Marburg viral disease - The Hindu
Context :
Six people have died in Rwanda following an outbreak of the Marburg virus.
Marburg Virus Disease
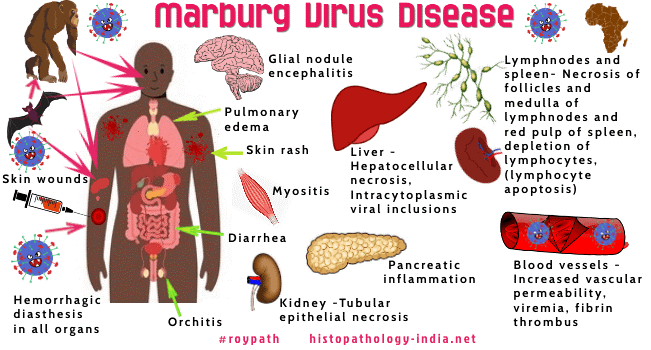
- About: A rare but severe hemorrhagic fever that affects both people and non-human primates.
- Cause: Caused by the Marburg virus, a genetically unique zoonotic (animal-borne) RNA virus (member of the Filoviridae family (filovirus)).
- Reservoir host of the Marburg virus: African fruit bat, Rousettus aegyptiacus.
- Transmission: Transmitted from bats to primates, including humans, and then spread through direct contact with blood or other body fluids from infected individuals.
- Symptoms: Fever, Chills, Headache, Muscle aches, Rash with both flat and raised bumps, often on the torso, Chest pain, Sore throat, Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Advanced symptoms may include liver failure, delirium, shock, bleeding (hemorrhaging), and multi-organ dysfunction.
- Fatality: Around 50%
- Treatment: No treatment or vaccine; supportive therapy, such as intravenous fluids, electrolyte replacement, supplemental oxygen, as well as blood and blood products replacement, improves survival.