.
- In semiconducting substrates for light-emitting diodes.
- As an abrasive because of its high hardness, which is surpassed only by diamond, cubic boron nitride and boron carbide.
Environment
40% OF AMAZON RAINFOREST MOST VITAL TO CLIMATE IS UNPROTECTED - Indian Express
Context
Scientists agree that preserving the Amazon rainforest is critical to combating global warming, but new data published recently indicate huge swathes of the jungles that are vital to the world’s climate remain unprotected.
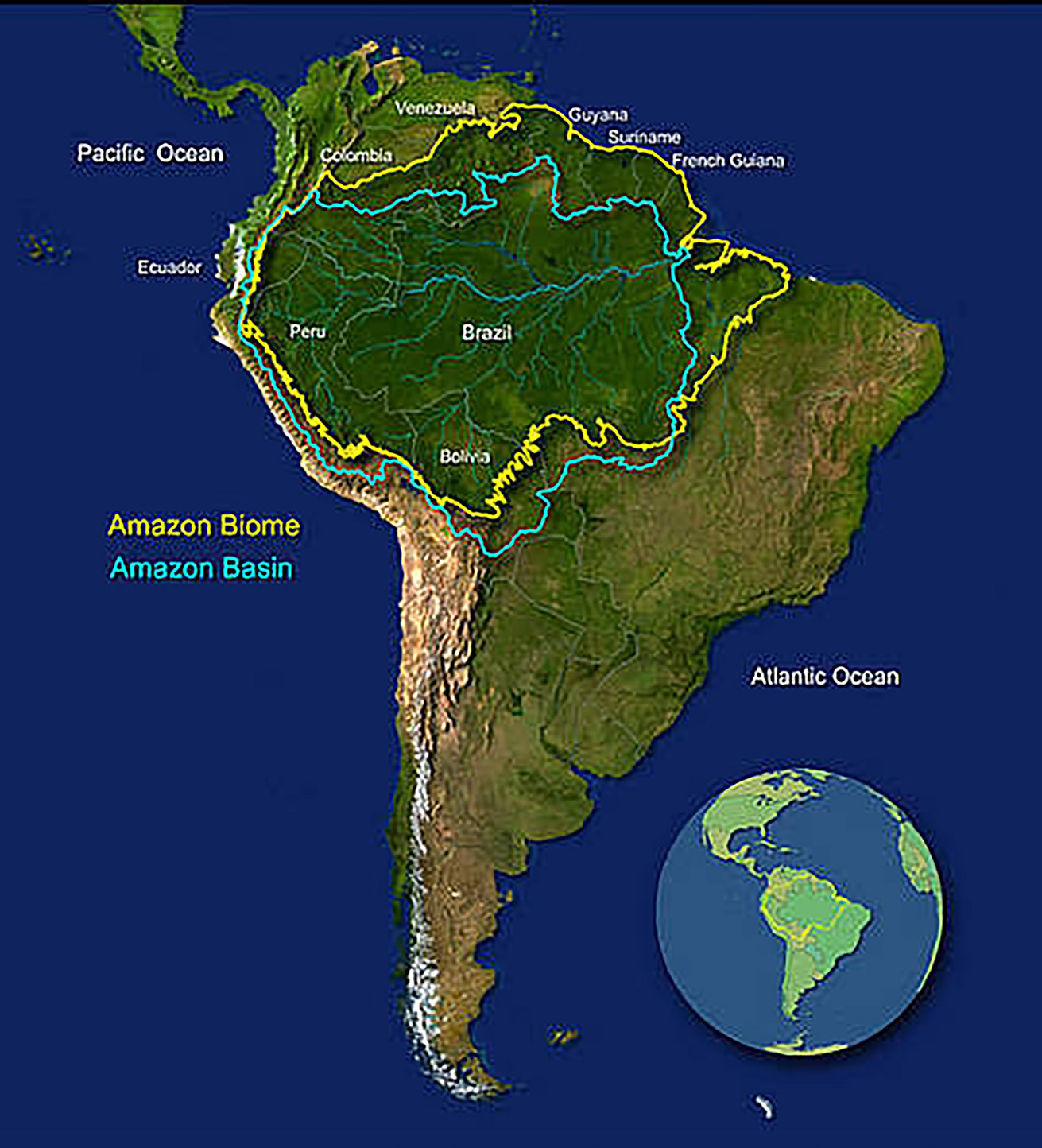
Amazon Rainforest
- About: Large tropical rainforests occupying the drainage basin of the Amazon River and its tributaries in northern South America
- Area: 6,000,000 square km (covers about 40% of Brazil’s total area).
- Climate: Receive more than 200 cm rainfall annually
- Temperatures: 20°C - 35°C
- Boundaries:
- North: Guiana Highlands
- West: Andes Mountains
- South: Brazilian central plateau
- East: Atlantic Ocean
- Significance: Amazon contained 71.5 billion tonnes of carbon, roughly double the global carbon dioxide emissions for 2022. Amazon just barely absorbed more carbon than it released in the decade leading up to 2022.
Bhadra Tiger Reserve - Indian Express
Context
An aggressive new weed (Mikania micrantha) is rapidly spreading its tentacles in the Bhadra Tiger Reserve (BTR) and threatening its biodiversity.
Bhadra Tiger Reserve (BTR)
- Location: Western Ghats region of Karnataka declared the 25th Project Tiger Reserve of India in 1998.
- Rivers: River Bhadra and its tributaries
- Vegetation: Dry deciduous, moist deciduous, shola, and semi-evergreen
- Flora: Teak, Rosewood, Mathi, Honne, Nandi, and many medicinal plants.
- Fauna: Tiger, Leopard, Leopard cat, Dholes, Indian Civet, ungulates like Gaur, Sambar, and Barking Deer.
Mikania micrantha
- About: A perennial creeping climber known for its vigorous and rampant growth.
- Distribtuion: A native of Central and South America& an invasive species in several parts of Southeast Asia, India and the Pacific Islands.
- Introduction in India: In the 1940s as ground cover in tea plantations.
- Climate: Grows where fertility, organic matter, soil moisture, and humidity are high.
- Impact on other plants:
- Kills other plants by cutting out the light and smothering them
- Climbs up other plants to reach the canopy for better sunlight.
- Can inhibit seed germination and seedling growth of other plants.
- Produces wind-dispersed seeds & can reproduce vegetatively through its roots, resulting in rapid and widespread invasion.