Centre to establish foot-and-mouth disease-free zones in eight States - The Hindu
Context
The Union government has decided to establish foot-and-mouth disease-free zones in eight States - Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Uttarakhand, Punjab, Haryana, Maharashtra, and Gujarat to expand export opportunities for Indian animal products, and enhance the country’s global market presence.
Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD)
- About: A severe, highly contagious viral diseaseof livestock that has a significant economic impact which affects cattle, swine, sheep, goats, and other cloven-hoofed ruminants but does not affect horses, dogs, or cats.
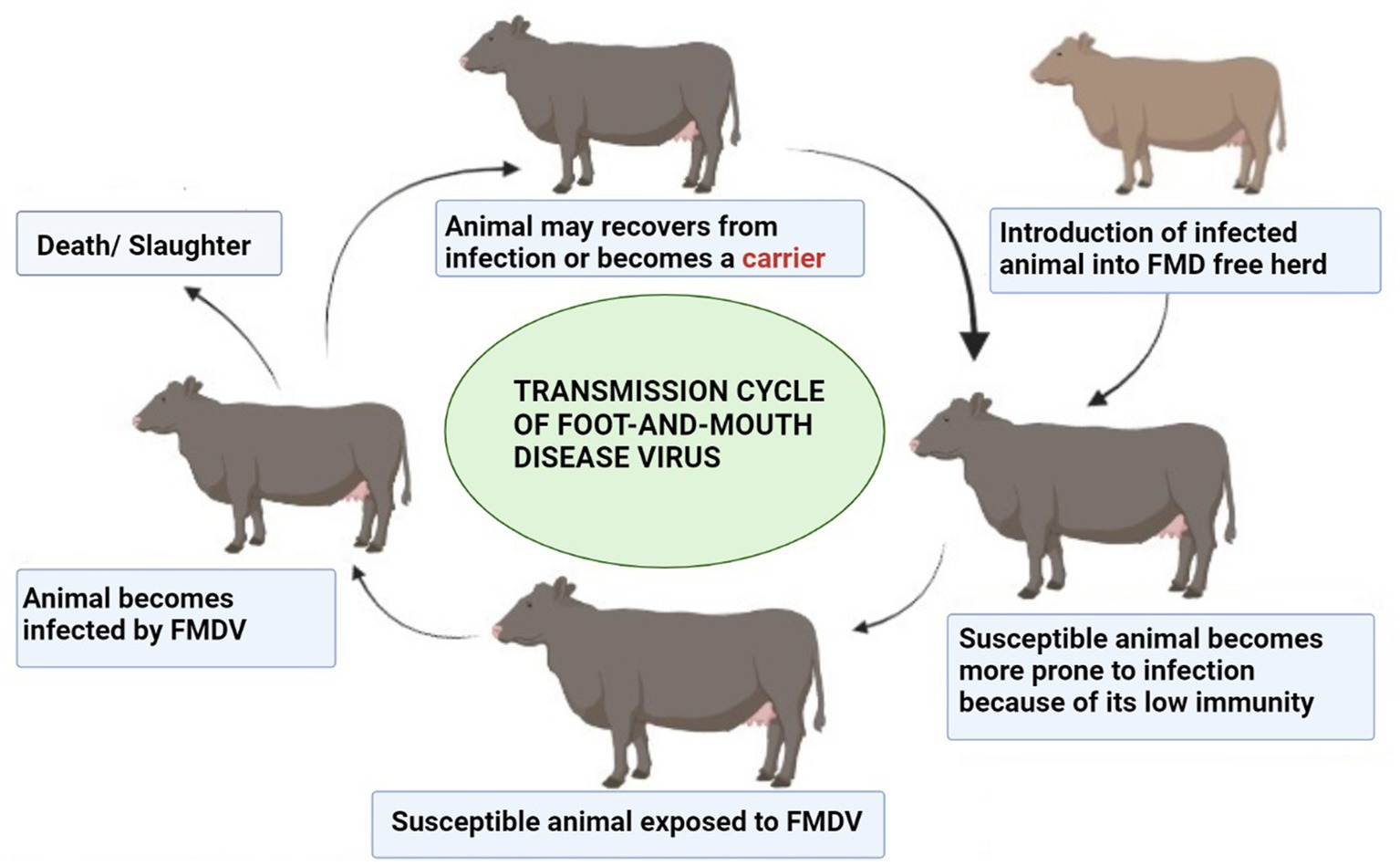
- A transboundary animal disease (TAD): Affects the production of livestock and disrupts regional and international trade in animals and animal products.
- Impact on humans: It is not a human health or food safety threat & not related to hand, foot, and mouth disease, a common childhood illness caused by a different virus.
- Cause: An aphthovirus of the family Picornaviridae.
- Strains: 7 strains (A, O, C, SAT1, SAT2, SAT3, and Asia1) endemic in different countries worldwide.
- Transmission: Found in all excretions and secretions from infected animals which breathe out a large amount of aerosolised virus, which can infect other animals via the respiratory or oral routes.
- Mortality: Rarely fatal in adult animals, but has high mortality in young animals.
- Symptoms: Fever and blister-like sores on the tongue and lips, in the mouth, on the teats, and between the hooves, depression, hypersalivation, loss of appetite, weight loss, growth retardation, and a drop in milk production, which can persist even after recovery.
- Specification: It was the first disease for which the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH, founded as OIE) established official status recognition.
- Treatment: Vaccines for FMD are available but must be matched to the specific type and subtype of virus causing the outbreak.