Supreme Court Seeks Report from Commission for Air Quality Management on Stubble-burning
The Hindu
Context
The Supreme Court has recently requested a report from the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) regarding incidents of stubble-burning and the actions taken to mitigate its effects.
Stubble Burning
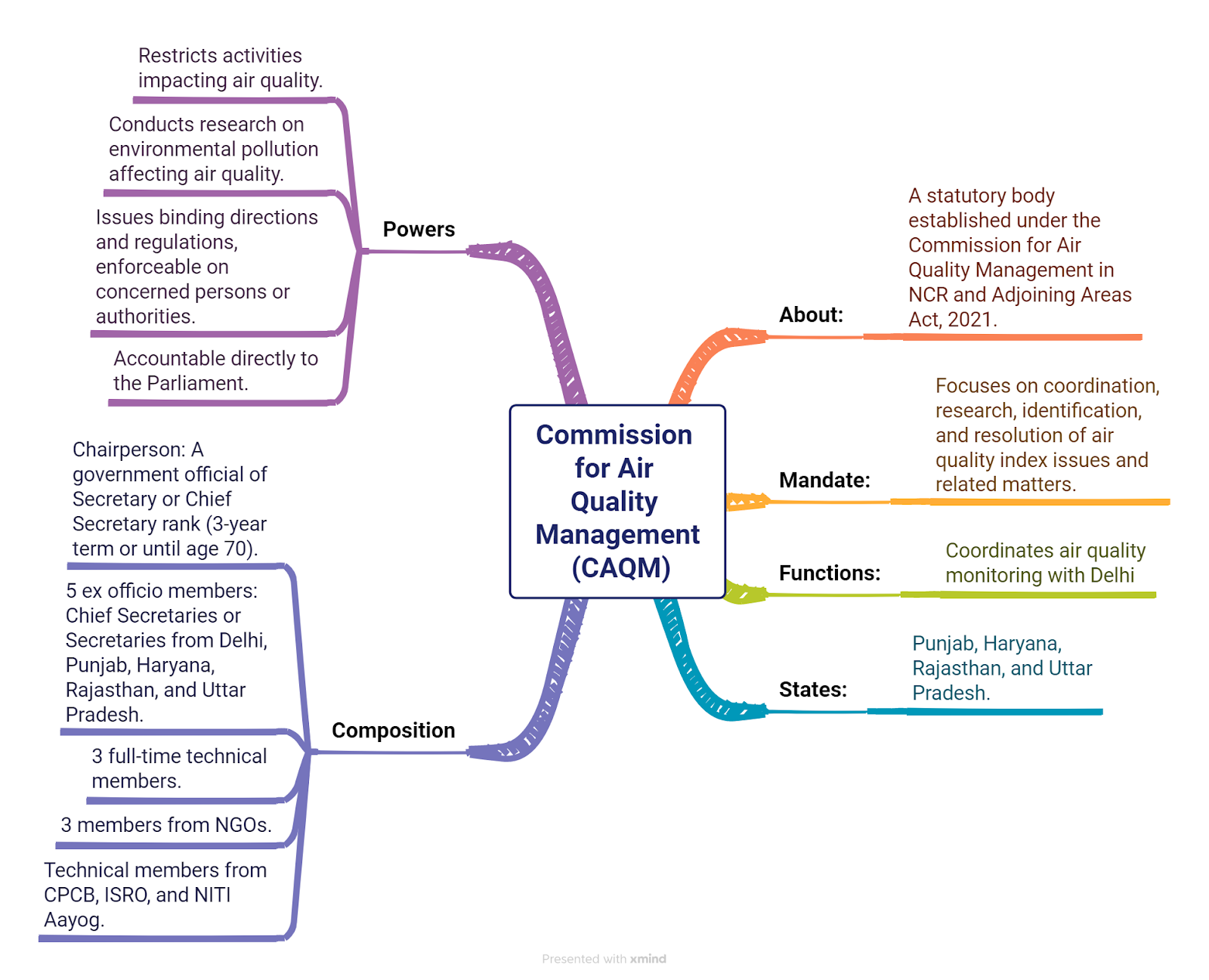
- About:
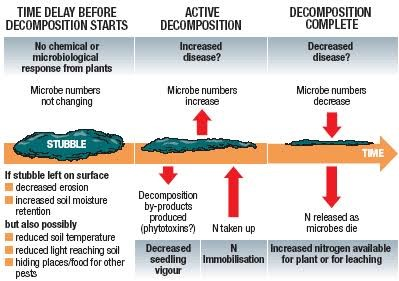
Stubble burning is a method used by farmers to quickly remove paddy crop residues, particularly after the harvest, to prepare fields for the next crop (usually wheat). It is a common practice from late September to November.
- Components:
The process involves burning leftover straw and stubble after crop harvesting, especially in areas using combined harvesting methods that leave large amounts of crop residues.
- Practice:
It is widespread in October and November in Northwest India, especially in the states of Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh.
- Effects:
- Pollution:
- Releases harmful pollutants such as methane, carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds, and carcinogenic substances.
- Major contributor to smog and severe health risks.
- Soil Fertility:
- Destroys essential nutrients in the soil, reducing its fertility for future crops.
- Heat Penetration:
- The heat generated reduces soil moisture and kills beneficial microbes that help maintain soil health.
Alternatives to Stubble Burning
- Turbo Happy Seeder (THS):
- A machine that can uproot stubble and simultaneously sow seeds, using the leftover residue as mulch for the field.
- Promotes a more environmentally sustainable method of dealing with crop residues.
Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM)
The CAQM is responsible for monitoring, managing, and taking action to improve air quality in regions affected by stubble burning and other sources of pollution